SLVSB71E February 2012 – September 2016 TLV62150 , TLV62150A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
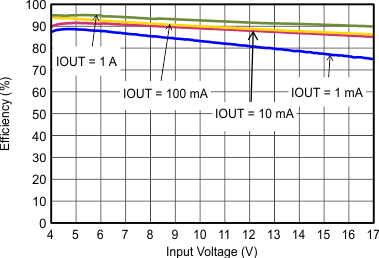
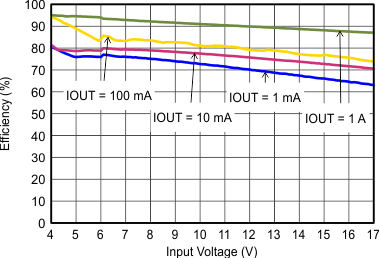
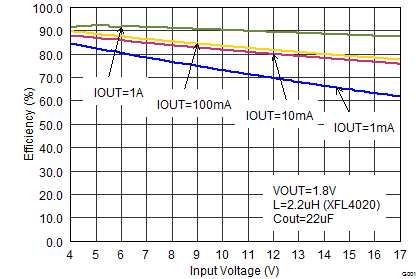
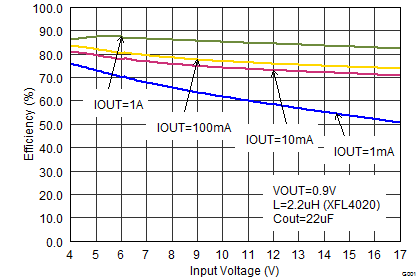
