SLVSAL5E November 2011 – October 2021 TPS62150 , TPS62150A , TPS62151 , TPS62152 , TPS62153
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.3 Application Curves
VIN= 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, (unless otherwise noted)
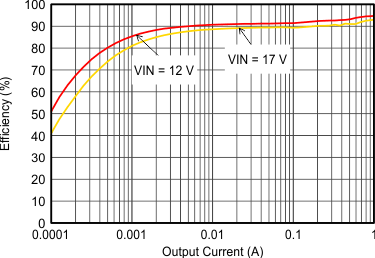
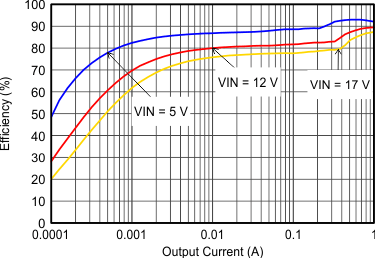
| VOUT = 5 V |
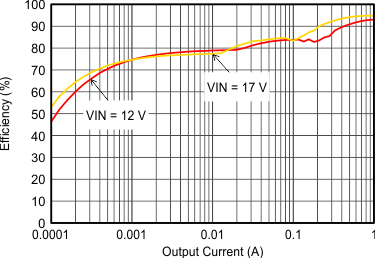
