SLVAFV8 July 2024 TPS25751
3 Unique Address Interface Protocol
The Unique Address Interface allows for complex interactions between an I2C controller and a single PD Controller. The I2C target unique address is used to receive or respond to Host Interface protocol commands. Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 show the write and read protocols, respectively. The Byte Count used during a register write can be longer than the number of bytes actually written, in other words the controller can issue the stop bit without writing N bytes. Similarly, during a register read, the controller can issue the stop bit before reading all N bytes. N bytes refers to the number of bytes to be read or written.
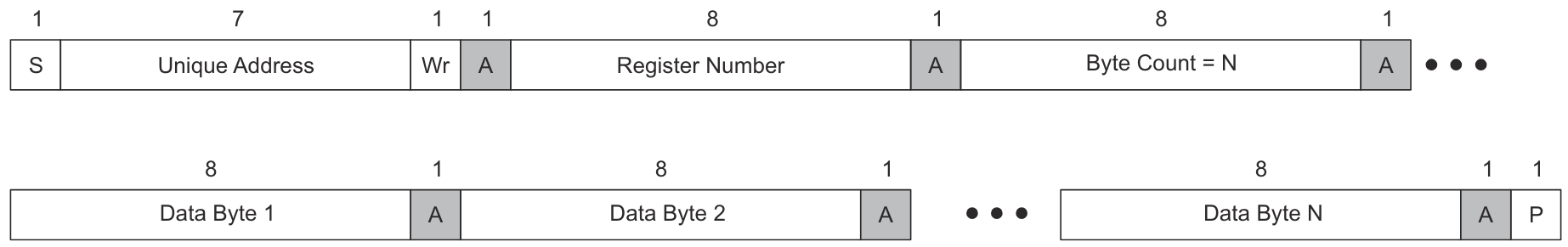 Figure 3-1 I2C Unique Address Write
Register Protocol
Figure 3-1 I2C Unique Address Write
Register Protocol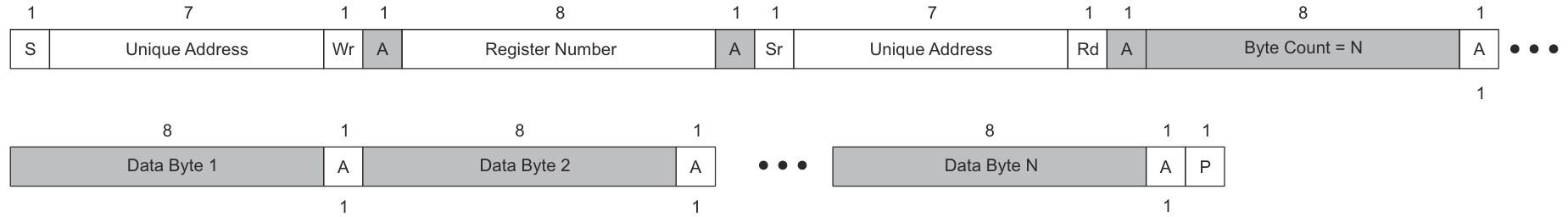 Figure 3-2 I2C Unique Address Read
Register Protocol
Figure 3-2 I2C Unique Address Read
Register Protocol