9.2.3 Application Curves
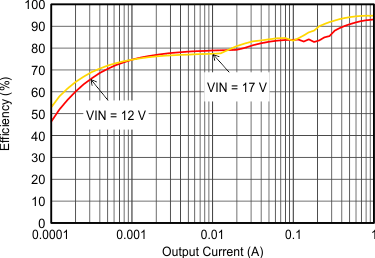
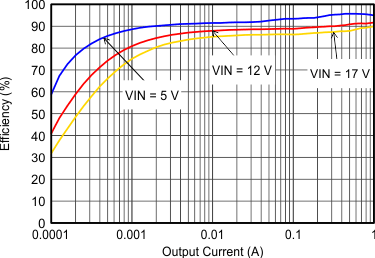
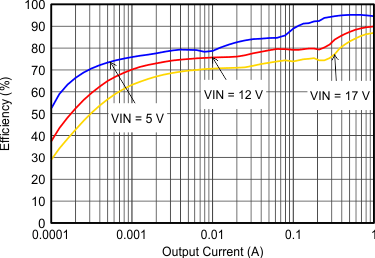
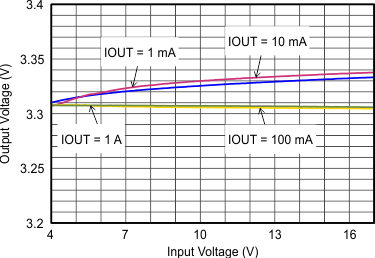
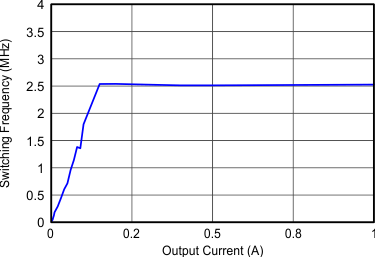
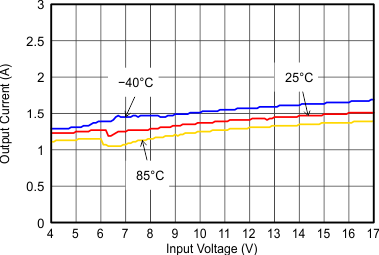
