SLUU943A May 2012 – December 2021 TPS53014
9 EVM Assembly Drawing and PCB Layout
The following figures (Figure 9-1 through Figure 9-5) show the design of the TPS53014EVM-126 printed circuit board. The EVM has been designed using a 4-layer, 2-ounce copper circuit board.
 Figure 9-1 TPS53014EVM-126 Top Layer
Assembly Drawing (Top View)
Figure 9-1 TPS53014EVM-126 Top Layer
Assembly Drawing (Top View)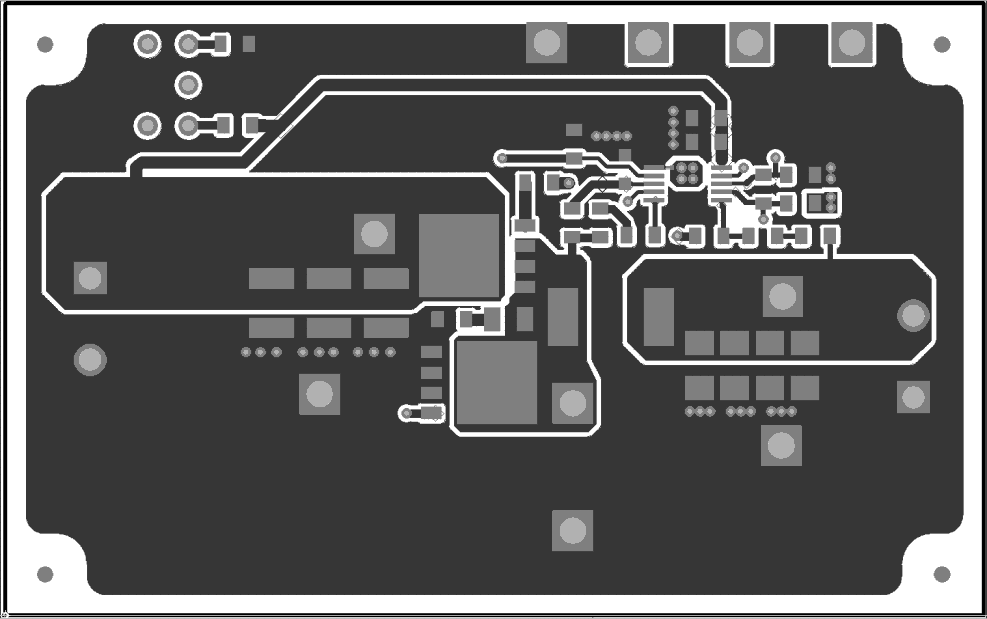 Figure 9-2 TPS53014EVM-126 Top
Copper (Top View)
Figure 9-2 TPS53014EVM-126 Top
Copper (Top View) Figure 9-3 TPS53014EVM-126 Layer 2
(Top View)
Figure 9-3 TPS53014EVM-126 Layer 2
(Top View) Figure 9-4 TPS53014EVM-126 Layer 3
(Top View)
Figure 9-4 TPS53014EVM-126 Layer 3
(Top View) Figure 9-5 TPS53014EVM-126 Bottom
Layer (Top View)
Figure 9-5 TPS53014EVM-126 Bottom
Layer (Top View)