SLVSAF6A June 2011 – January 2016 TPS65835
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4 Specifications
-
5 Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Feature Description
- 5.4 Device Functional Modes
- 5.5
MSP430 CORE
- 5.5.1
MSP430 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.5.1.1 MSP430 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5.1.2 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5.1.3 Typical Characteristics, Active Mode Supply Current (Into VCC)
- 5.5.1.4 Low-Power Mode Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.5.1.5 Typical Characteristics, Low-Power Mode Supply Currents
- 5.5.1.6 Schmitt-Trigger Inputs, Ports Px
- 5.5.1.7 Leakage Current, Ports Px
- 5.5.1.8 Outputs, Ports Px
- 5.5.1.9 Output Frequency, Ports Px
- 5.5.1.10 Typical Characteristics, Outputs
- 5.5.1.11 Pin-Oscillator Frequency - Ports Px
- 5.5.1.12 Typical Characteristics, Pin-Oscillator Frequency
- 5.5.1.13 POR/Brownout Reset (BOR)
- 5.5.1.14 Typical Characteristics, POR/Brownout Reset (BOR)
- 5.5.1.15 DCO Frequency
- 5.5.1.16 Calibrated DCO Frequencies, Tolerance
- 5.5.1.17 Wake-Up From Lower-Power Modes (LPM3/4)
- 5.5.1.18 Typical Characteristics, DCO Clock Wake-Up Time From LPM3/4
- 5.5.1.19 Crystal Oscillator, XT1, Low-Frequency Mode
- 5.5.1.20 Internal Very-Low-Power Low-Frequency Oscillator (VLO)
- 5.5.1.21 Timer_A
- 5.5.1.22 USCI (UART Mode)
- 5.5.1.23 USCI (SPI Master Mode)
- 5.5.1.24 USCI (SPI Slave Mode)
- 5.5.1.25 USCI (I2C Mode)
- 5.5.1.26 Comparator_A+
- 5.5.1.27 Typical Characteristics - Comparator_A+
- 5.5.1.28 10-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- 5.5.1.29 10-Bit ADC, Built-In Voltage Reference
- 5.5.1.30 10-Bit ADC, External Reference
- 5.5.1.31 10-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- 5.5.1.32 10-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