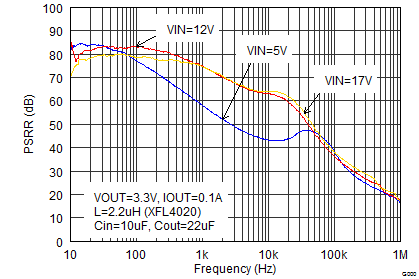
VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, (unless otherwise noted)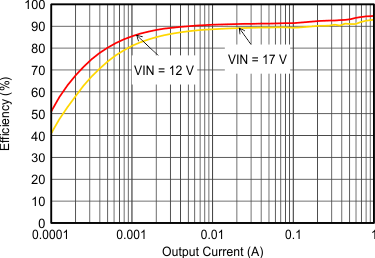
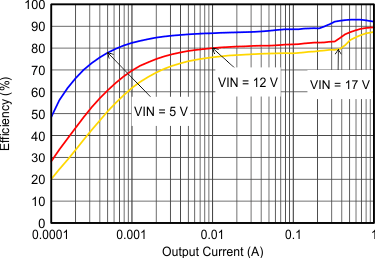
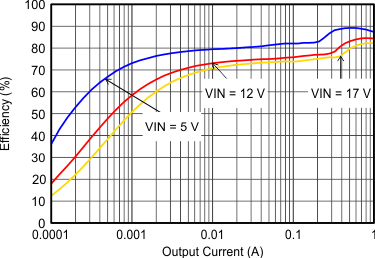
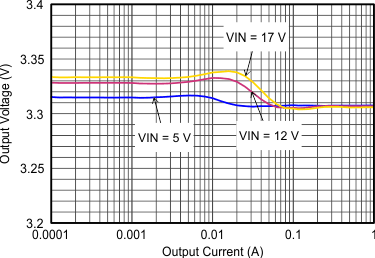
