SLVAEV0A July 2020 – July 2022 TPS25833-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TPS25833-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 and Figure 4-2 show the TPS25833-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the TPS25833-Q1 data sheet.
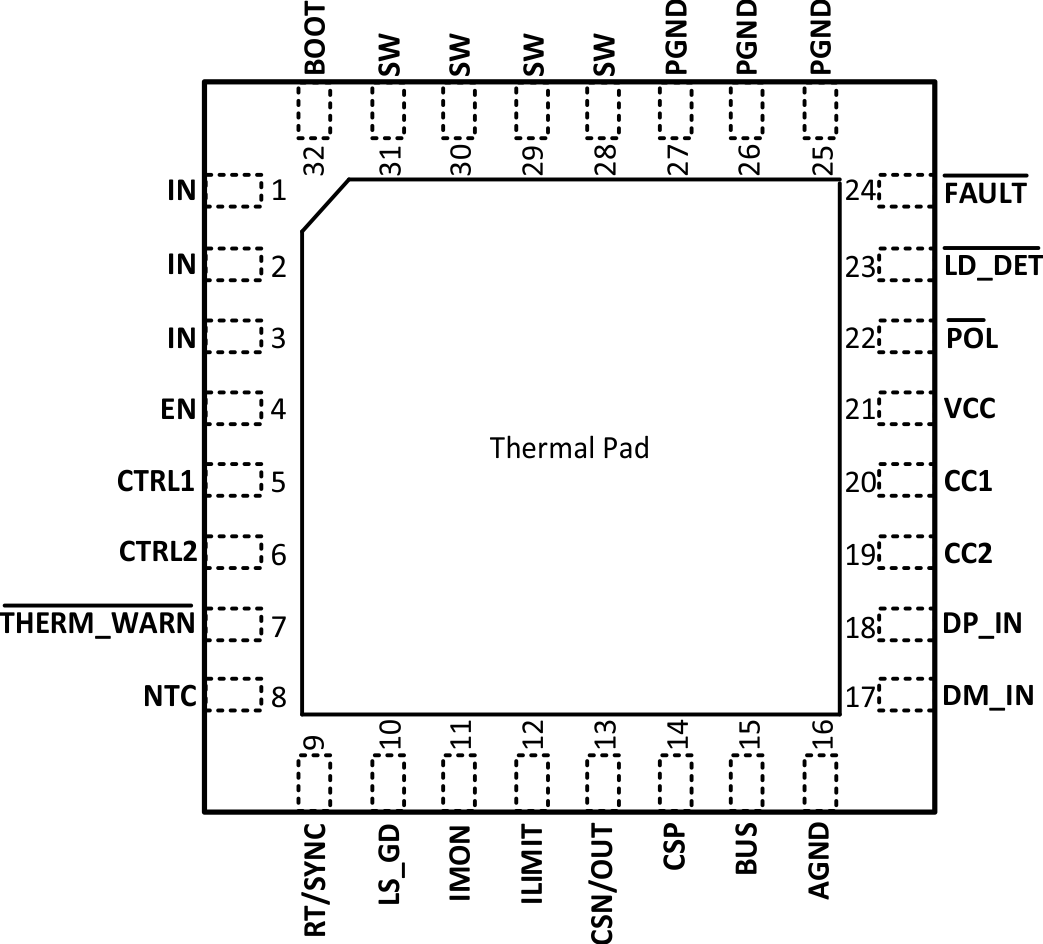 Figure 4-1 TPS25833QCWRHBRQ1 Pin
Diagram
