SLUSEC9B October 2020 – July 2024 BQ25618E , BQ25619E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 8.3.2 Device Power Up From Battery Without Input Source
- 8.3.3 Power Up From Input Source
- 8.3.4 Power Path Management
- 8.3.5 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.6 Ship Mode and QON Pin
- 8.3.7 Status Outputs ( STAT, INT , PG )
- 8.3.8 Protections
- 8.3.9 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
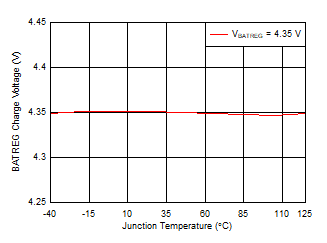
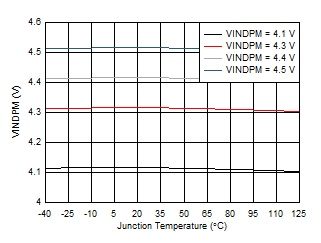
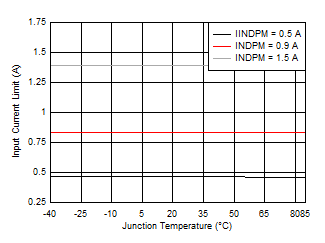
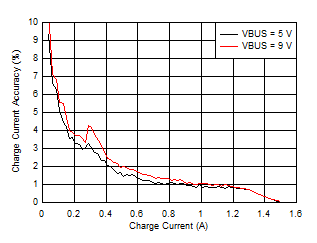
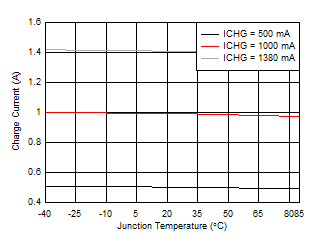
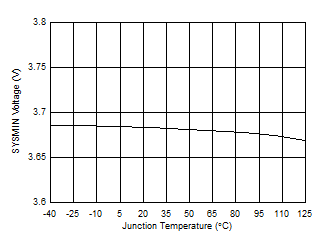
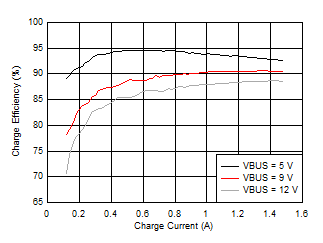
7.7 Typical Characteristics
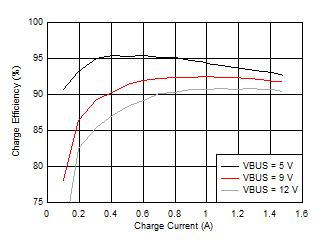
| BQ25619EVM | VBAT = 3.8 V | Inductor 2.2 µH, DCR = 40 mΩ |
| BQ25618EVM | VBAT = 3.8 V | Inductor 1.0 µH, DCR = 27 mΩ |