SLUSEC9B October 2020 – July 2024 BQ25618E , BQ25619E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 8.3.2 Device Power Up From Battery Without Input Source
- 8.3.3 Power Up From Input Source
- 8.3.4 Power Path Management
- 8.3.5 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.6 Ship Mode and QON Pin
- 8.3.7 Status Outputs ( STAT, INT , PG )
- 8.3.8 Protections
- 8.3.9 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.5.4.1 JEITA Guideline Compliance During Charging Mode
To improve the safety of charging Li-ion batteries, the JEITA guideline was released on April 20, 2007. The guideline emphasized the importance of avoiding a high charge current and high charge voltage at certain low and high temperature ranges.
To initiate a charge cycle, the voltage on TS pin, as a percentage of VREGN, must be within the VT1_FALL% to VT5_RISE% thresholds. If the TS voltage percentage exceeds the T1-T5 range, the controller suspends charging, a TS fault is reported and waits until the battery temperature is within the T1 to T5 range.
At cool temperature (T1-T2), the charge current is reduced to a programmable fast charge current (0%, 20% default, 50%, 100% of ICHG, by JEITA_ISET). At warm temperature (T3-T5), the charge voltage is reduced to 4.1 V or kept at VREG (JEITA_VSET). and the charge current can be reduced to a programmable level (0%, 20%, 50%, 100% default). Battery termination is disabled in T3-T5. The charger provides more flexible settings on T2 and T3 threshold as well to program the temperature profile beyond JEITA. When the T1 is set to 0°C and T5 is set to 60°C, T2 can be programmed to 5.5°C/10°C(default)/15°C/20°C, and T3 can be programmed to 40°C/45.5°C(default)/50.5°C/54.5°C.
When charger does not need to monitor the NTC, host sets TS_IGNORE bit to 1 to ignore the TS pin condition during charging mode. If TS_IGNORE bit is set to 1, TS pin is ignored and the charger ignore TS pin input. In this case, NTC_FAULT bits are 000 to report normal TS status.
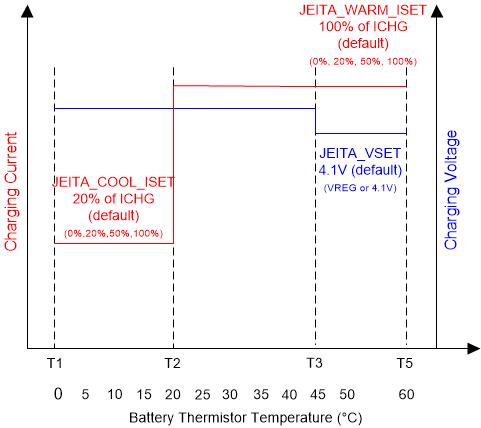 Figure 8-3 JEITA Profile
Figure 8-3 JEITA Profile
Equation 1 through Equation 2 describe how to calculate resistor divider values on TS
pin.
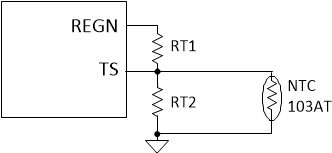 Figure 8-4 TS
Pin Resistor Network
Figure 8-4 TS
Pin Resistor Network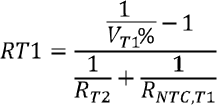
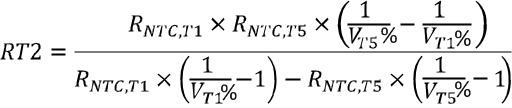
In the equations above, RNTC, T1 is NTC thermistor resistance value at temperature T1 and RNTC, T5 is NTC thermistor resistance values at temperature T5. Select 0°C to 60°C range for Li-ion or Li-polymer battery then
- RNTC,T1 = 27.28 KΩ (0°C)
- RNTC,T5 = 3.02 KΩ (60°C)
- RT1 = 5.3 KΩ
- RT2 = 31.14 KΩ