Figure 4-1 TPS25833QCWRHBRQ1 Pin
Diagram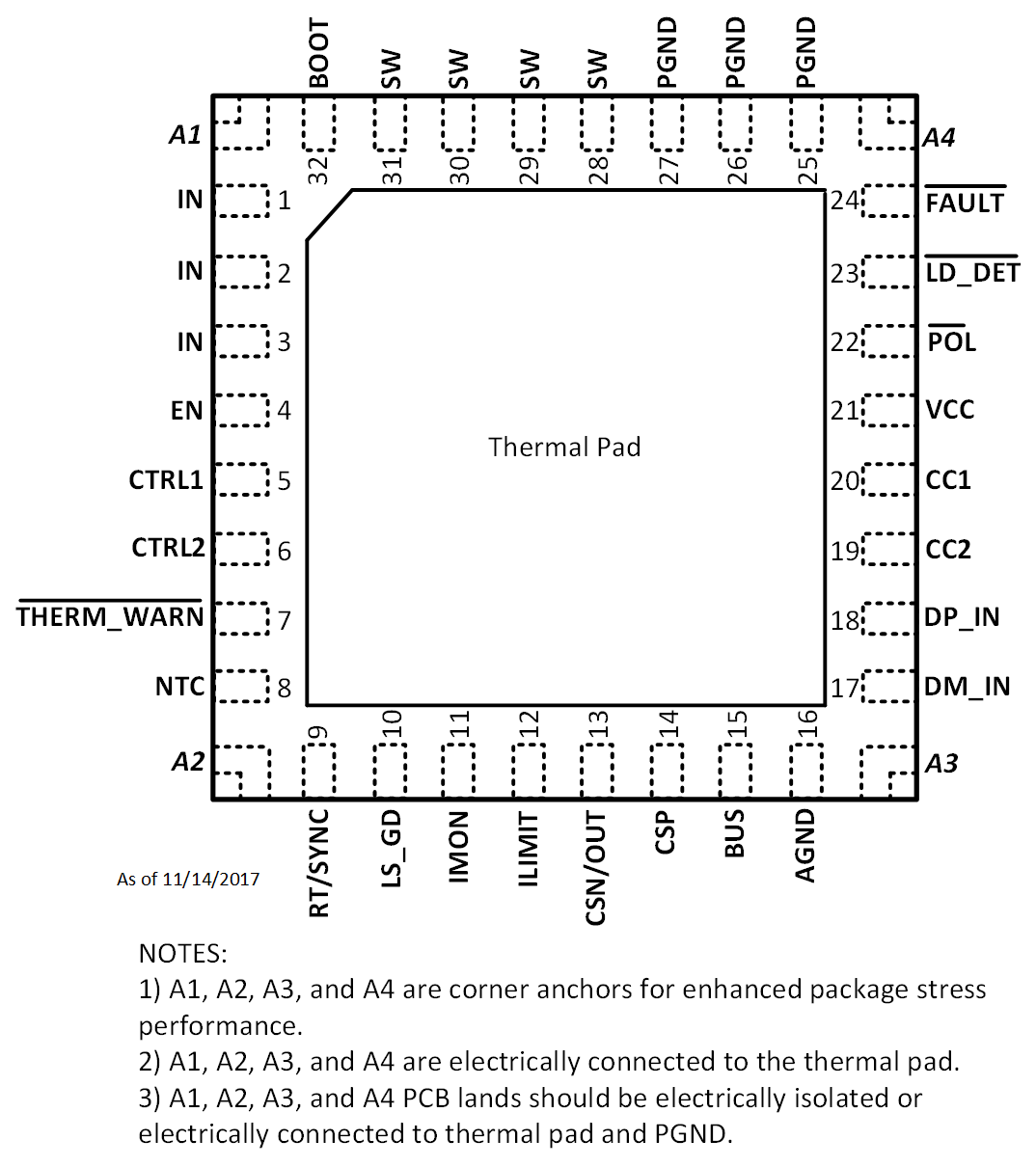 Figure 4-2 TPS25833QWRHBRQ1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-2 TPS25833QWRHBRQ1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
-
Device used within the 'Recommended Operating Conditions' and the 'Absolute Maximum Ratings' found in the appropriate device data sheet.
