SLVS941G April 2009 – August 2016 TPS62230
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3
Application Curves
- 9.2.3.1 VOUT = 1.1 V - TPS622311
- 9.2.3.2 VOUT = 1.2 V - TPS62232/TPS62235
- 9.2.3.3 VOUT = 1.8 V - TPS62231
- 9.2.3.4 VOUT = 1.85 V - TPS62236
- 9.2.3.5 VOUT = 2.5 V - TPS62230
- 9.2.3.6 VOUT = 3.0 V - TPS62233
- 9.2.3.7 Start-Up
- 9.2.3.8 PFM / PWM Operation
- 9.2.3.9 Peak-to-Peak Output Ripple Voltage
- 9.2.3.10 Power-Supply Rejection
- 9.2.3.11 Spurious Output Noise
- 9.2.3.12 Line Transient Response
- 9.2.3.13 Mode Transition
- 9.2.3.14 AC-Load Regulation
- 9.2.3.15 Load Transient Response
- 9.3 System Examples
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
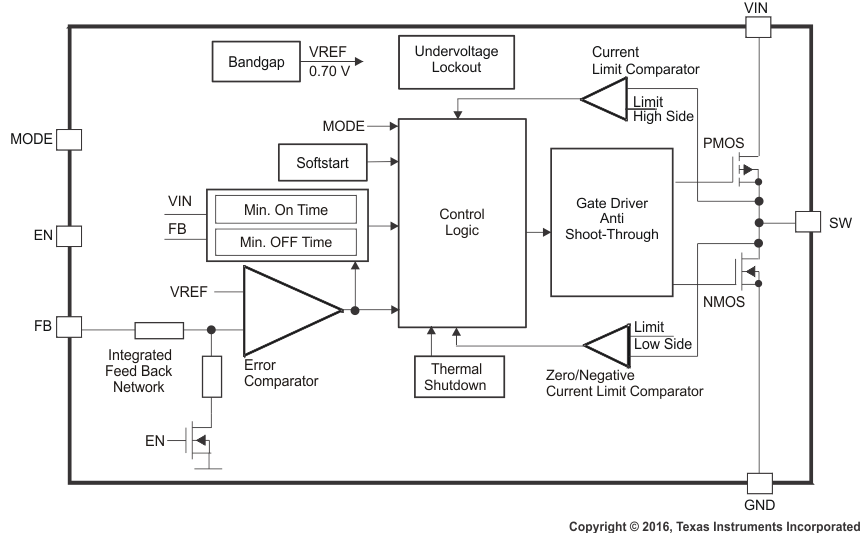
The TPS6223x synchronous step-down DC – DC converter family includes a unique hysteretic PWM controller scheme which enables switch frequencies over 3 MHz, excellent transient and AC load regulation as well as operation with cost-competitive external components.
The controller topology supports forced PWM mode as well as power-save mode operation. Power-save mode operation reduces the quiescent current consumption down to 22 μA and ensures high conversion efficiency at light loads by skipping switch pulses. In forced PWM mode, the device operates on a quasi-fixed frequency, avoids pulse skipping, and allows filtering of the switch noise by external filter components.
The TPS6223x devices offer fixed output voltage options featuring smallest solution size by using only three external components.
The internal switch current limit of typical 850 mA supports output currents of up to 500 mA, depending on the operating condition.
A significant advantage of TPS6223x compared to other hysteretic PWM controller topologies is its excellent DC and AC load regulation capability in combination with low-output voltage ripple over the entire load range which makes this part well suited for audio and RF applications.
Once the output voltage falls below the threshold of the error comparator, a switch pulse is initiated, and the high-side switch is turned on. It remains turned on until a minimum ON-time of tONmin expires and the output voltage trips the threshold of the error comparator or the inductor current reaches the high-side switch current limit. Once the high-side switch turns off, the low-side switch rectifier is turned on and the inductor current ramps down until the high-side switch turns on again or the inductor current reaches zero.
In forced PWM mode operation, negative inductor current is allowed to enable continuous conduction mode even at no load condition.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout
The undervoltage lockout circuit prevents the device from misoperation at low input voltages. It prevents the converter from turning on the switch or rectifier MOSFET under undefined conditions. The TPS6223x devices have a UVLO threshold set to 1.8 V (typical). Fully functional operation is permitted for input voltage down to the falling UVLO threshold level. The converter starts operation again once the input voltage trips the rising UVLO threshold level.
8.3.2 Enable and Shutdown
The device starts operation when EN is set high and starts up with the soft-start as previously described. For proper operation, the EN pin must be terminated and must not be left floating, except for the TPS622319, which has an integrated 1MΩ always active pull-down resistor.
