SLVAFW1 August 2024 DRV8818
3.1 Experiment and Results
The DRV8452 and DRV8462 can be configured to operate in the standstill power saving (SPS) mode by setting EN_STSL to 1b when no step pulses are being sent by the MCU. Power dissipation is reduced by lowering coil current from run current to the holding current value. Further details on how to configure the device for power saving can be found in the Standstill Power Saving Mode section of the DRV8462: 65 V, 5-10 A Stepper Motor Driver for High Efficiency and Noiseless Operation,.data sheet.
An experiment was run with a DRV8462EVM for a comparative study in the operation of a stepper motor with and without standstill power saving mode. Test conditions are mentioned in Table 3-1.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| VM | 24V |
| Microstepping | 1/16 |
| ITRIP | 2A |
| Running time | 250ms |
| Standstill time | 100ms |
| Holding Current | 20% of Running Current |
The following figures display waveforms and pictures from a thermal camera with SPS mode disabled and enabled. For images from the thermal camera, the left image shows the initial temperature while the right image shows the final temperature. The results showing temperature difference are summarized in Table 3-2.
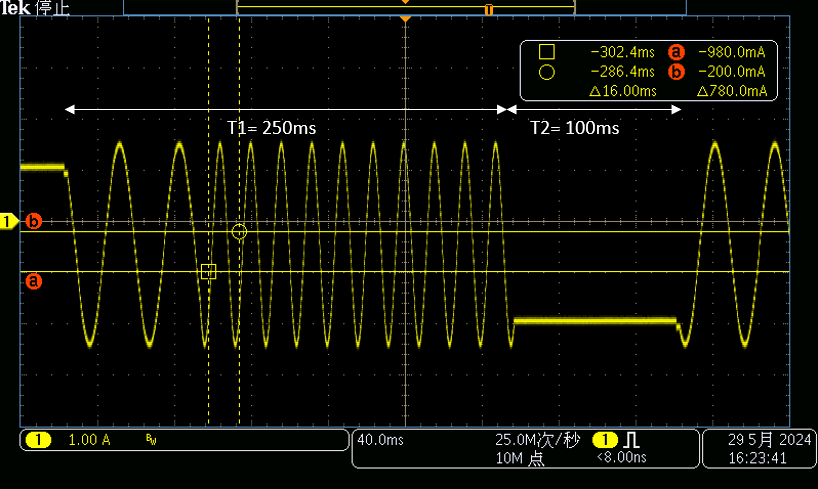 Figure 3-4 Standstill Power Saving
Mode Disabled
Figure 3-4 Standstill Power Saving
Mode Disabled Figure 3-6 Temperature Difference in
Motor - SPS Mode Disabled
Figure 3-6 Temperature Difference in
Motor - SPS Mode Disabled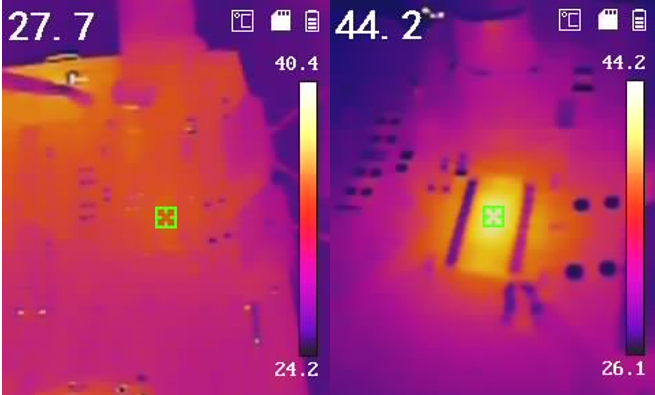 Figure 3-8 Temperature Difference in
IC - SPS Mode Disabled
Figure 3-8 Temperature Difference in
IC - SPS Mode Disabled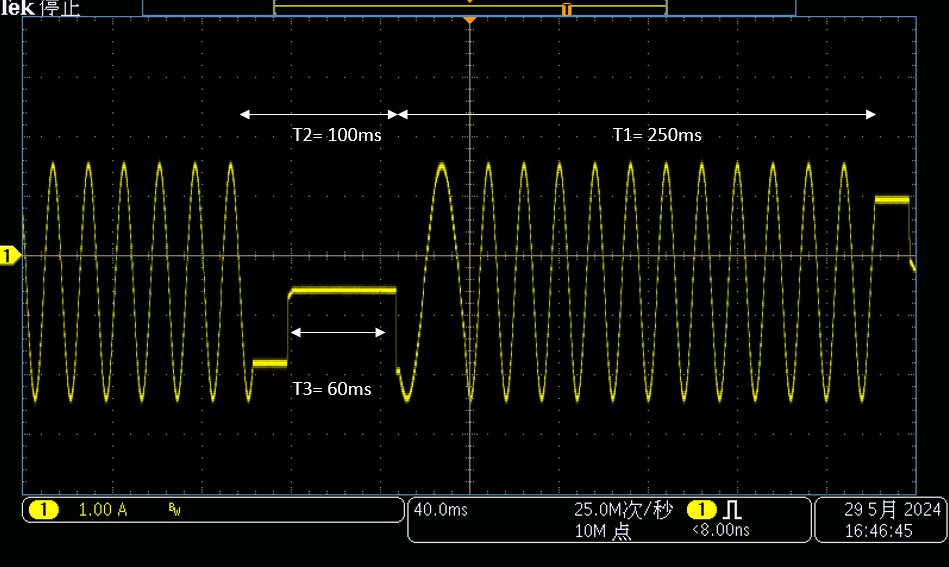 Figure 3-5 Standstill Power Saving
Mode Enabled
Figure 3-5 Standstill Power Saving
Mode Enabled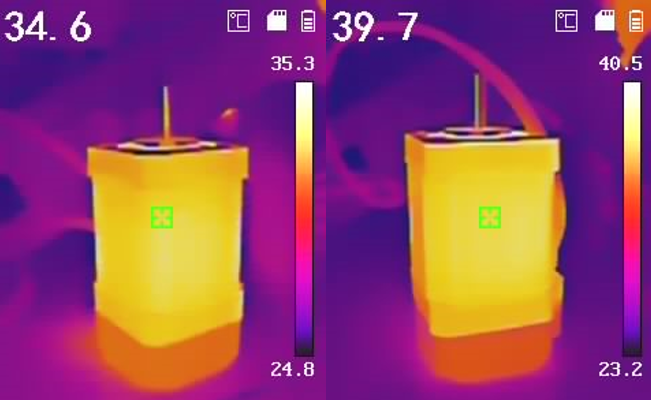 Figure 3-7 Temperature Difference in
Motor - SPS Mode Enabled
Figure 3-7 Temperature Difference in
Motor - SPS Mode Enabled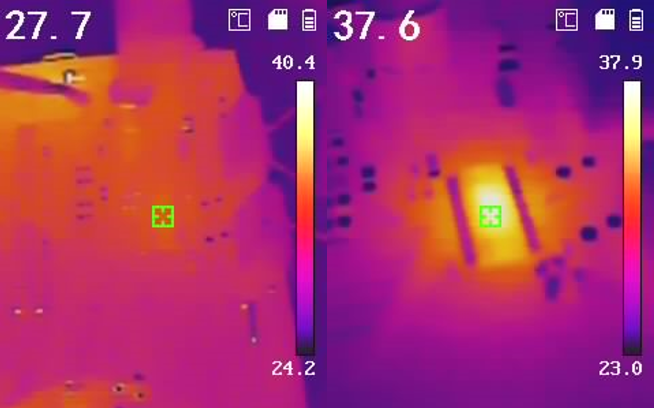 Figure 3-9 Temperature Difference in
IC - SPS Mode Enabled
Figure 3-9 Temperature Difference in
IC - SPS Mode Enabled| Standstill Power Saving Mode | Disabled | Enabled |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Temperature Difference | 18.4°C | 5.1°C |
| IC Temperature Difference | 16.5°C | 9.9°C |