SLVSAA4G June 2010 – February 2018 TPS65251
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 8.3.2 Synchronization
- 8.3.3 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 8.3.4 Delayed Start-Up
- 8.3.5 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.7 Input Capacitor
- 8.3.8 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.3.9 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.10 Loop Compensation
- 8.3.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.12 Powergood
- 8.3.13 Current Limit Protection
- 8.3.14 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 8.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Loop Compensation Circuit
- 9.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 9.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 9.2.2.6 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 9.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.8 Adjustable Current Limiting Resistor Selection
- 9.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 9.2.2.10 Compensation
- 9.2.2.11 3.3-V and 6.5-V LDO Regulators
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.1 Low-Power Mode Operation
By pulling the LOW_P pin high all converters will operate in pulse-skipping mode, greatly reducing the overall power consumption at light and no load conditions. Although each buck converter has a skip comparator that makes sure regulation is not lost when a heavy load is applied and low-power mode is enabled, system design needs to make sure that the LP pin is pulled low for continuous loading in excess of 100 mA.
When low-power is implemented, the peak inductor current used to charge the output capacitor is:

Where TSLEEP_CLK is half of the converter switching period, 2/fSW.
The size of the additional ripple added to the output is:
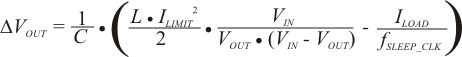
And the peak output voltage during low-power operation is:
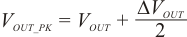
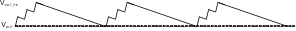 Figure 20. Peak Output Voltage During Low-Power Operation
Figure 20. Peak Output Voltage During Low-Power Operation