| VOUT = 5 V |
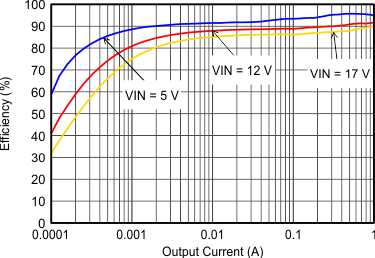
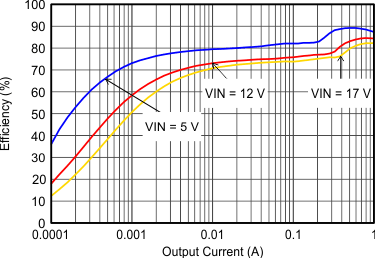
| VOUT = 3.3 V |
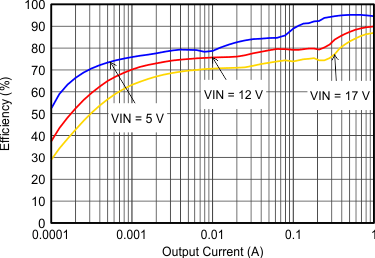
| VOUT = 3.3 V |
| VOUT = 1.8 V |
| VOUT = 0.9 V |
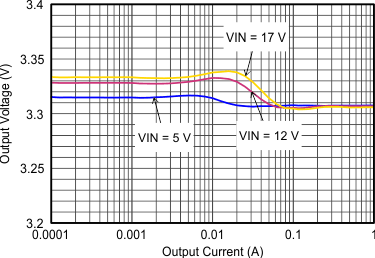 Figure 9-16 Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)