-
Configuration as shown in the 'Example Application Circuit' found in the appropriate device data sheet.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | Device does not operate. No output voltage is generated. | B |
| VIN | 2 | Device does not operate. No output voltage is generated. | B |
| VIN | 3 | Device does not operate. No output voltage is generated. | B |
| EN | 4 | Loss of ENABLE functionality. Device remains in shutdown mode. | B |
| CTRL1 | 5 | Device stays at reserved mode or DCP auto mode. When in the reserved mode, the output charging is abnormal. | B |
| CTRL2 | 6 | Device stay at reserved mode or SDP mode. When in the reserved mode, the output charging is abnormal. | B |
| /THERM_WARN | 7 | Loss of THERM_WARN functionality. Device always appears to be in the thermal warning condition. | C |
| NTC | 8 | Loss of Temperature Sense functionality. Device cannot sense the external PCB temperature. | C |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | Device internal buck switching frequency goes up to 4.6 MHz, and the CSN pin voltage up to 7 V. It makes the output charging. | B |
| LS_GD | 10 | Device cannot drive external FET for current limit. | B |
| IMON | 11 | Loss of Cable Compensation functionality. Device cannot make a cable compensation. | C |
| ILIMT | 12 | Loss of Current Limit functionality. Device uses the maximum current limit value of 3.5 A. | C |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | Device internal buck output short circuits. Device enters hiccup mode. | B |
| CSP | 14 | Device internal buck output short circuits. Device enters hiccup mode. | B |
| BUS | 15 | Device hiccups and output current limit does work. | B |
| AGND | 16 | No effect | D |
| DM_IN | 17 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/DCP auto charging mode. | B |
| DP_IN | 18 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/DCP auto charging mode. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | Device hiccups and output voltage is abnormal. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | Device hiccups and output voltage is abnormal. | B |
| VCC | 21 | Device hiccups and cannot be powered on. | B |
| /POL | 22 | Loss of /POL functionality. Device always appears to the CC2 pin is connected to the CC line in the cable. | C |
| /LD_DET | 23 | Loss of /LD_DET functionality. Device always appears to a Type-C UFP is identified on the CC lines. | C |
| /FAULT | 24 | Loss of /FAULT functionality. Device always appears to be in the fault condition. | C |
| PGND | 25 | No effect | D |
| PGND | 26 | No effect | D |
| PGND | 27 | No effect | D |
| SW | 28 | Device internal buck hiccup. Long-term reliability can impact. | A |
| SW | 29 | Device internal buck hiccup. Long-term reliability can impact. | A |
| SW | 30 | Device internal buck hiccup. Long-term reliability can impact. | A |
| SW | 31 | Device internal buck hiccup. Long-term reliability can impact. | A |
| BOOT | 32 | Device internal buck stop switching. No output voltage in VSN/OUT. | B |
| Thermal Pad | — | No effect | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| VIN | 2 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| VIN | 3 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| EN | 4 | Device off and on cannot be controlled and is off and on depending on how EN floats. | B |
| CTRL1 | 5 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode cannot be controlled, and is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode depending on how CTRL1 floats. | B |
| CTRL2 | 6 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode cannot be controlled, and is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode depending on how CTRL2 floats. | B |
| /THERM_WARN | 7 | Loss of THERM_WARN functionality. Device cannot be determined whether it is in the overtemperature condition. | C |
| NTC | 8 | Device overtemperature or not cannot be controlled, and is depending on how NTC floats. | C |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | Device internal buck switching frequency drop and loading current are limited to about a small value. This fact causes abnormal charging. | B |
| LS_GD | 10 | Device cannot drive external FET for current limit. | B |
| IMON | 11 | VOUT/CSN goes up to 6.9 V. This action can cause VBUS voltage over compensation and fail at the BC1.2 certification test. | B |
| ILIMT | 12 | Device internal buck hiccups. | B |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | Device internal buck output voltage is abnormal. | B |
| CSP | 14 | Device cannot sense the output current signal. The output current limit and VBUS cable compensation don not work. | C |
| BUS | 15 | Loss of VBUS OVP functionality. IEC ESD test is impacted. | B |
| AGND | 16 | The device tries to power up by forward-biasing the ESD diode from the GND to another pin. Strange results are observed. | B |
| DM_IN | 17 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/DCP auto charging mode. | B |
| DP_IN | 18 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/DCP auto charging mode. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | Device Nothing attached/UFP connected/No UFP connected cannot be controlled. It depends on the state of CC1. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | Device Nothing attached/UFP connected/No UFP connected cannot be controlled. It depends on the state of CC2. | B |
| VCC | 21 | Device cannot start up. Internal buck stops switching. | B |
| /POL | 22 | Loss of /POL functionality, cannot give cable orientation information. | C |
| /LD_DET | 23 | Loss of /LD_DET functionality. Cannot identify the Type-C UFP. | C |
| /FAULT | 24 | Loss of /FAULT functionality, cannot check whether the device is in the fault condition. | C |
| PGND | 25 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| PGND | 26 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| PGND | 27 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 28 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 29 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 30 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 31 | Long-term reliability can impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| BOOT | 32 | Device internal buck HS FET cannot be turned on. VSN/OUT cannot get up to target voltage. | B |
