SLVSDR2B November 2018 – March 2021 ADC12DJ3200QML-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Dual-Channel Mode)
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Single-Channel Mode)
- 6.9 Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Timing Diagrams
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Analog Inputs
- 7.3.2 ADC Core
- 7.3.3 Timestamp
- 7.3.4 Clocking
- 7.3.5 Digital Down Converters (Dual-Channel Mode Only)
- 7.3.6 JESD204B Interface
- 7.3.7 Alarm Monitoring
- 7.3.8 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 7.3.9 Analog Reference Voltage
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Dual-Channel Mode
- 7.4.2 Single-Channel Mode (DES Mode)
- 7.4.3 JESD204B Modes
- 7.4.4 Power-Down Modes
- 7.4.5 Test Modes
- 7.4.6 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 7.4.7 Offset Calibration
- 7.4.8 Trimming
- 7.4.9 Offset Filtering
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
7.3.5.1.4 Rational NCO Frequency Setting Mode
In basic NCO frequency mode, the frequency step size is very small and many frequencies can be synthesized, but sometimes an application requires very specific frequencies that fall between two frequency steps. For example with ƒS equal to 2457.6 MHz and a desired ƒ(NCO) equal to 5.02 MHz, the value for FREQAx is 8773085.867. Truncating the fractional portion results in an ƒ(NCO) equal to 5.0199995 MHz, which is not the desired frequency.
To produce the desired frequency, the NCO_RDIV parameter is used to force the phase accumulator to arrive at specific frequencies without error. First, select a frequency step size (ƒ(STEP)) that is appropriate for the NCO frequency steps required. The typical value of ƒ(STEP) is 10 kHz. Next, use Equation 5 to program the NCO_RDIV value.
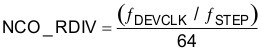
The result of Equation 5 must be an integer value. If the value is not an integer, adjust either of the parameters until the result is an integer value.
For example, select a value of 1920 for NCO_RDIV.
NCO_RDIV values larger than 8192 can degrade the NCO SFDR performance and are not recommended.
Now use Equation 6 to calculate the FREQAx register value.
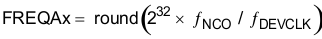
Alternatively, the following equations can be used:
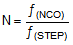
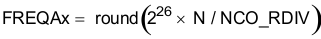
Table 7-9 lists common values for NCO_RDIV in 10-kHz frequency steps.
| fCLK (MHz) | NCO_RDIV |
|---|---|
| 3200 | 5000 |
| 3072 | 4800 |
| 2949.12 | 4608 |
| 2457.6 | 3840 |
| 1966.08 | 3072 |
| 1600 | 2500 |
| 1474.56 | 2304 |
| 1228.8 | 1920 |