SLVSBB2F May 2012 – August 2024 TPS65131-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 TPS65131-Q1 With VPOS = 10.5V, VNEG = –10V
- 8.2.2 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.4 Analog Supply Input Filter
- 8.2.5 Thermal Information
- 8.2.6 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.3.5.1 Feedforward Capacitors
As a recommendation, to speed up the control loop, place feedforward capacitors in the feedback divider, parallel to R1 (boost converter) and R3 (inverting converter). Equation 11 shows how to calculate the appropriate value for the boost converter, and Equation 12 for the inverting converter.
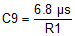
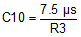
In this application example, C9 = 6.8pF and C10 = 7.5pF match the choices of R1 and R3.
To avoid coupling noise into the control loop from the feedforward capacitors, it is possible to place a series resistor to limit the bandwidth of the feedforward effect. Any value between 10kΩ and 100kΩ is suitable. The higher the resistance, the lower the noise coupled into the control loop system.