Figure 9-16 Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)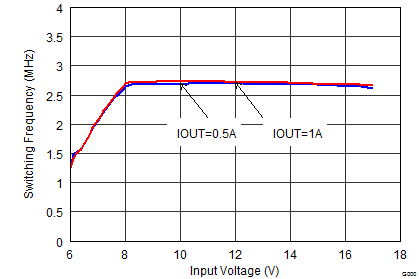
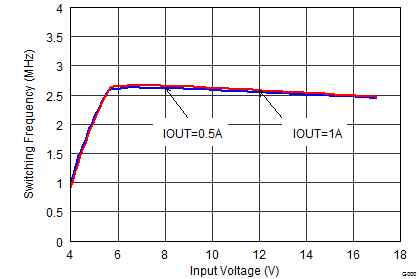
| FSW = low | VOUT = 5 V |
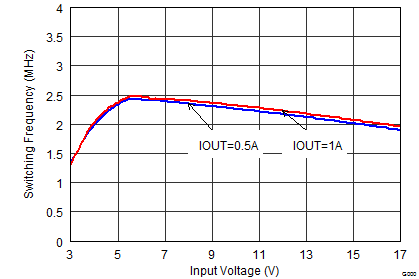
| FSW = low | VOUT = 3.3 V |
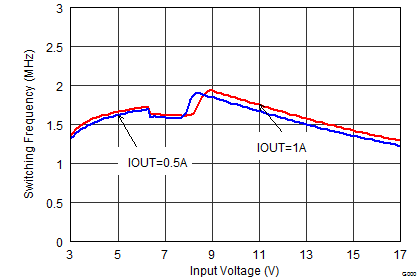
| FSW = low | VOUT = 1.8 V |
| FSW = low | VOUT = 1 V |
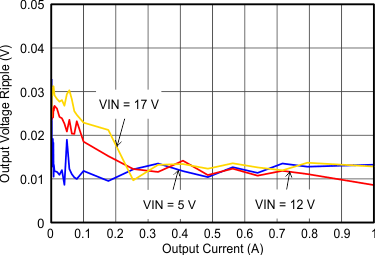 Figure 9-26 Output Voltage Ripple
