SLUSEC9B October 2020 – July 2024 BQ25618E , BQ25619E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 8.3.2 Device Power Up From Battery Without Input Source
- 8.3.3 Power Up From Input Source
- 8.3.4 Power Path Management
- 8.3.5 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.6 Ship Mode and QON Pin
- 8.3.7 Status Outputs ( STAT, INT , PG )
- 8.3.8 Protections
- 8.3.9 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.9.3 Byte Format
Every byte on the SDA line must be 8 bits long. The number of bytes to be transmitted per transfer is unrestricted. Each byte has to be followed by an Acknowledge bit. Data is transferred with the Most Significant Bit (MSB) first. If a slave cannot receive or transmit another complete byte of data until it has performed some other function, it can hold the clock line SCL low to force the master into a wait state (clock stretching). Data transfer then continues when the slave is ready for another byte of data and release the clock line SCL.
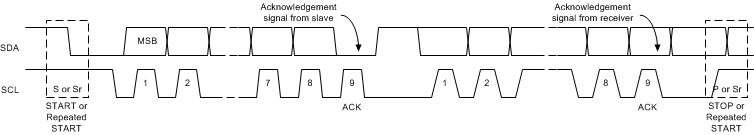 Figure 8-8 Data Transfer on the I2C Bus
Figure 8-8 Data Transfer on the I2C Bus