SLVSEN7D april 2019 – may 2023 TPS7H4001-SP
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics - All Devices
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: CDFP and KGD Options
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: HTSSOP (SHP) Option
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics: HTSSOP (QMLP) Option
- 7.9 Quality Conformance Inspection
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 VIN and Power VIN Pins (VIN and PVIN)
- 8.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.3 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Safe Start-Up Into Prebiased Outputs
- 8.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.6 Enable and Adjust UVLO
- 8.3.7 Adjustable Switching Frequency and Synchronization (SYNC)
- 8.3.8 Soft-Start (SS/TR)
- 8.3.9 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 8.3.10 Sequencing
- 8.3.11 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.12 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.14 Turn-On Behavior
- 8.3.15 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Operating Frequency
- 9.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Set Point
- 9.2.2.7 Output Voltage Feedback Resistor Selection
- 9.2.2.8 Compensation Component Selection
- 9.2.3 Parallel Operation
- 9.2.4 Application Curve
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.7.1 Minimum Output Voltage
Due to the internal design of the TPS7H4001-SP, there is a minimum output voltage limit for any given input voltage. The output voltage can never be lower than the internal voltage reference of 0.604 V. Above 0.604 V, the output voltage may be limited by the minimum controllable on time. The minimum output voltage in this case is given by Equation 32.
Equation 32. 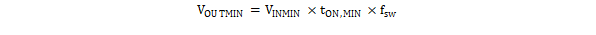
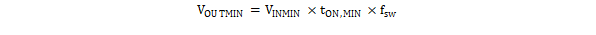
In this equation:
- VOUTMIN is the minimum output voltage
- VINMIN is the minimum input voltage for the application
- tON,MIN is the minimum on-time for the device, for which the maximum specification is 235 ns
- fsw is the switching frequency of the application.