Figure 9-26 Output Voltage Ripple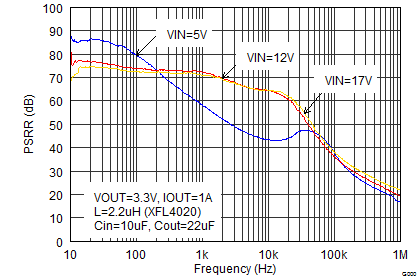
| IOUT = 1 A | fSW= 2.5 MHz |
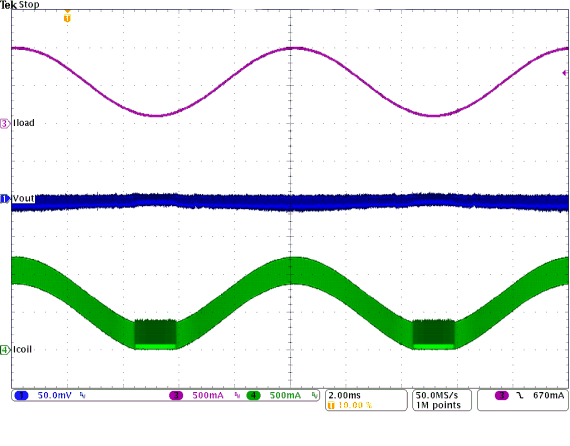 Figure 9-30 PWM-to-PSM Transition
Figure 9-30 PWM-to-PSM Transition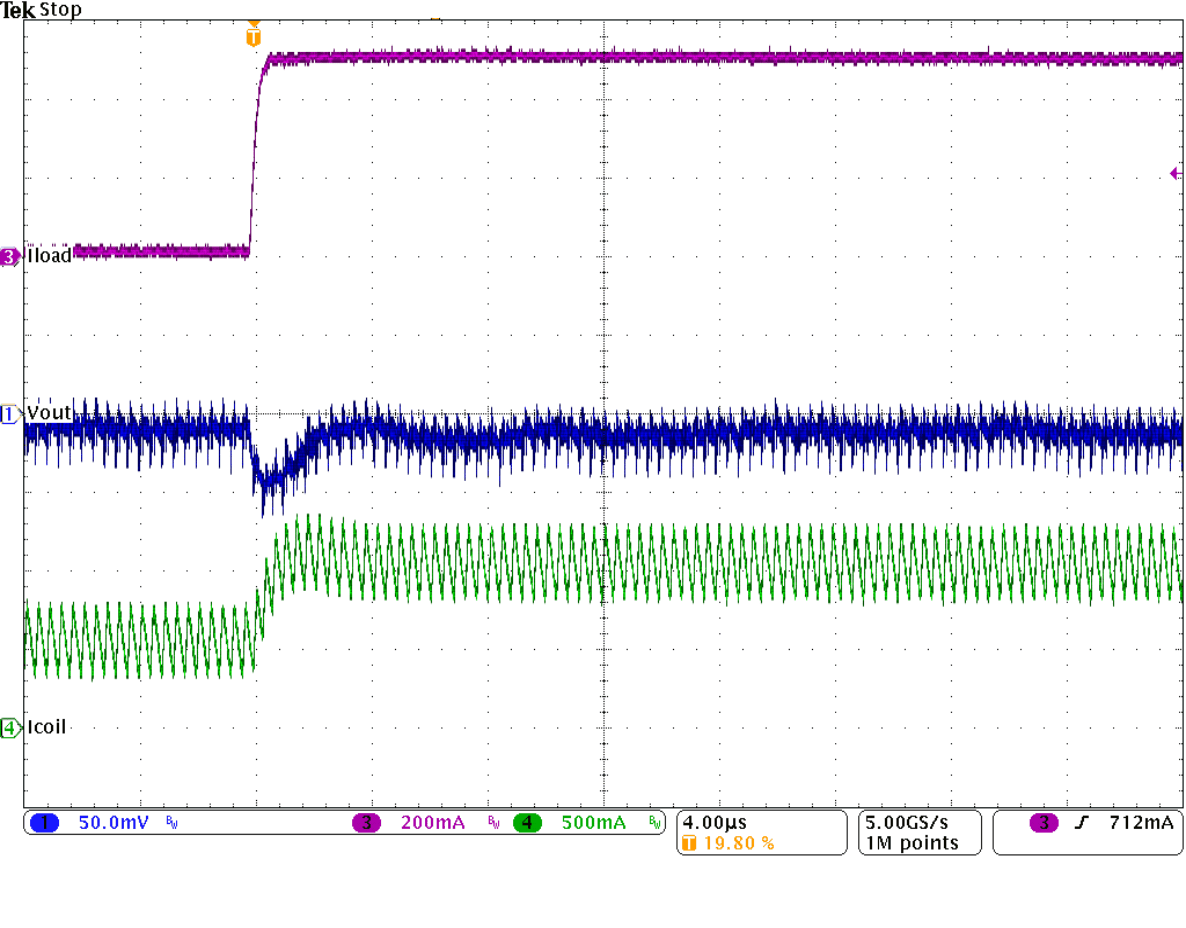 Figure 9-32 Load
Transient Response, Rising Edge
Figure 9-32 Load
Transient Response, Rising Edge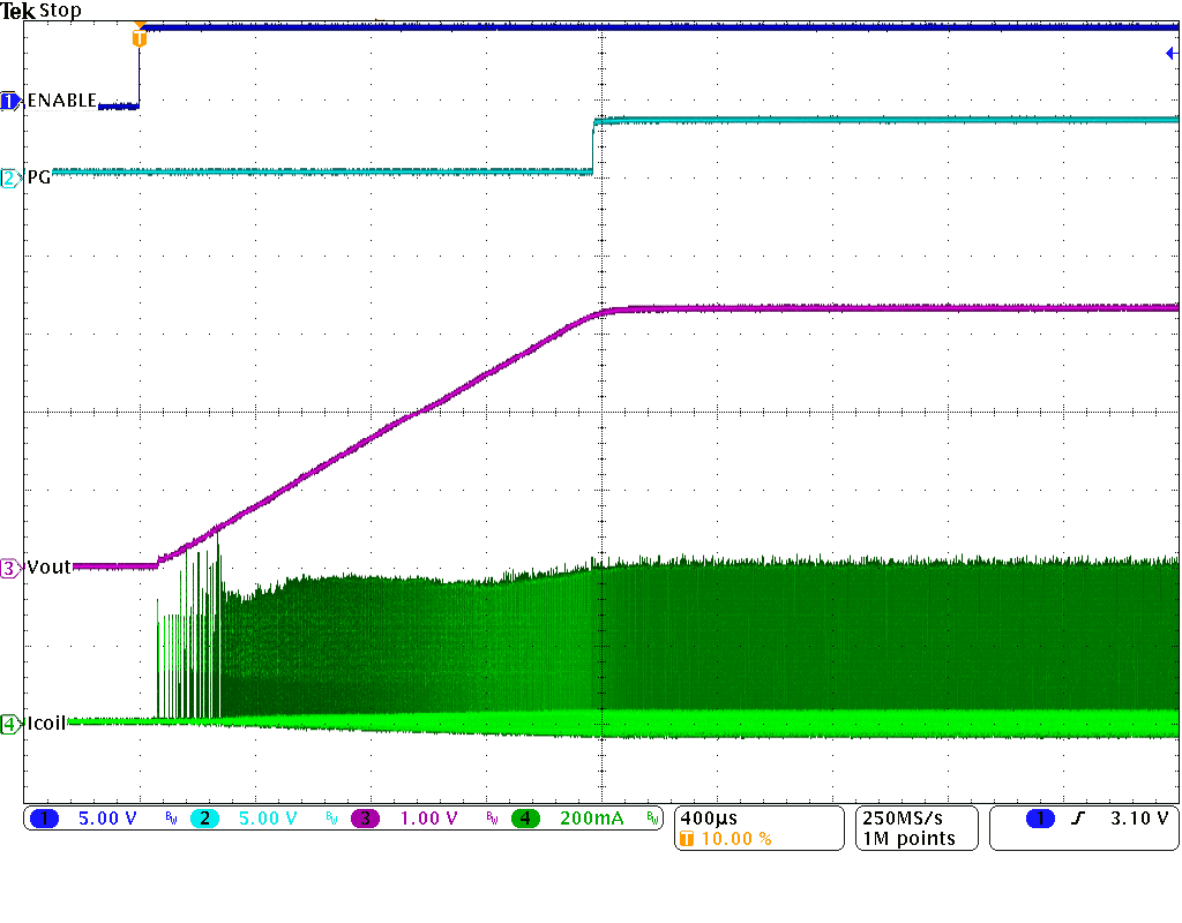 Figure 9-34 Start-Up Into 100 mA
