SLVSCN0C june 2014 – may 2023 TPS65263
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 8.3.3 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.4 Power-Up Sequencing
- 8.3.5 V7V Low Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 8.3.6 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 8.3.7 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.8 Pulse Skipping Mode (PSM)
- 8.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.10 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.11 Power Good
- 8.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 Register Description
- 8.5.2 VOUT1_SEL: Vout1 Voltage Selection Register (offset = 0x00H)
- 8.5.3 VOUT2_SEL: Vout2 Voltage Selection Register (offset = 0x01H)
- 8.5.4 VOUT3_SEL: Vout3 Voltage Selection Register (offset = 0x02H)
- 8.5.5 VOUT1_COM: Buck1 Command Register (offset = 0x03H)
- 8.5.6 VOUT2_COM: Buck2 Command Register (offset = 0x04H)
- 8.5.7 VOUT3_COM: Buck3 Command Register (offset = 0x05H)
- 8.5.8 SYS_STATUS: System Status Register (offset = 0x06H)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
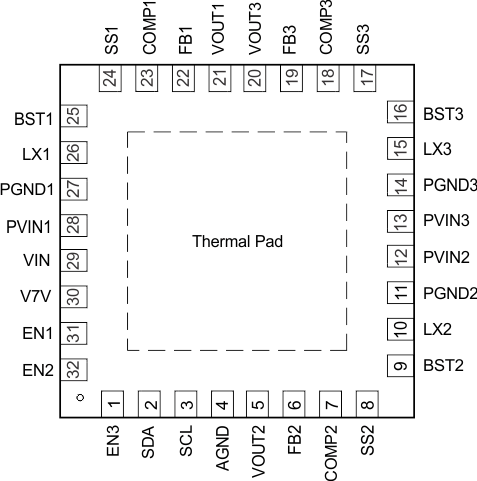
(There is no
electric signal down bonded to thermal pad inside IC. Exposed thermal pad must
be soldered to PCB for optimal thermal performance.)
Figure 6-1 RHB Package32 PinTop ViewTable 6-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |
| EN3 | 1 | Enable for buck3. Float to enable. Can use this pin to adjust the input undervoltage lockout (UVLO) of buck3 with a resistor divider. |
| SDA | 2 | I2C interface data pin |
| SCL | 3 | I2C interface clock pin |
| AGND | 4 | Analog ground common to buck controllers and other analog circuits. It must be routed separately from high current power grounds to the (–) terminal of bypass capacitor of input voltage VIN. |
| VOUT2 | 5 | Buck2 output voltage sense pin. |
| FB2 | 6 | Feedback Kelvin sensing pin for buck2 output voltage. Connect this pin to buck2 resistor divider. |
| COMP2 | 7 | Error amplifier output and Loop compensation pin for buck2. Connect a series resistor and capacitor to compensate the control loop of buck2 with peak current PWM mode. |
| SS2 | 8 | Soft-start and tracking input for buck2. An internal 5uA pullup current source is connected to this pin. The soft-start time can be programmed by connecting a capacitor between this pin and ground. |
| BST2 | 9 | Boot strapped supply to the high side floating gate driver in buck2. Connect a capacitor (recommend 47nF) from BST2 pin to LX2 pin. |
| LX2 | 10 | Switching node connection to the inductor and bootstrap capacitor for buck2. The voltage swing at this pin is from a diode voltage below the ground up to PVIN2 voltage. |
| PGND2 | 11 | Power ground connection of buck2. Connect PGND2 pin as close as practical to the (–) terminal of PVIN2 input ceramic capacitor. |
| PVIN2 | 12 | Input power supply for buck2. Connect PVIN2 pin as close as practical to the (+) terminal of an input ceramic capacitor (suggest 10 µF). |
| PVIN3 | 13 | Input power supply for buck3. Connect PVIN3 pin as close as practical to the (+) terminal of an input ceramic capacitor (suggest 10 µF). |
| PGND3 | 14 | Power ground connection of buck3. Connect PGND3 pin as close as practical to the (–) terminal of PVIN3 input ceramic capacitor. |
| LX3 | 15 | Switching node connection to the inductor and bootstrap capacitor for buck3. The voltage swing at this pin is from a diode voltage below the ground up to PVIN3 voltage. |
| BST3 | 16 | Boot strapped supply to the high side floating gate driver in buck3. Connect a capacitor (recommend 47 nF) from BST3 pin to LX3 pin. |
| SS3 | 17 | Soft-start and tracking input for buck3. An internal 5-µA pullup current source is connected to this pin. The soft-start time can be programmed by connecting a capacitor between this pin and ground. |
| COMP3 | 18 | Error amplifier output and Loop compensation pin for buck3. Connect a series resistor and capacitor to compensate the control loop of buck3 with peak current PWM mode. |
| FB3 | 19 | Feedback Kelvin sensing pin for buck3 output voltage. Connect this pin to buck3 resistor divider. |
| VOUT3 | 20 | Buck3 output voltage sense pin. |
| VOUT1 | 21 | Buck1 output voltage sense pin. |
| FB1 | 22 | Feedback Kelvin sensing pin for buck1 output voltage. Connect this pin to buck1 resistor divider. |
| COMP1 | 23 | Error amplifier output and Loop compensation pin for buck1. Connect a series resistor and capacitor to compensate the control loop of buck1 with peak current PWM mode. |
| SS1 | 24 | Soft-start and tracking input for buck1. An internal 5-µA pullup current source is connected to this pin. The soft-start time can be programmed by connecting a capacitor between this pin and ground. |
| BST1 | 25 | Boot strapped supply to the high side floating gate driver in buck1. Connect a capacitor (recommend 47 nF) from BST1 pin to LX1 pin. |
| LX1 | 26 | Switching node connection to the inductor and bootstrap capacitor for buck1. The voltage swing at this pin is from a diode voltage below the ground up to PVIN1 voltage. |
| PGND1 | 27 | Power ground connection of Buck1. Connect PGND1 pin as close as practical to the (–) terminal of PVIN1 input ceramic capacitor. |
| PVIN1 | 28 | Input power supply for buck1. Connect PVIN1 pin as close as practical to the (+) terminal of an input ceramic capacitor (suggest 10 µF). |
| VIN | 29 | Buck controller power supply. |
| V7V | 30 | Internal LDO for gate driver and internal controller. Connect a 10-µF capacitor from the pin to power ground. |
| EN1 | 31 | Enable for buck1. Float to enable. Can use this pin to adjust the input UVLO of buck1 with a resistor divider. |
| EN2 | 32 | Enable for buck2. Float to enable. Can use this pin to adjust the input UVLO of buck2 with a resistor divider. |
| PAD | — | There is no electric signal down bonded to thermal pad inside IC. Exposed thermal pad must be soldered to PCB for optimal thermal performance. |