SLVSAB2G May 2010 – December 2015 DRV8830
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The VCC pin should be bypassed to GND using low-ESR ceramic bypass capacitors with a recommended value of 0.1-μF rated for VCC. This capacitor should be placed as close to the VCC pin as possible with a thick trace or ground plane connection to the device GND pin.
The VCC pin must be bypassed to ground using an appropriate bulk capacitor. This component may be an electrolytic and should be located close to the DRV8830.
10.2 Layout Example
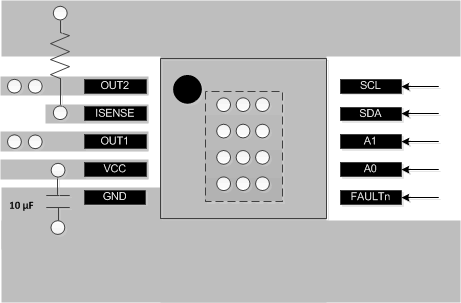 Figure 18. Layout Recommendation
Figure 18. Layout Recommendation
10.3 Thermal Considerations
The DRV8830 has thermal shutdown (TSD) as described in Thermal Shutdown (TSD). If the die temperature exceeds approximately 160°C, the device will be disabled until the temperature drops to a safe level. Any tendency of the device to enter TSD is an indication of either excessive power dissipation, insufficient heatsinking, or too high an ambient temperature.
10.3.1 Power Dissipation
Power dissipation in the DRV8830 is dominated by the power dissipated in the output FET resistance, or RDS(ON). Average power dissipation when running a stepper motor can be roughly estimated by Equation 3.
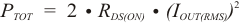
where PTOT is the total power dissipation, RDS(ON) is the resistance of each FET, and IOUT(RMS) is the RMS output current being applied to each winding. IOUT(RMS) is equal to the approximately 0.7x the full-scale output current setting. The factor of 2 comes from the fact that at any instant two FETs are conducting winding current for each winding (one high-side and one low-side).
The maximum amount of power that can be dissipated in the device is dependent on ambient temperature and heatsinking.
Note that RDS(ON) increases with temperature, so as the device heats, the power dissipation increases. This must be taken into consideration when sizing the heatsink.