SLVSFF0B June 2020 – July 2022 DRV8436E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.6 Linear Voltage Regulators
A linear voltage regulator is integrated in the device. The DVDD regulator can be used to provide a reference voltage. DVDD can supply a maximum of 2 mA load. For proper operation, bypass the DVDD pin to GND using a ceramic capacitor.
The DVDD output is nominally 5-V. When the DVDD LDO current load exceeds 2 mA, the output voltage drops significantly.
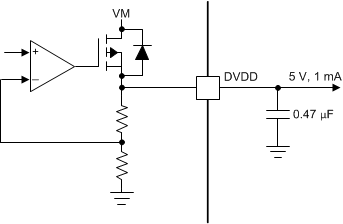 Figure 7-11 Linear Voltage Regulator Block Diagram
Figure 7-11 Linear Voltage Regulator Block DiagramIf a digital input must be tied permanently high (that is, ADECAY, BDECAY or TOFF), tying the input to the DVDD pin instead of an external regulator is preferred. This method saves power when the VM pin is not applied or in sleep mode: the DVDD regulator is disabled and current does not flow through the input pulldown resistors. For reference, logic level inputs have a typical pulldown of 200 kΩ.
The nSLEEP pin cannot be tied to DVDD, else the device will never exit sleep mode.