Figure 9-34 Start-Up Into 100 mA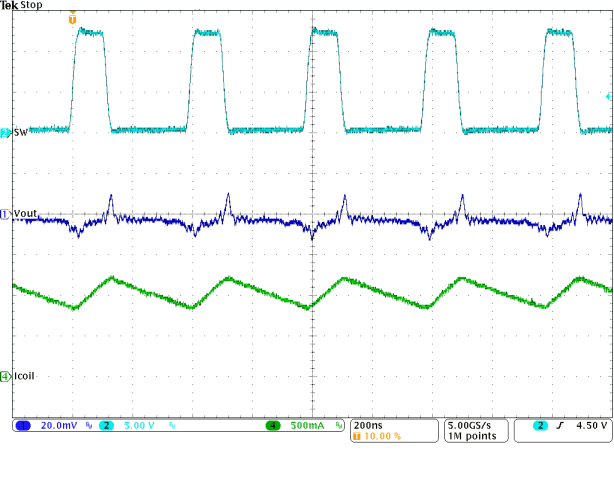
| IOUT = 1 A |
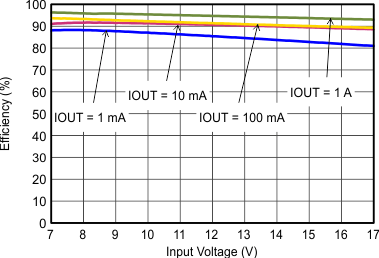
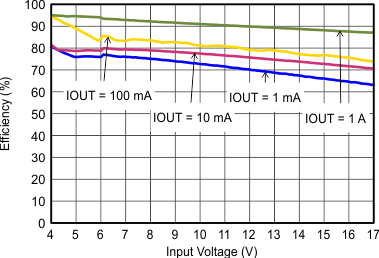
| VOUT = 5 V |
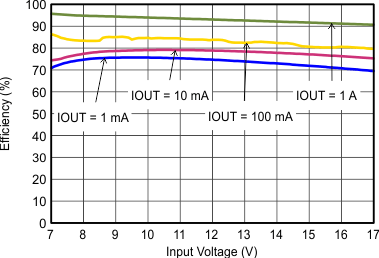
| VOUT = 5 V |
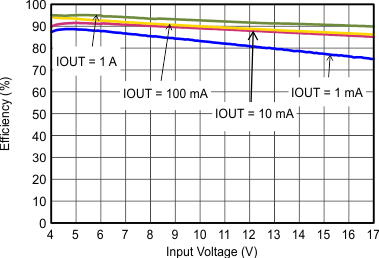
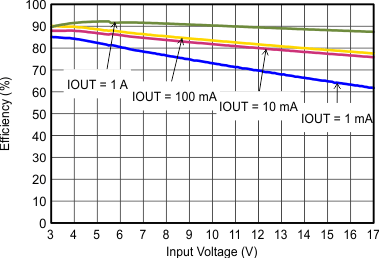
| VOUT = 3.3 V |