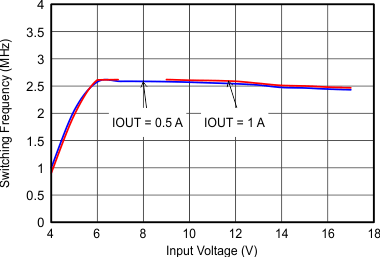
| FSW=Low |
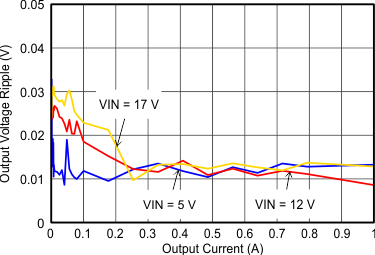
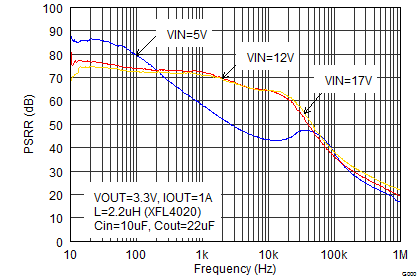
| IOUT = 1 A |
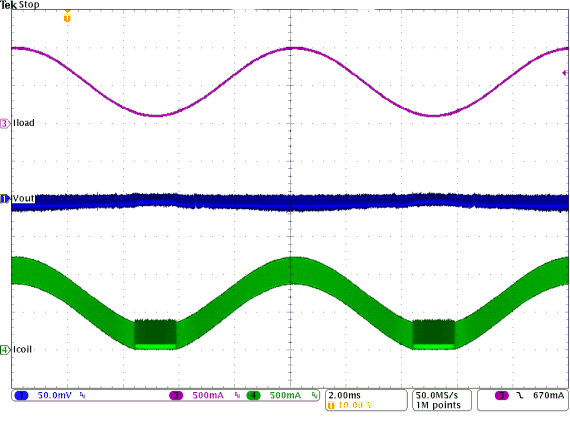 Figure 28. PWM-PSM-Transition
Figure 28. PWM-PSM-Transition
(VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V With 50 mV/div)
