SLVSDH0C December 2016 – January 2018 TPS22810
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.5.2.3 Inrush Current
To determine how much inrush current is caused by the CL capacitor, use Equation 9.
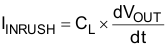
where
- IINRUSH is the amount of inrush caused by CL
- CL is the capacitance on VOUT
- dt is the Output Voltage rise time during the ramp up of VOUT when the device is enabled
- dVOUT is the change in VOUT during the ramp up of VOUT when the device is enabled
The appropriate rise time can be calculated using the design requirements and the inrush current equation. As we calculate the rise time (measured from 10% to 90% of VOUT), we account for this in our dVOUT parameter (80% of VOUT = 9.6 V) as shown in Equation 10 and Equation 11.
To ensure an inrush current of less than 400 mA, choose a CT value that yields a rise time of more than 528 μs. Consulting Table 2 at VIN = 12 V, CT = 4700 pF provides a typical rise time of 957 μs. Using this rise time and voltage into Equation 9, yields Equation 12 and Equation 13.
An appropriate CL value must be placed on VOUT such that the IMAX and IPLS specifications of the device are not violated.