Pulling the EN pin low forces the device into shutdown, with a shutdown quiescent current of typically 0.1 μA. In this mode, the P- and N-channel MOSFETs are turned off, the internal resistor feedback divider is disconnected, and the entire internal-control circuitry is switched off.
The EN input can be used to control power sequencing in a system with various DC – DC converters. The EN pin can be connected to the output of another converter, to drive the EN pin high and getting a sequencing of supply rails.
8.3.3 Thermal Shutdown
As soon as the junction temperature, TJ, exceeds 150°C (typical) the device goes into thermal shutdown. In this mode, the high-side and low-side MOSFETs are turned off. The device continues its operation when the junction temperature falls below the thermal shutdown hysteresis.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Soft-Start
The TPS6223x has an internal soft start circuit that controls the ramp up of the output voltage and limits the inrush current during start-up. This limits input voltage drops when a battery or a high-impedance power source is connected to the input of the converter.
The soft-start system generates a monotonic ramp up of the output voltage and reaches the nominal output voltage typically 100 μs after EN pin was pulled high.
If the output voltage does not reached its target value by this time, such as in the case of heavy load, the converter then operates in a current limit mode set by its switch current limits.
TPS6223x is able to start into a prebiased output capacitor. The converter starts with the applied bias voltage and ramps the output voltage to its nominal value.
8.4.2 Power-Save Mode
Connecting the MODE pin to GND enables the automatic PWM and power-save mode operation. The converter operates in quasi-fixed frequency PWM mode at moderate to heavy loads and in the pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode during light loads, which maintains high efficiency over a wide load current range. In PFM mode, the device starts to skip switch pulses and generates only single pulses with an ON-time of tONmin. The PFM mode frequency depends on the load current and the external inductor and output capacitor values. The PFM mode of TPS6223x is optimized for low-output voltage ripple if small external components are used. Even at low output currents, the PFM frequency is above the audible noise spectrum and makes this operation mode suitable for audio applications.
The ON-time tONmin can be estimated to:
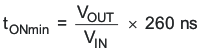
Therefore, the peak inductor current in PFM mode is approximately:
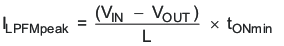
The transition from PFM into PWM mode and vice versa can be estimated to:
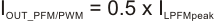
where
- tON: High-side switch ON-time [ns]
- VIN: Input voltage [V]
- VOUT: Output voltage [V]
- L: Inductance [μH]
- ILPFMpeak: PFM inductor peak current [mA]
- IOUT_PFM/PWM: Output current for PFM to PWM mode transition and vice versa [mA]
8.4.3 Forced PWM Mode
Pulling the MODE pin high forces the converter to operate in a continuous conduction PWM mode even at light load currents. The advantage is that the converter operates with a quasi-fixed frequency that allows simple filtering of the switching frequency for noise-sensitive applications. In this mode, the efficiency is lower compared to the power save mode during light loads. This pin must be terminated except for the TPS622319 , which has an integrated 1MΩ always active pull-down resistor.
For additional flexibility, it is possible to switch from power-save mode to forced PWM mode during operation. This allows efficient power management by adjusting the operation of the converter to the specific system requirements.
8.4.4 100% Duty Cycle Low Dropout Operation
The device starts to enter 100% duty cycle mode once the input voltage comes close to the nominal output voltage. To maintain the output voltage, the high side switch is turned on 100% for one or more cycles.
With further decreasing VIN the high-side MOSFET switch is turned on completely. In this case the converter offers a low input-to-output voltage difference. This is particularly useful in battery-powered applications to achieve longest operation time by taking full advantage of the whole battery voltage range.
The minimum input voltage to maintain regulation depends on the load current and output voltage, and can be calculated as:
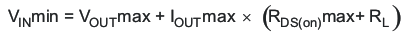
where
- IOUTmax: maximum output current plus inductor ripple current
- RDS(on)max: maximum P-channel switch RDSon
- RL: DC resistance of the inductor
- VOUTmax: nominal output voltage plus maximum output voltage tolerance
8.4.5 Short Circuit Protection
The TPS6223x integrates a high-side and low-side MOSFET current limit to protect the device against heavy load or short circuit. The current in the switches is monitored by current limit comparators. When the current in the P-channel MOSFET reaches its current limit, the P-channel MOSFET is turned off and the N-channel MOSFET is turned on to ramp down the current in the inductor. The high-side MOSFET switch can only turn on again, once the current in the low side MOSFET switch has decreased below the threshold of its current limit comparator.