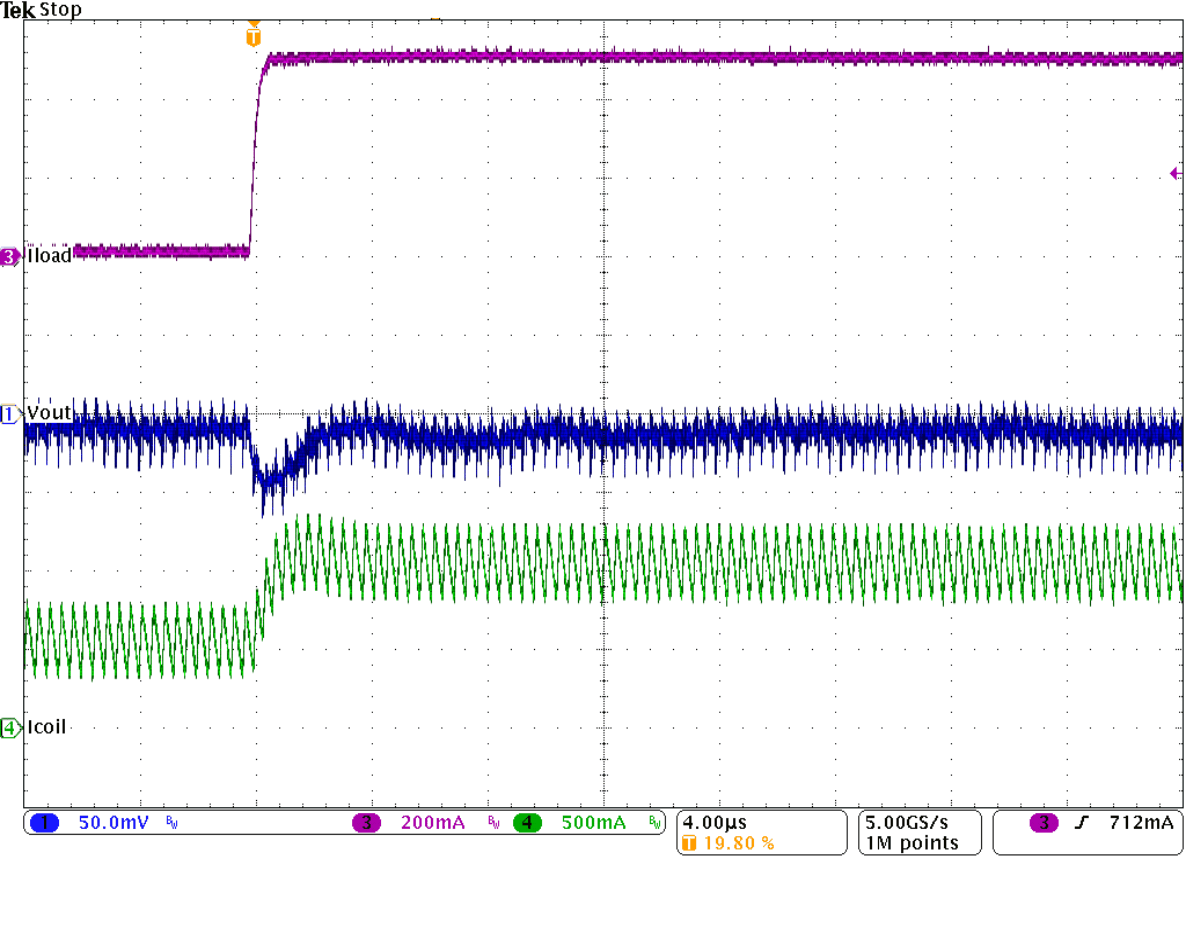 Figure 30. Load Transient Response of Figure 29,
Figure 30. Load Transient Response of Figure 29,
Rising Edge
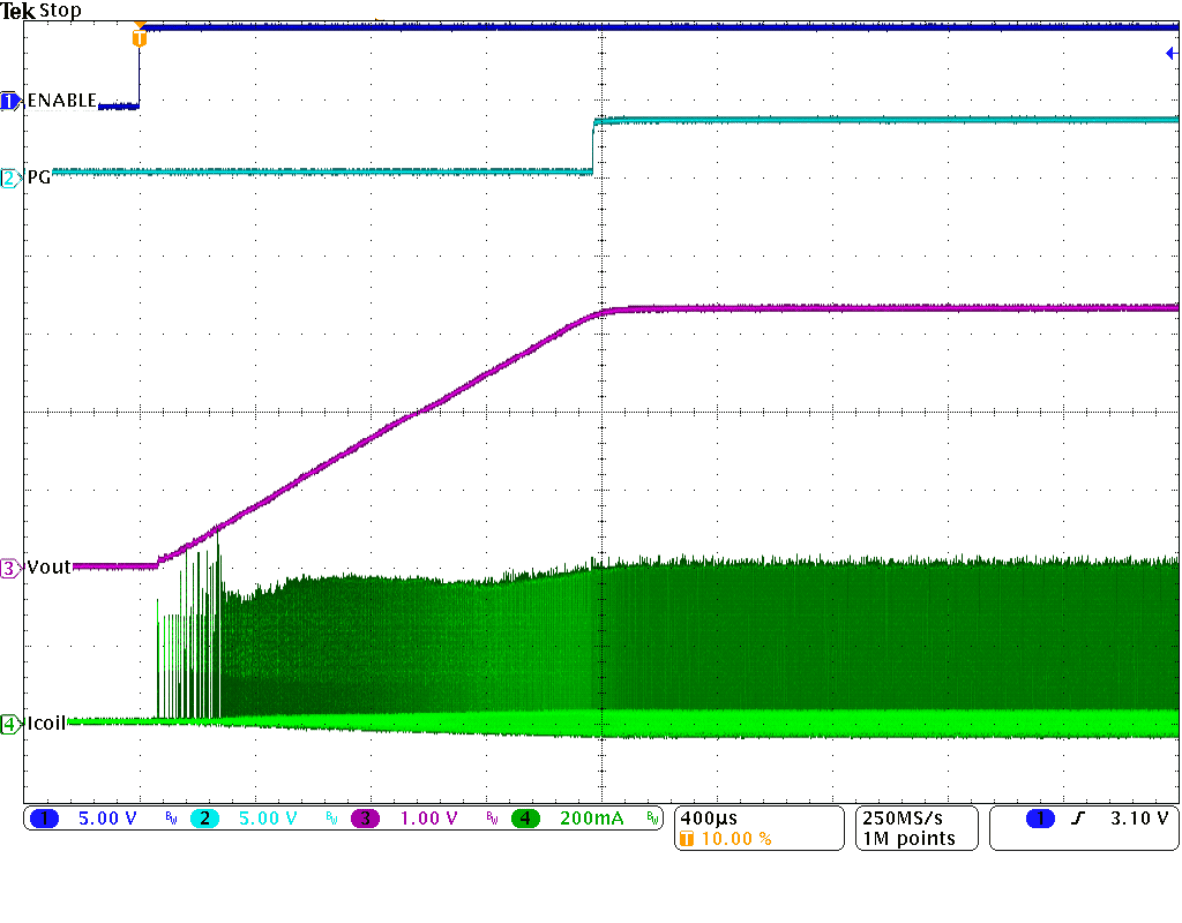 Figure 32. Startup Into 100 mA
Figure 32. Startup Into 100 mA