- 5.5.1.33 10-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In VMID
- 5.5.1.34 Flash Memory
- 5.5.1.35 RAM
- 5.5.1.36 JTAG and Spy-Bi-Wire Interface
- 5.5.1.37 JTAG Fuse
- 5.5.2 MSP430 Core Operation
- 5.5.1
MSP430 Electrical Characteristics
- 6 Application and Implementation
- 7 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
3 Terminal Configuration and Functions
3.1 Pin Diagram
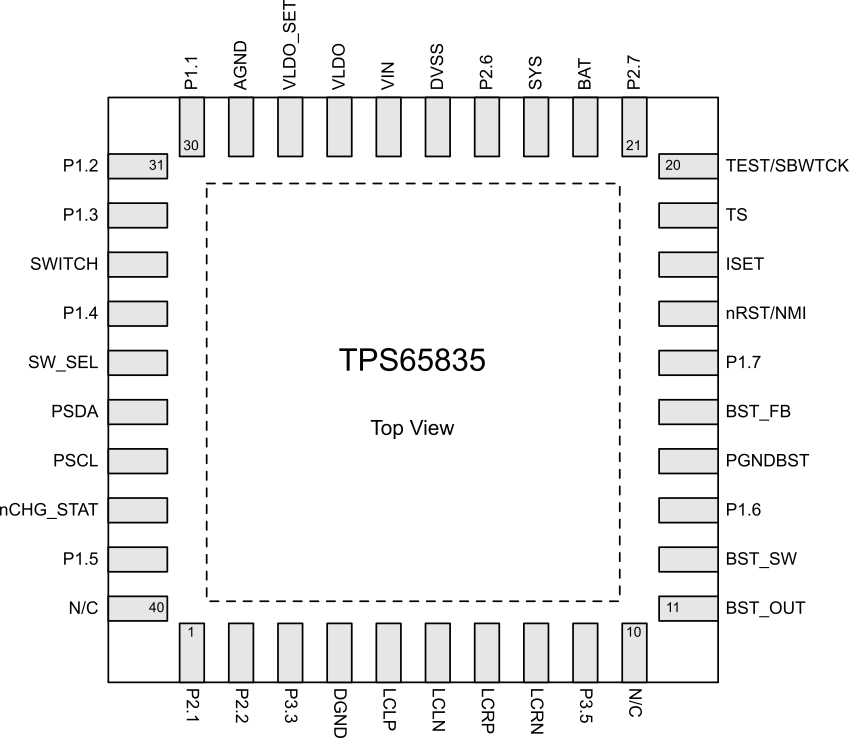
A. Pins 10 and 40 = N/C. No internal connection; connect to main system ground.
Figure 3-1 40-Pin RKP VQFN (Top View)
3.2 Pin Functions
Table 3-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| POWER MANAGEMENT CORE (PMIC) | |||
| 4 | DGND | - | PMIC Digital Ground(2) |
| 5 | LCLP | O | H-Bridge Output for Left LC Shutter, Positive Terminal |
| 6 | LCLN | O | H-Bridge Output for Left LC Shutter, Negative Terminal |
| 7 | LCRP | O | H-Bridge Output for Right LC Shutter, Positive Terminal |
| 8 | LCRN | O | H-Bridge Output for Right LC Shutter, Negative Terminal |
| 11 | BST_OUT | O | Boost Output |
| 12 | BST_SW | I | Boost Switch Node |
| 14 | PGNDBST | — | PMIC Boost Power Ground(2) |
| 15 | BST_FB | I | Boost Feedback Node |
| 18 | ISET | I/O | Fast-Charge Current Setting Resistor |
| 19 | TS | I | Pin for 10-kΩ NTC Thermistor Connection FLOAT IF THERMISTOR / TS FUNCTION IS NOT USED |
| 22 | BAT | I/O | Charger Power Stage Output and Battery Voltage Sense Input |
| 23 | SYS | O | Output Terminal to System |
| 26 | VIN | I | AC or USB Adapter Input |
| 27 | VLDO | O | LDO Output |
| 28 | VLDO_SET | I | Sets LDO Output Voltage (see Table 5-2) |
| 29 | AGND | — | PMIC Analog Ground(2) |
| 33 | SWITCH | I | Switch Input for Device Power On/Off |
| 35 | SW_SEL | I | Selects Type of Switch Connected to SWITCH Pin (see Table 5-6) |
| 36 | PSDA | I/O | I2C Data Pin (only used for TI debug and test) GROUND PIN IN APPLICATION |
| 37 | PSCL | I/O | I2C Clock Pin (only used for TI debug and test) GROUND PIN IN APPLICATION |
| 38 | nCHG_STAT | O | Open-drain Output, Charger Status Indication CONNECT TO GROUND IF FUNCTION IS NOT USED |
| MSP430 MICROCONTROLLER | |||
| 1 | P2.1/ TA1.1 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer1_A, capture: CCI1A input, compare: Out1 output |
| 2 | P2.2/ TA1.1 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer1_A, capture: CCI1B input, compare: Out1 output |
| 3 | P3.3/ TA1.2 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer1_A, compare: Out2 output |
| 9 | P3.5/ TA0.1 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer0_A, compare: Out0 output |
| 13 | P1.6/ TA0.1/ A6/ CA6/ UCB0SOMI/ UCB0SCL/ TDI/TCLK |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer0_A, compare: Out1 output ADC10 analog input A6 Comparator_A+, CA6 input USCI_B0 slave out/master in SPI mode USCI_B0 SCL I2C clock in I2C mode JTAG test data input or test clock input during programming and test |
| 16 | P1.7/ A7/ CA7/ CAOUT/ UCB0SIMO/ UCB0SDA/ TDO/TDI |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin ADC10 analog input A7 Comparator_A+, CA7 input Comparator_A+, output USCI_B0 slave in/master out in SPI mode USCI_B0 SDA I2C data in I2C mode JTAG test data output terminal or test data input during programming and test(3) |
| 17 | nRST/ NMI/ SBWTDIO |
I/O | Reset Nonmaskable interrupt input Spy-Bi-Wire test data input/output during programming and test |
| 20 | TEST/ SBWTCK |
I | Selects test mode for JTAG pins on Port 1. The device protection fuse is connected to TEST. Spy-Bi-Wire test clock input during programming and test |
| 21 | P2.7/ XOUT |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Output terminal of crystal oscillator(1)) |
| 24 | P2.6/ XIN/ TA0.1 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin XIN, Input terminal of crystal oscillator TA0.1, Timer0_A, compare: Out1 output |
| 25 | DVSS | — | MSP430 Ground reference(2) |
| 30 | P1.1/ TA0.0/ UCA0RXD/ UCA0SOMI/ A1/ CA1 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer0_A, capture: CCI0A input, compare: Out0 output USCI_A0 receive data input in UART mode USCI_A0 slave data out/master in SPI mode ADC10 analog input A1 Comparator_A+, CA1 input |
| 31 | P1.2/ TA0.1/ UCA0TXD/ UCA0SIMO/ A2/ CA2 |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer0_A, capture: CCI1A input, compare: Out1 output USCI_A0 transmit data output in UART mode USCI_A0 slave data in/master out in SPI mode ADC10 analog input A2 Comparator_A+, CA2 input |
| 32 | P1.3/ ADC10CLK/ A3 VREF-/VEREF-/ CA3/ CAOUT |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin ADC10, conversion clock output ADC10 analog input A3 ADC10 negative reference voltage Comparator_A+, CA3 input Comparator_A+, output |
| 34 | P1.4/ SMCLK/ UCB0STE UCA0CLK/ A4 VREF+/VEREF+/ CA4 TCK |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin SMCLK signal output USCI_B0 slave transmit enable USCI_A0 clock input/output ADC10 analog input A4 ADC10 positive reference voltage Comparator_A+, CA4 input JTAG test clock, input terminal for device programming and test |
| 39 | P1.5/ TA0.0/ UCB0CLK/ UCA0STE/ A5/ CA5/ TMS |
I/O | General-purpose digital I/O pin Timer0_A, compare: Out0 output USCI_B0 clock input/output USCI_A0 slave transmit enable ADC10 analog input A5 Comparator_A+, CA5 input JTAG test mode select, input terminal for device programming and test |
| MISCELLANEOUS AND PACKAGE | |||
| 10, 40 | N/C | — | All N/C pins are not connected internally (package to die). They should be connected to the main system ground. |
| 41 | Thermal PAD | — | There is an internal electrical connection between the exposed thermal pad and the AGND ground pin of the device. The thermal pad must be connected to the same potential as the AGND pin on the printed circuit board. Do not use the thermal pad as the primary ground input for the device. AGND pin must be connected to ground at all times. |
(1) If P2.7 is used as an input, excess current will flow until P2SEL.7 is cleared. This is due to the oscillator output driver connection to this pad after reset.
(2) MSP430 ground and grounds for PMIC (Power Management Core) are connected internally.
(3) TDO or TDI is selected via JTAG instruction.