SLVSEM3D May 2020 – September 2021 TPS25850-Q1 , TPS25851-Q1 , TPS25852-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Power-Down or Undervoltage Lockout
- 10.3.2 Input Overvoltage Protection (OVP) - Continuously Monitored
- 10.3.3 Buck Converter
- 10.3.4 FREQ/SYNC
- 10.3.5 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 10.3.6 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time
- 10.3.7 Internal Compensation
- 10.3.8 Selectable Output Voltage (VSET)
- 10.3.9 Current Limit and Short Circuit Protection
- 10.3.10 Cable Compensation
- 10.3.11 Thermal Management With Temperature Sensing (TS) and OTSD
- 10.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 10.3.13 USB Enable On/Off Control (TPS25852-Q1)
- 10.3.14 FAULT Indication (TPS25851-Q1 and TPS25852-Q1)
- 10.3.15 USB Specification Overview
- 10.3.16 USB Type-C® Basics
- 10.3.17 USB Port Operating Modes
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11.2 Typical Applications
The TPS2585x-Q1 only requires a few external components to convert from a wide voltage range supply to a 5-V output to power USB devices. Figure 11-1 shows the TPS25850-Q1 typical application schematic for Dual Type-C charging ports.
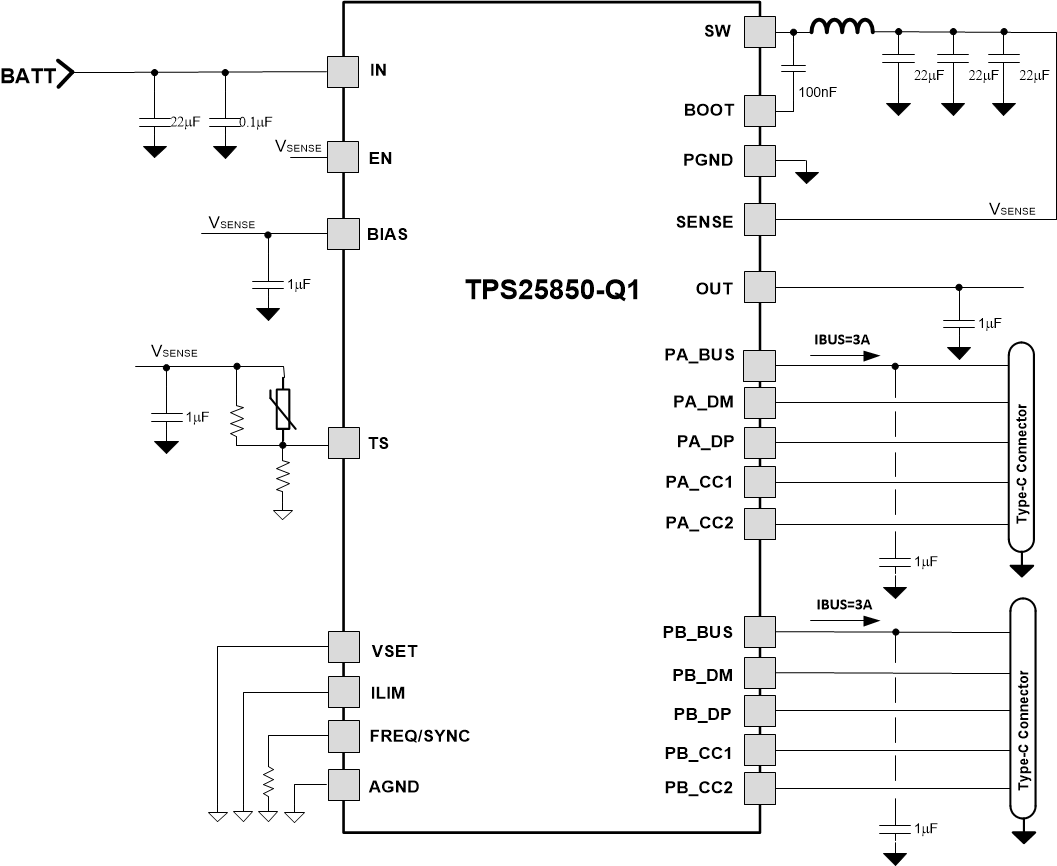 Figure 11-1 TPS25850-Q1 Typical
Application Circuit for 2.1-MHz fSW
Figure 11-1 TPS25850-Q1 Typical
Application Circuit for 2.1-MHz fSWAs a quick start guide, Table 11-1 provides typical component values for some of the most common configurations. The values given in Table 11-1 are typical. Other values can be used to enhance certain performance criterion as required by the application. The integrated buck regulator of TPS2585x-Q1 is internally compensated and optimized for a reasonable selection of external inductance and capacitance. The external components have to fulfill the needs of the application, but also the stability criteria of the control loop of the device.
| fSW | VOUT WITHOUT CABLE COMPENSATION | L | CHF + CIN | CBOOT | RATED COUT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 KHZ | 5.17 V | 3.3 µH | 1 × 100 nF + 1 × 47 µF | 1 × 100 nF | 3 × 47 µF |
| 2.1 MHz | 5.17 V | 0.68 µH | 1 × 100 nF + 1 × 22 µF | 1 × 100 nF | 3 × 22 µF |
- The inductance value is calculated based on max VIN = 18 V.
- All the COUT values are after derating and use low ESR ceramic capacitors.
- The COUT is the buck regulator output capacitors at the SENSE pin.