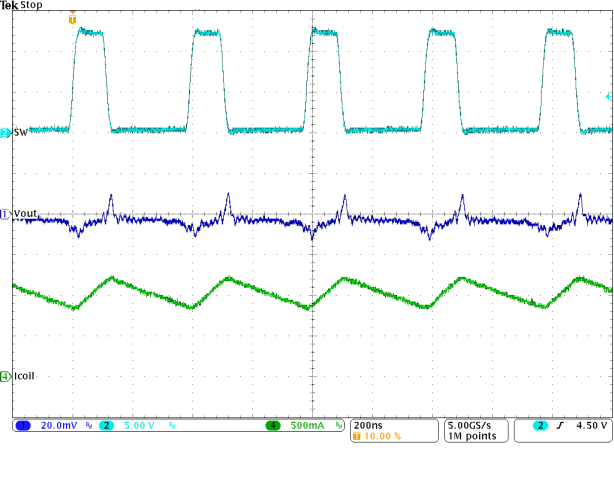 Figure 34. Typical Operation In PWM Mode
Figure 34. Typical Operation In PWM Mode
(IOUT = 1 A)
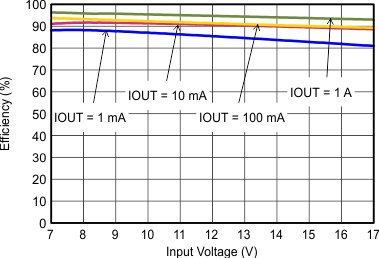
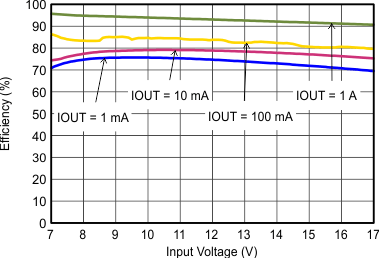
| FSW=Low |
| IOUT = 0.1 A |