| Thermal Pad | — | Long-term reliability can impact if the device operates beyond the rate junction temperature for extended time because a heat path is interrupted. | C |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | VIN | No effect | D |
| VIN | 2 | VIN | No effect | D |
| VIN | 3 | EN | Device is enabled and cannot be disabled. | D |
| EN | 4 | CTRL1 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/reserve mode and enable/disable cannot be controlled. It is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/ reserve mode and enable/disable depending on how EN and CTRL1 circuits interact. | B |
| CTRL1 | 5 | CTRL2 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode cannot be controlled. It is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode depending on how CTRL1 and CTRL2 circuits interact. | B |
| CTRL2 | 6 | /THERM_WARN | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode cannot be controlled. It is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode depending on how CTRL2 and /THERM_WARN circuits interact. | B |
| /THERM_WARN | 7 | NTC | The NTC thermal sensing does not work, THERM_WARN flag and charging state do not report correctly. | B |
| NTC | 8 | RT/SYNC | Device internal buck switching is interrupted by NTC. | B |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | LS_GD | The LS_GD goes down from 11.3 V to 0.5 V, and the internal buck switching frequency is abnormal. Device cannot drive the external FET for current limit | B |
| LS_GD | 10 | IMON | LS_GD voltage set low, device cannot drive the external FET for current limit. | B |
| IMON | 11 | ILIMT | Current limit threshold and cable compensation value are impacted. | C |
| ILIMT | 12 | CSN/OUT | Ilimit is pulled up over 1 V, device behaves as average current limit and keeps hiccup. | B |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | CSP | Average current limit, external FET current limit and cable compensation function are bypassed. | C |
| CSP | 14 | BUS | Average current limit, external FET current limit and cable compensation function are bypassed. | C |
| BUS | 15 | AGND | Device goes into hiccup mode. | B |
| AGND | 16 | DM_IN | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/DCP auto charging mode. | B |
| DM_IN | 17 | DP_IN | Device only supports BC1.2 DCP mode. | C |
| DP_IN | 18 | CC2 | If shorted before charging, the device cannot charge. If shorted after charge, no effect. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | CC1 | Pin short before power up, device internal buck is not switching. Pin short during normal condition, no impact. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | VCC | Device stops working, CSN/OUT does not output voltage. | B |
| VCC | 21 | /POL | Loss of /POL functionality, the /POL always goes into high, device always appears to have the CC1 pin connected to the CC line. | C |
| /POL | 22 | /LD_DET | Loss of /POL and /LD_LET functionality. | C |
| /LD_DET | 23 | /FAULT | Loss of /FAULT and /LD_LET functionality. | C |
| /FAULT | 24 | PGND | Loss of /FAULT functionality, device always appears to be in the fault condition. | C |
| PGND | 25 | PGND | No effect | D |
| PGND | 26 | PGND | No effect | D |
| PGND | 27 | SW | Device internal buck hiccup, long-term reliability can be impacted. | A |
| SW | 28 | SW | No effect | D |
| SW | 29 | SW | No effect | D |
| SW | 30 | SW | No effect | D |
| SW | 31 | BOOT | Device internal buck HS FET stops working, no output voltage in CSN/OUT. | B |
| Thermal Pad | — | Any of the numbered pins in the above rows. | The thermal pad is connected to the board ground. Treat shorts to the thermal pad as shorts to ground. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | No effect | D |
| VIN | 2 | No effect | D |
| VIN | 3 | No effect | D |
| EN | 4 | Device is enabled and cannot be disabled. | D |
| CTRL1 | 5 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| CTRL2 | 6 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| /THERM_WARN | 7 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| NTC | 8 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| LS_GD | 10 | External FET cannot do current limit. | C |
| IMON | 11 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| ILIMT | 12 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | VBUS OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| CSP | 14 | VBUS OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| BUS | 15 | VBUS OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| AGND | 16 | Former power supply can be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| DM_IN | 17 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| DP_IN | 18 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| CC2 | 19 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| CC1 | 20 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| VCC | 21 | Device broken, VCC pin voltage exceeds the ABS maximum value. | A |
| /POL | 22 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| /LD_DET | 23 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| /FAULT | 24 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| PGND | 25 | Former power supply can be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| PGND | 26 | Former power supply can be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| PGND | 27 | Former power supply can be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| SW | 28 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| SW | 29 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| SW | 30 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| SW | 31 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| BOOT | 32 | Above ABS voltage, device can be damaged. | A |
| Thermal Pad | — | Thermal pad is connected to PGND on the PCB board. Former power supply can be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |