SLVA528D September 2012 – August 2021 TPS65381-Q1 , TPS65381A-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Product Overview
- 3Development Process for Management of Systematic Faults
- 4TPS65381x-Q1 Product Architecture for Management of Random Faults
-
5TPS65381x-Q1 Architecture Safety Mechanisms and Assumptions of Use
- 5.1 Power Supply
- 5.2 Regulated Supplies
- 5.3
Diagnostic, Monitoring, and Protection Functions
- 5.3.1 External MCU Fault Detection and Management
- 5.3.2 Voltage Monitor (VMON)
- 5.3.3 Loss-of-Clock Monitor (LCMON)
- 5.3.4 Junction Temperature Monitoring and Current Limiting
- 5.3.5 Analog and Digital MUX (AMUX and DMUX) and Diagnostic Output Pin (DIAG_OUT)
- 5.3.6 Analog Built-In Self-Test (ABIST)
- 5.3.7 Logic Built-In Self-Test (LBIST)
- 5.3.8 Device Configuration Register Protection
- 6Application Diagrams
- 7TPS65381x-Q1 as Safety Element out of Context (SEooC)
- 8Revision History
5.3.6 Analog Built-In Self-Test (ABIST)
The ABIST is the controller and monitor circuit for performing self-checking diagnostics on critical analog functions:
- VMON undervoltage and overvoltage comparators
- Clock monitor (LCMON)
- EEPROM analog trim content check (CRC protection)
During the self-test on the VMON undervoltage and overvoltage comparators, the monitored voltage rails themselves do not change, so no real undervoltage or overvoltage occurs on any of these rails. Furthermore, also during the self-check on the clock monitor, the actual oscillator frequency (4 MHz) is not changed.
In case of an ABIST failure while in the DIAGNOSTIC state, including a power-up event, the device enters the SAFE state without asserting a reset to the external MCU and the ABIST_ERR status flag remain latched in the digital core until a successful ABIST run. This allows the external MCU to detect the ABIST failure by reading the ABIST_ERR bits in the SAFETY_STAT_3 register. In case of an ABIST failure while in the ACTIVE state, the device sets the ABIST_ERR status flag, but no state transition occurs.
In the DIAGNOSTIC or ACTIVE state, the external MCU can activate ABIST. During an active ABIST run, the device cannot monitor the state of regulated supplies.
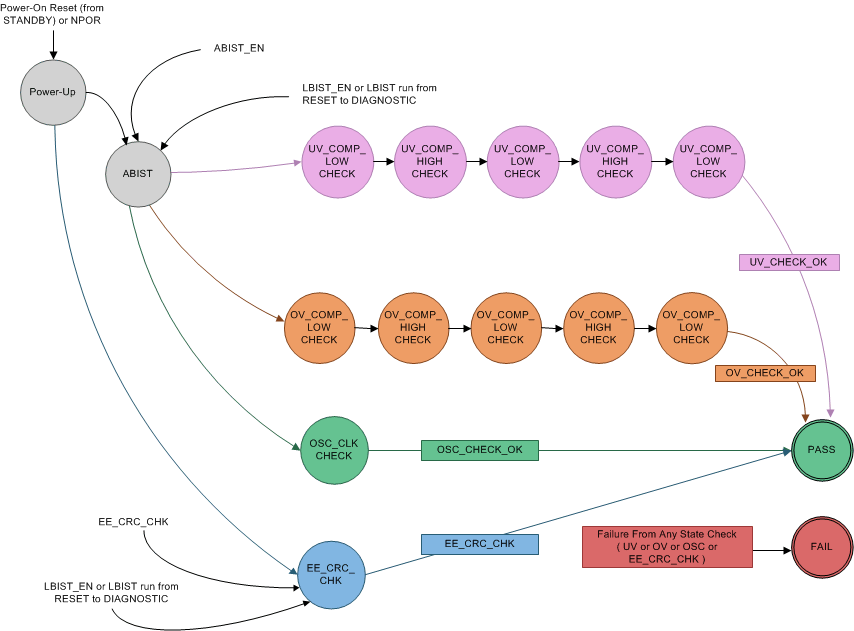 Figure 5-10 ABIST Run States
Figure 5-10 ABIST Run States