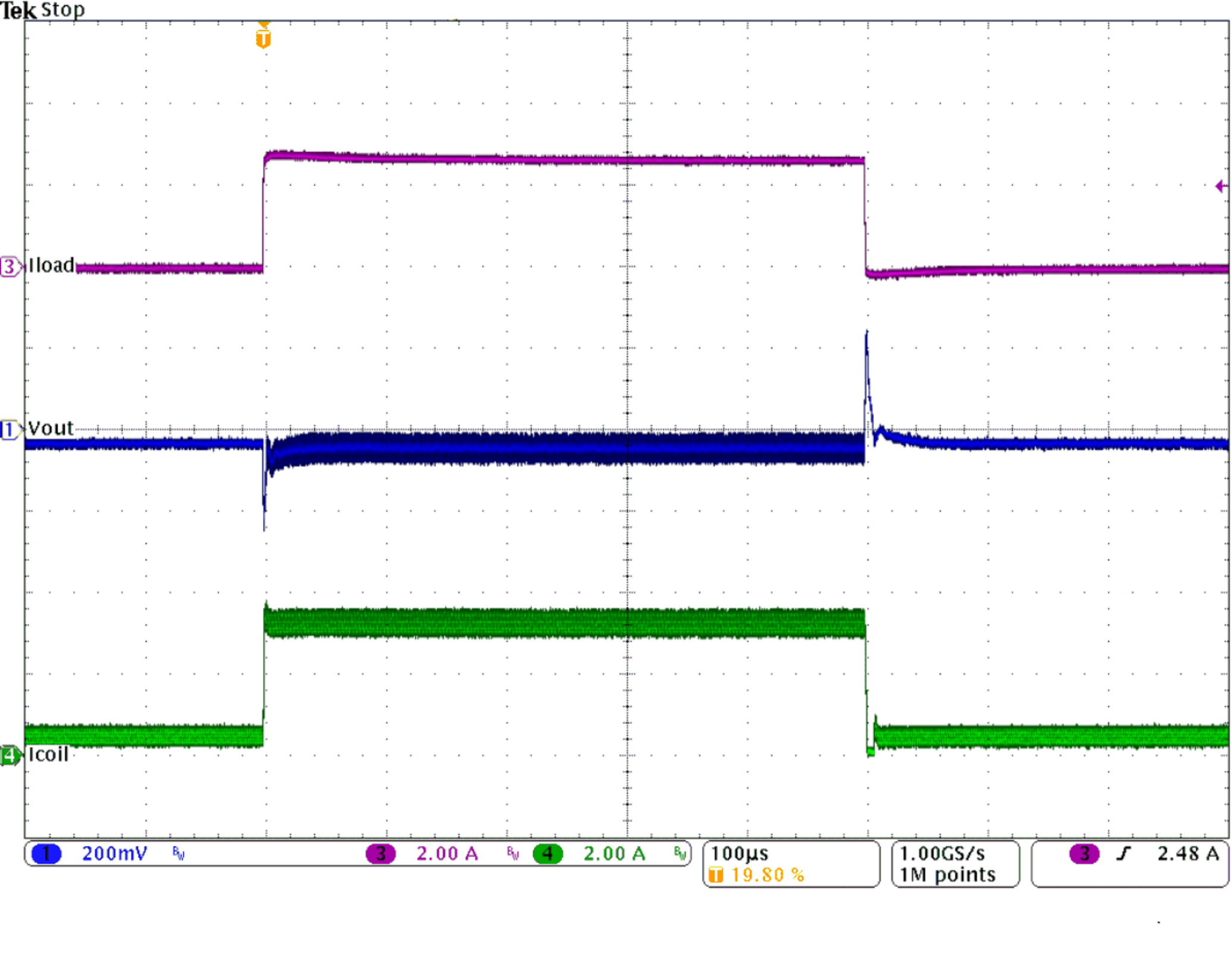 Figure 29. Load Transient Response
Figure 29. Load Transient Response
(IOUT= 0.5 to 1 to 0.5 A, VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V)
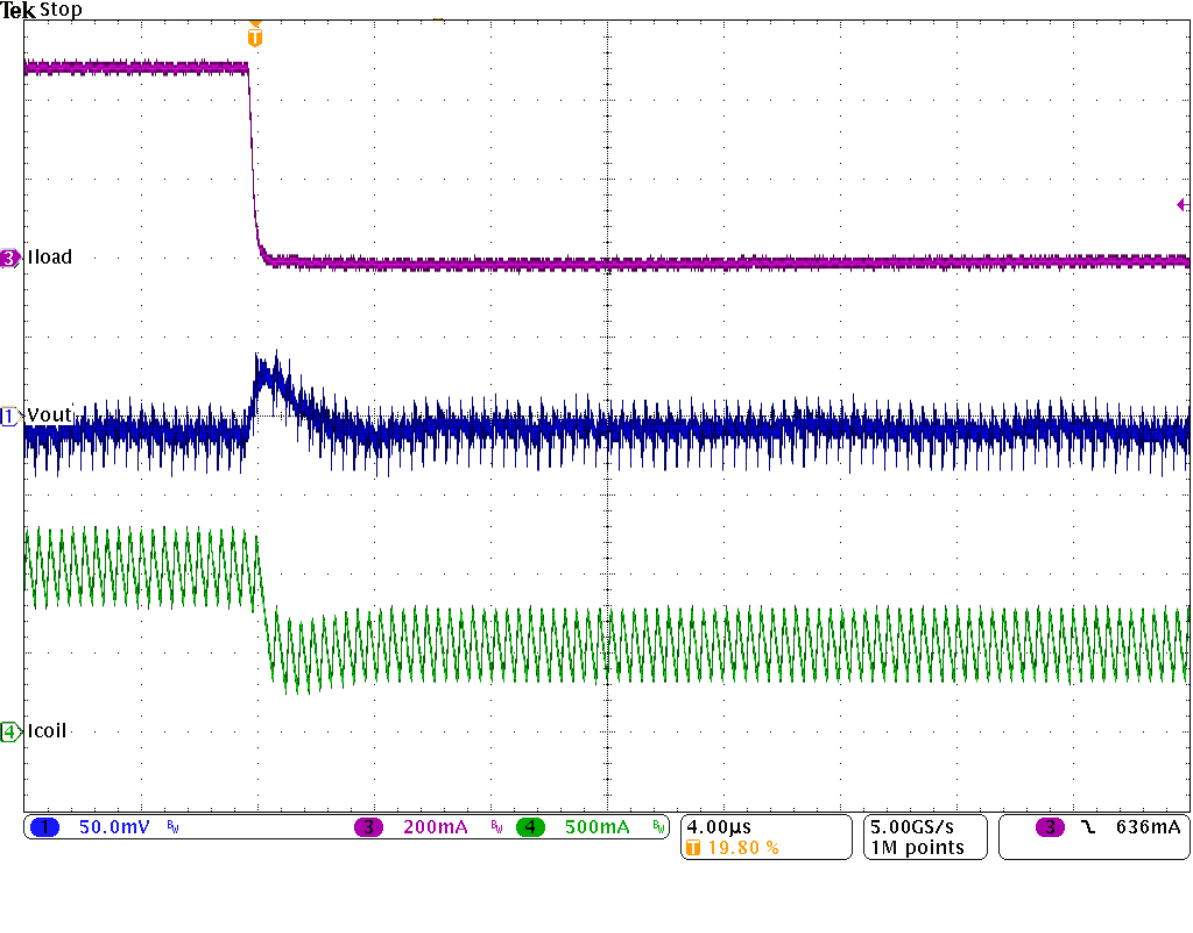 Figure 31. Load Transient Response of Figure 29,
Figure 31. Load Transient Response of Figure 29,
