SLVS675E August 2006 – January 2024 TPS5410
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Oscillator Frequency
- 6.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 6.3.3 Enable (ENA) and Internal Slow-Start
- 6.3.4 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 6.3.5 Boost Capacitor (BOOT)
- 6.3.6 Output Feedback (VSENSE)
- 6.3.7 Internal Compensation
- 6.3.8 Voltage Feed-Forward
- 6.3.9 Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) Control
- 6.3.10 Overcurrent Limiting
- 6.3.11 Overvoltage Protection
- 6.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
-
7 Applications and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1 Application Circuit
- 7.2.2 Using All Ceramic Capacitors
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.2.2.2 External Compensation Network
When using ceramic output capacitors, additional circuitry is required to stabilize the closed loop system. For this circuit the external components are R3, C5, C6 and C7. To determine the value of these components, first calculate the LC resonant frequency of the output filter:
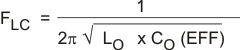
For this example the effective resonant frequency is calculated as 2306 Hz
The network composed of R1, R2, R3, C5, C6 and C7 has two poles and two zeros that are used to tailor the overall response of the feedback network to accommodate the use of the ceramic output capacitors. The pole and zero locations are given by the following equations:
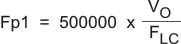
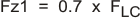
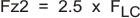
The final pole is located at a frequency too high to be of concern. The values for R1 and R2 are fixed by the 5-V output voltage as calculated using Equation 12. Now the values of R3, C5, C6 and C7 are determined using Equation 21, Equation 22, and Equation 23:
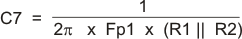

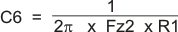
For this design, using the closest standard values, C7 is 0.056 μF, R3 is 1.76 kΩ and C6 is 2700 pF. C5 is added to improve load regulation performance. C5 is effectively in parallel with C6 in the location of the second pole frequency, so it must be small in relationship to C6. C5 must be less the 1/10 the value of C6. For this example, 150 pF works well.
For additional information on external compensation of the TPS5410 or other wide voltage range devices, see Using TPS5410/20/30/31/50 With Aluminum/Ceramic Output Capacitors application report.