SLVSB71E February 2012 – September 2016 TLV62150 , TLV62150A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
RGT Package
16-Pin VQFN
Top View
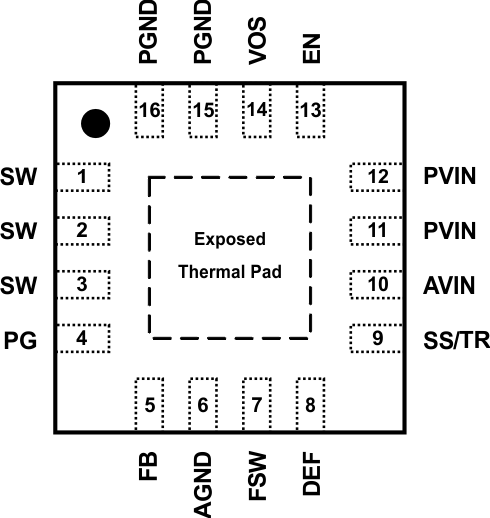
Pin Functions
| PIN(1) | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 6 | — | Analog Ground. Must be connected directly to the Exposed Thermal Pad and common ground plane. |
| AVIN | 10 | I | Supply voltage for control circuitry. Connect to same source as PVIN. |
| DEF | 8 | I | Output Voltage Scaling (Low = nominal, High = nominal + 5%)(3) |
| EN | 13 | I | Enable input (High = enabled, Low = disabled)(3) |
| FB | 5 | I | Voltage feedback. Connect resistive voltage divider to this pin. |
| FSW | 7 | I | Switching Frequency Select (Low ≈ 2.5 MHz, High ≈ 1.25 MHz(2) for typical operation)(3) |
| SW | 1,2,3 | O | Switch node, which is connected to the internal MOSFET switches. Connect inductor between SW and output capacitor. |
| PG | 4 | O | Output power good (High = VOUT ready, Low = VOUT below nominal regulation) ; open drain (requires pull-up resistor) |
| PGND | 15,16 | — | Power ground. Must be connected directly to the Exposed Thermal Pad and common ground plane. |
| PVIN | 11,12 | I | Supply voltage for power stage. Connect to same source as AVIN. |
| SS/TR | 9 | I | Soft-Start / Tracking Pin. An external capacitor connected to this pin sets the internal voltage reference rise time. It can be used for tracking and sequencing. |
| VOS | 14 | I | Output voltage sense pin and connection for the control loop circuitry. |
| Exposed Thermal Pad | — | — | Must be connected to AGND (pin 6), PGND (pin 15,16) and common ground plane. See the Layout Example. Must be soldered to achieve appropriate power dissipation and mechanical reliability. |
(1) For more information about connecting pins, see Detailed Description and Application and Implementation sections.
(2) Connect FSW to VOUT or PG in this case.
(3) An internal pull-down resistor keeps logic level low, if pin is floating.