Falling Edge
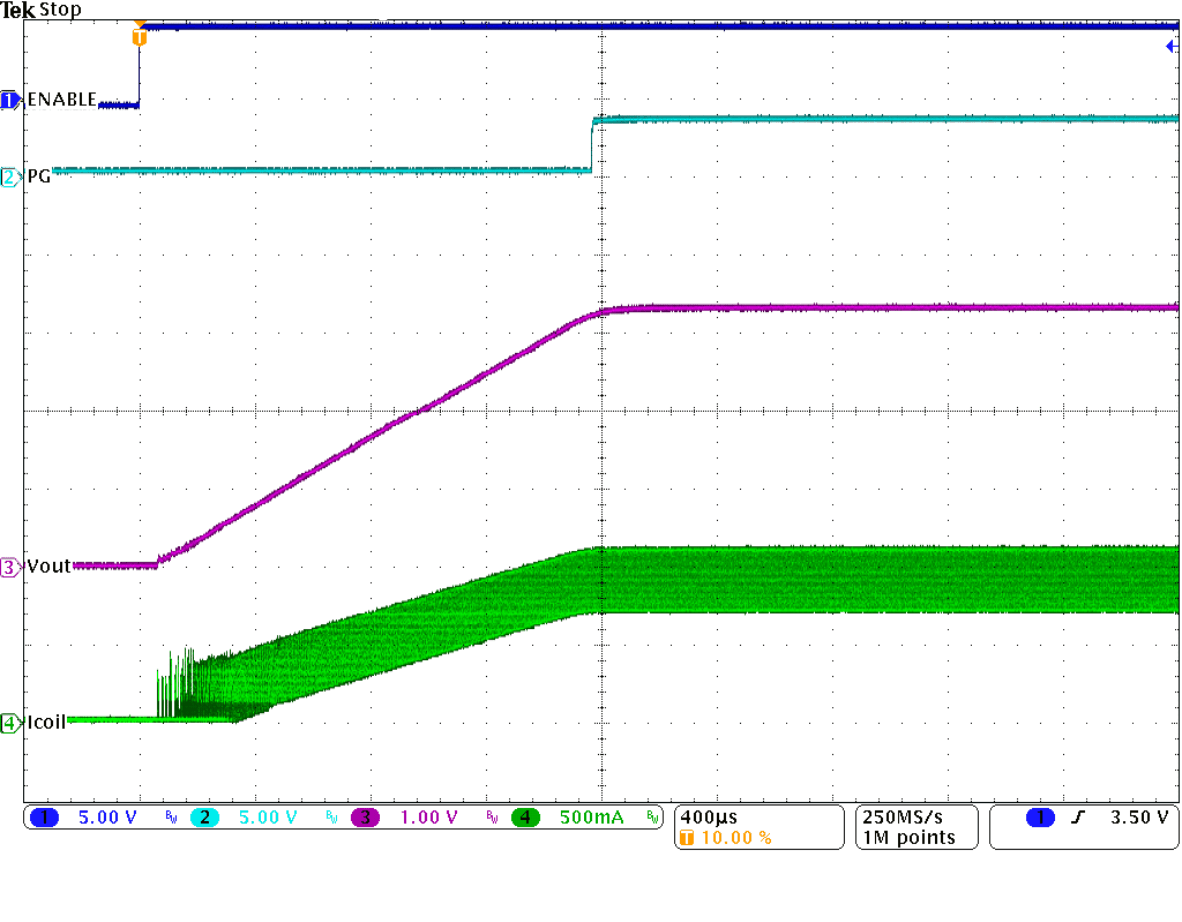 Figure 33. Startup Into 1 A
Figure 33. Startup Into 1 A
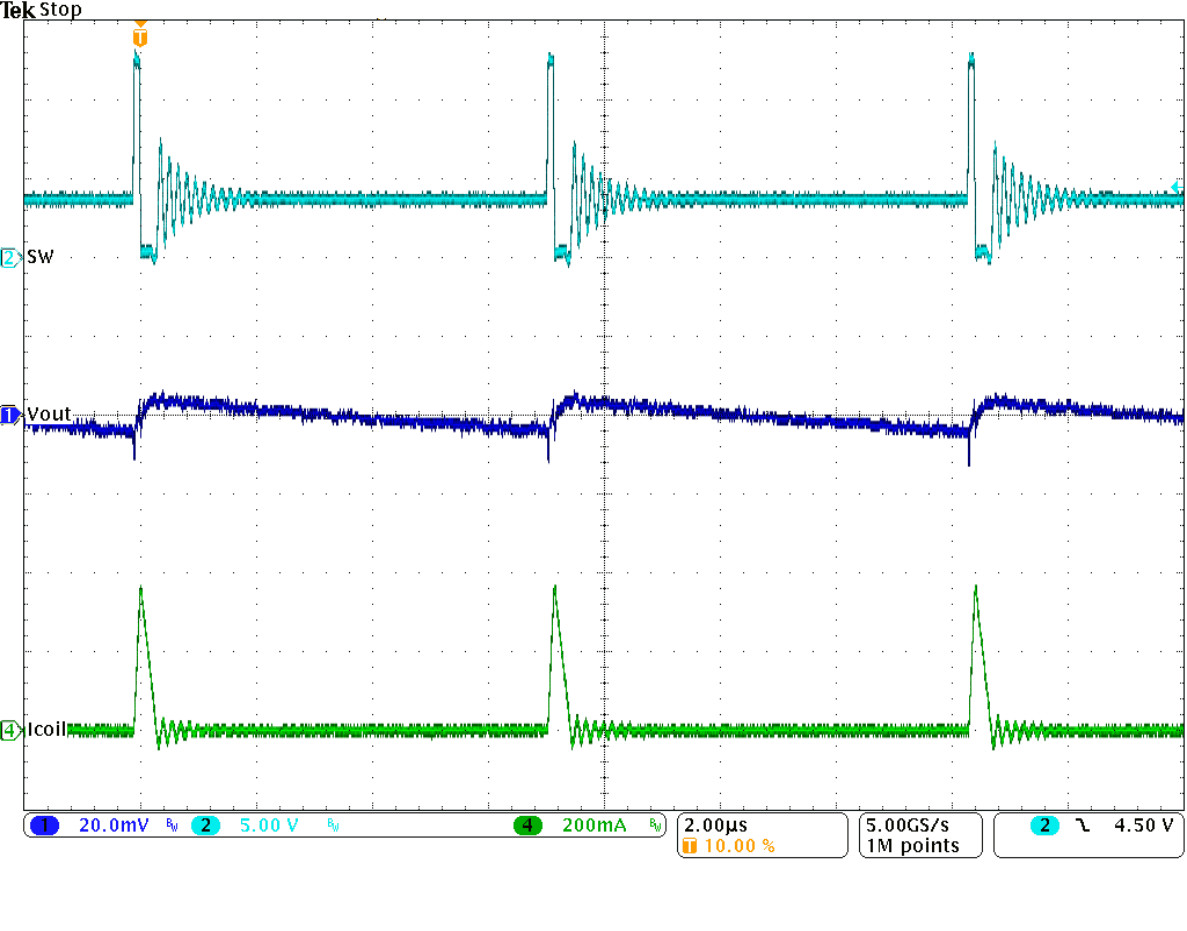 Figure 35. Typical Operation in Power Save Mode
Figure 35. Typical Operation in Power Save Mode
(IOUT = 10 mA)