| VOUT = 3.3 V |
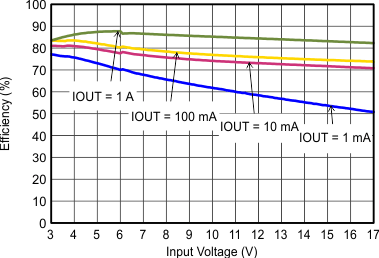
| VOUT = 1.8 V |
| VOUT = 0.9 V |
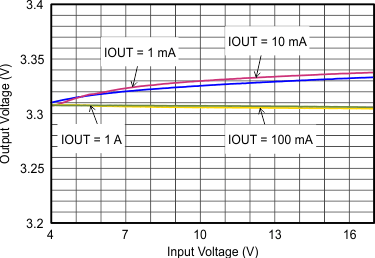 Figure 9-17 Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)
Figure 9-17 Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)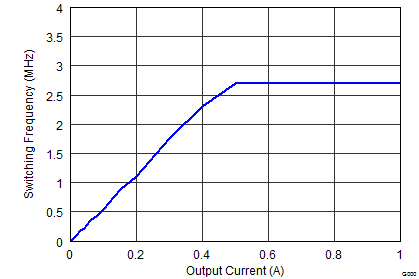
| FSW = low | VOUT = 0.9 V |
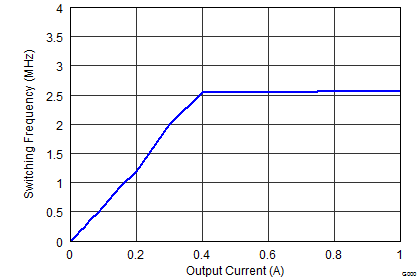
