SLUU297B December 2007 – January 2022 TPS40195
8 EVM Assembly Drawings and Layout
The following figures (Figure 8-1 through Figure 8-3) show the design of the TPS40195EVM printed circuit board. The EVM has been designed using a 2-layer, 2-oz copper-clad circuit board with all components on the top side. Moving components to both sides of the PCB or using additional internal layers can offer additional size reduction for space constrained systems.
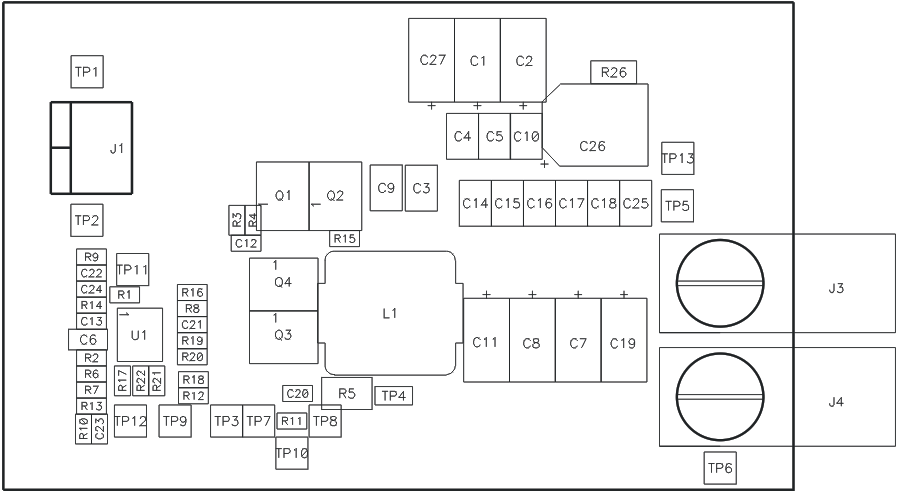 Figure 8-1 TPS40195EVM Component
Placement (Viewed from Top)
Figure 8-1 TPS40195EVM Component
Placement (Viewed from Top)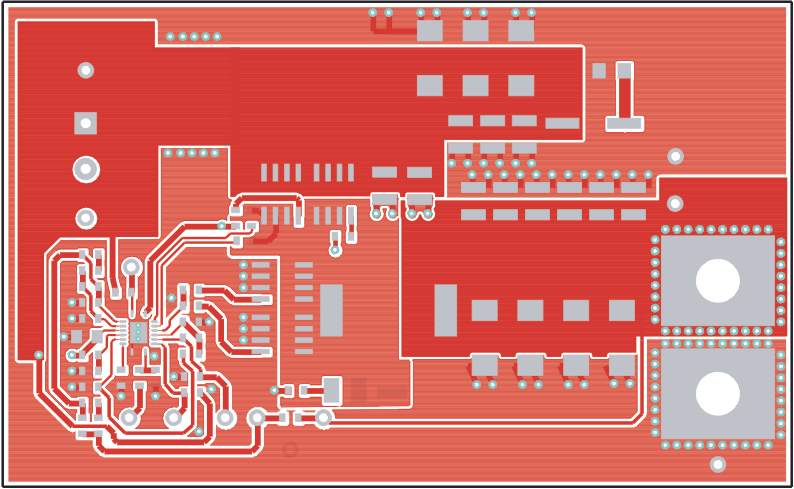 Figure 8-2 TPS40195EVM Top Copper
(Viewed from Top)
Figure 8-2 TPS40195EVM Top Copper
(Viewed from Top) Figure 8-3 TPS40195EVM Bottom Copper
(X-ray Viewed from Top)
Figure 8-3 TPS40195EVM Bottom Copper
(X-ray Viewed from Top)