| FSW = low | VOUT = 3.3 V |
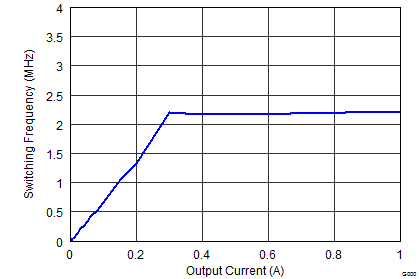
| FSW = low | VOUT = 1.8 V |
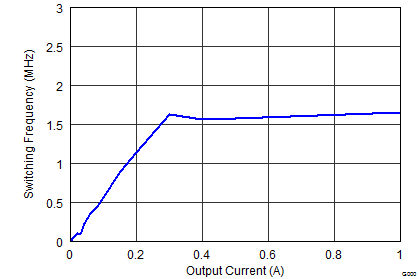
| FSW = low | VOUT = 1 V |
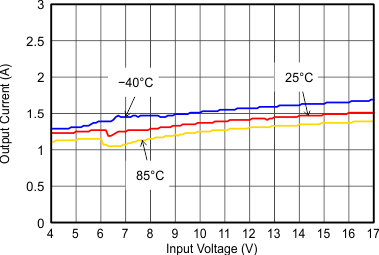 Figure 9-27 Maximum Output Current
Figure 9-27 Maximum Output Current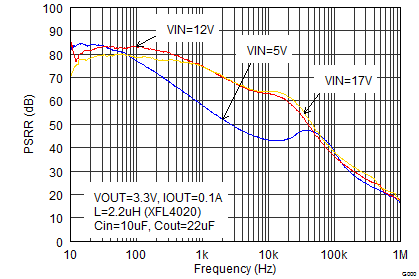
| IOUT = 0.1 A | fSW = 2.5 MHz |
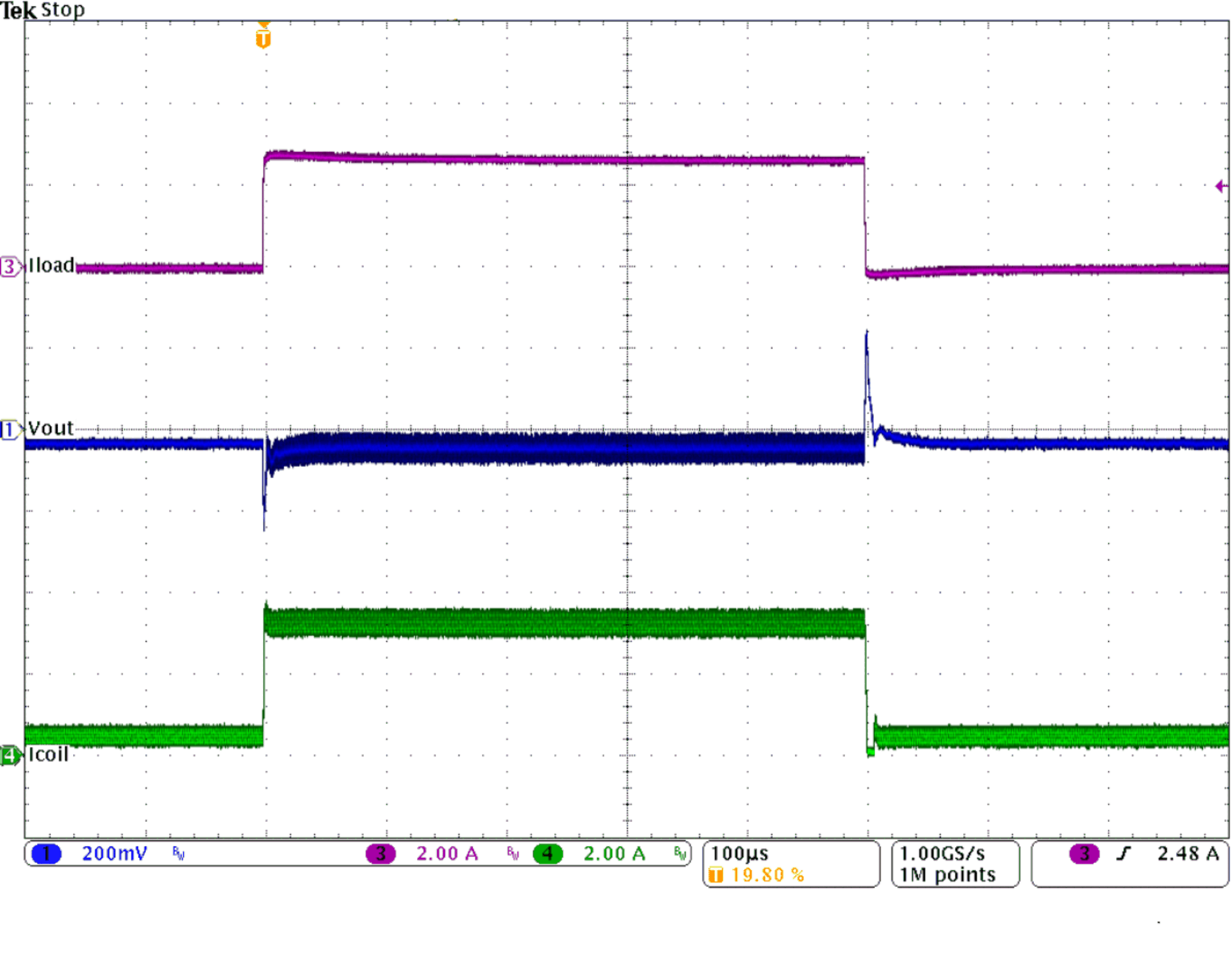 Figure 9-31 Load
Transient Response
Figure 9-31 Load
Transient Response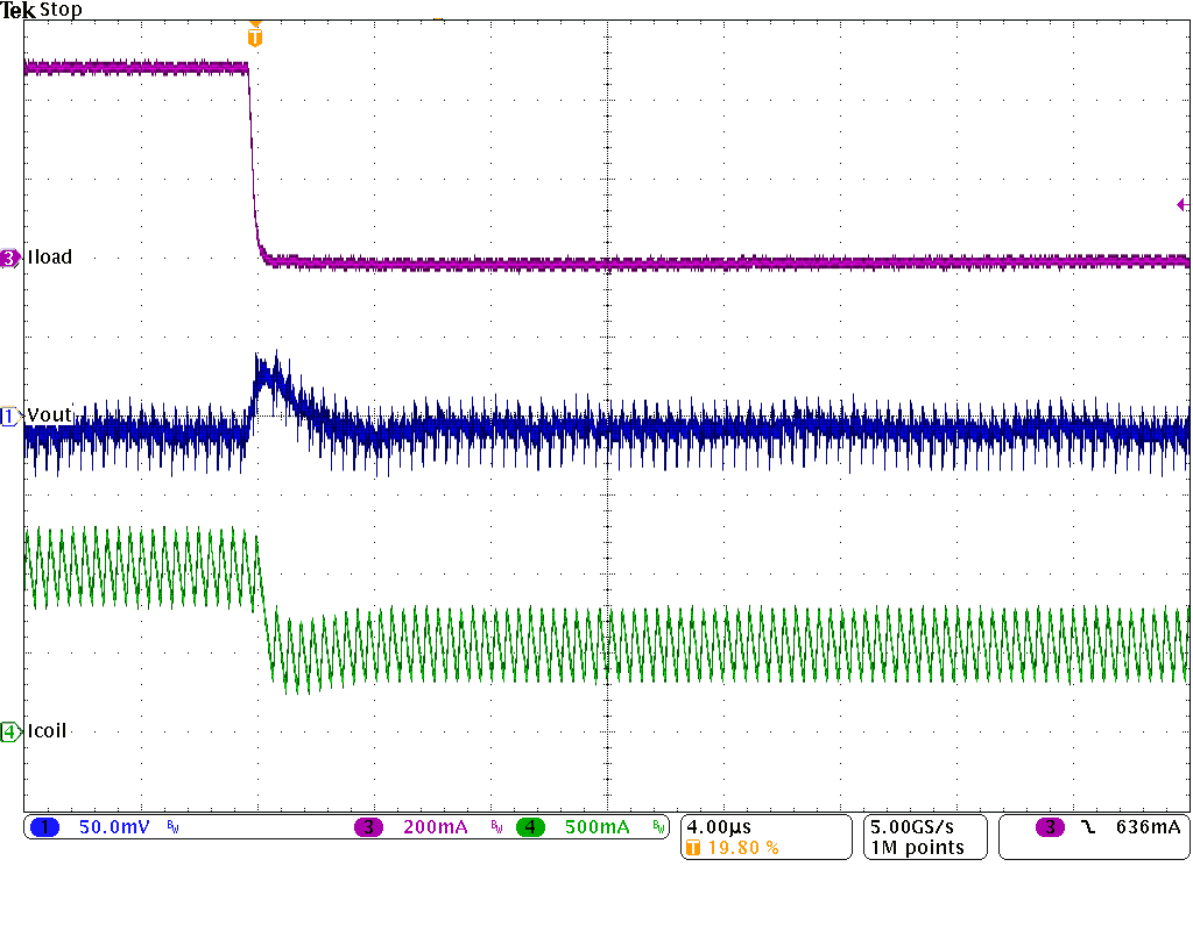 Figure 9-33 Load
Transient Response, Falling Edge
Figure 9-33 Load
Transient Response, Falling Edge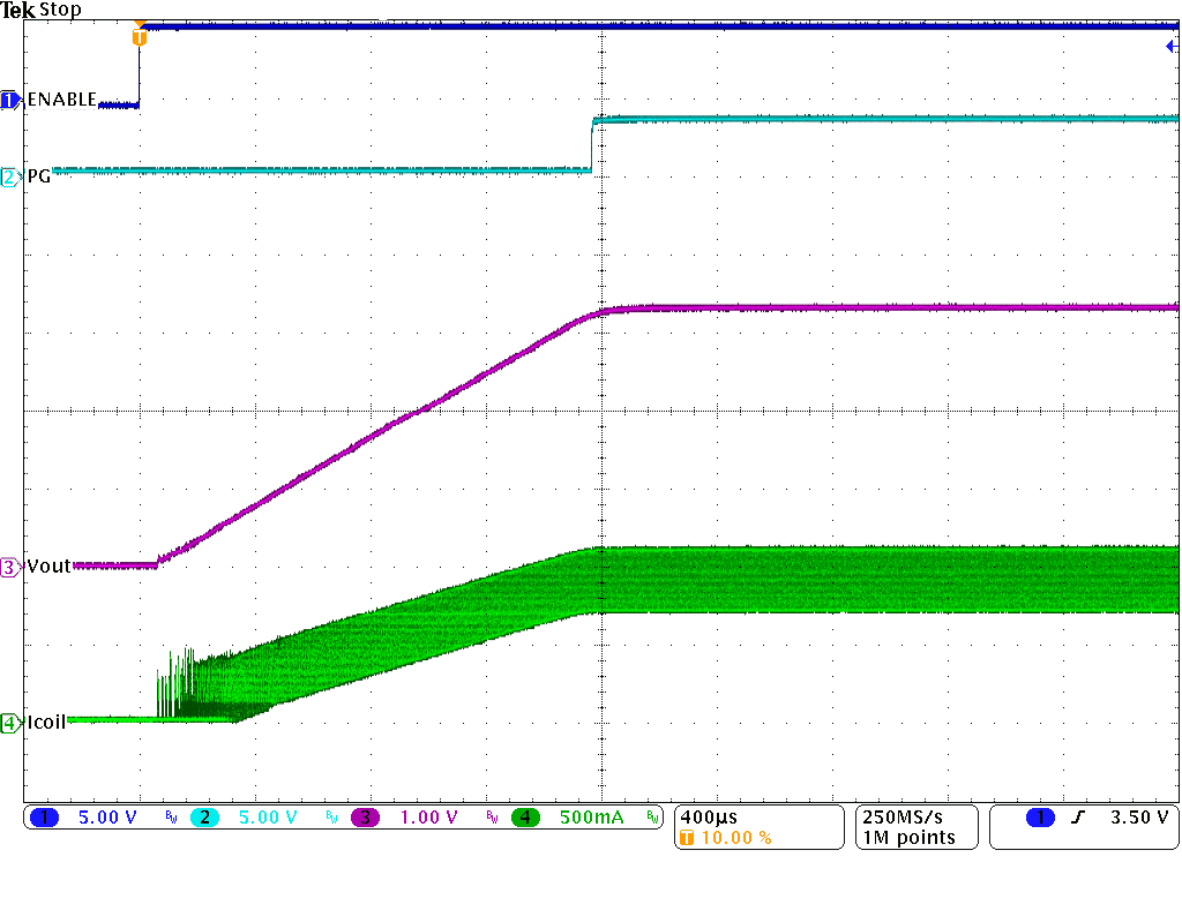 Figure 9-35 Start-Up Into 1 A
Figure 9-35 Start-Up Into 1 A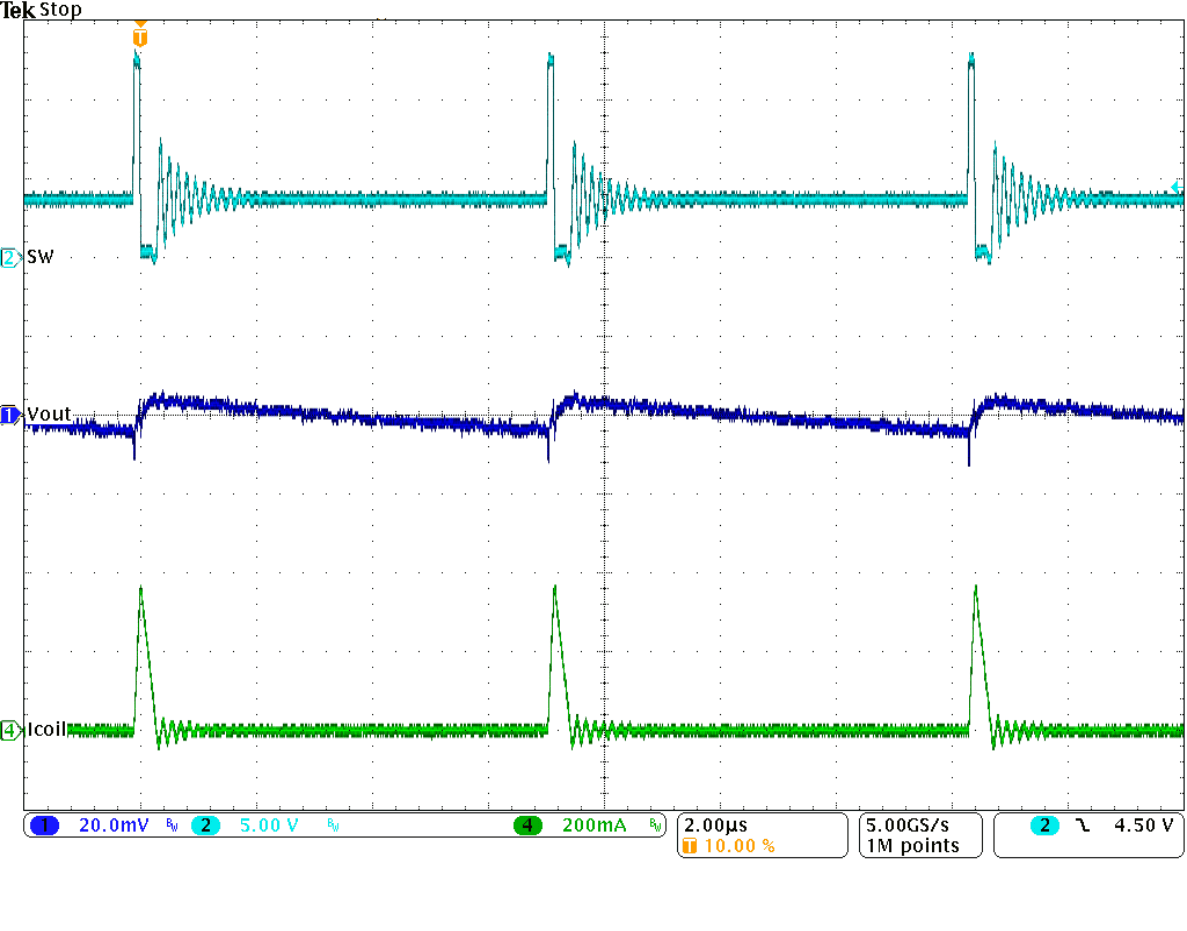
| IOUT = 10 mA |