SLVSFG1A January 2021 – May 2021 TPS2116
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.4 Reverse Current Blocking
The TPS2116 initiates reverse current blocking (RCB) when the VOUT voltage is externally biased and exceeds the input voltage supply being used. Once the output voltage is higher than the input voltage by 42mV (VRCB,R), the device will shut off. During this state, the leakage into VOUT and out of VIN is defined by IREV. Once the voltage difference between the output and input lowers to 17mV (VRCB,F), the channel will turn back on.
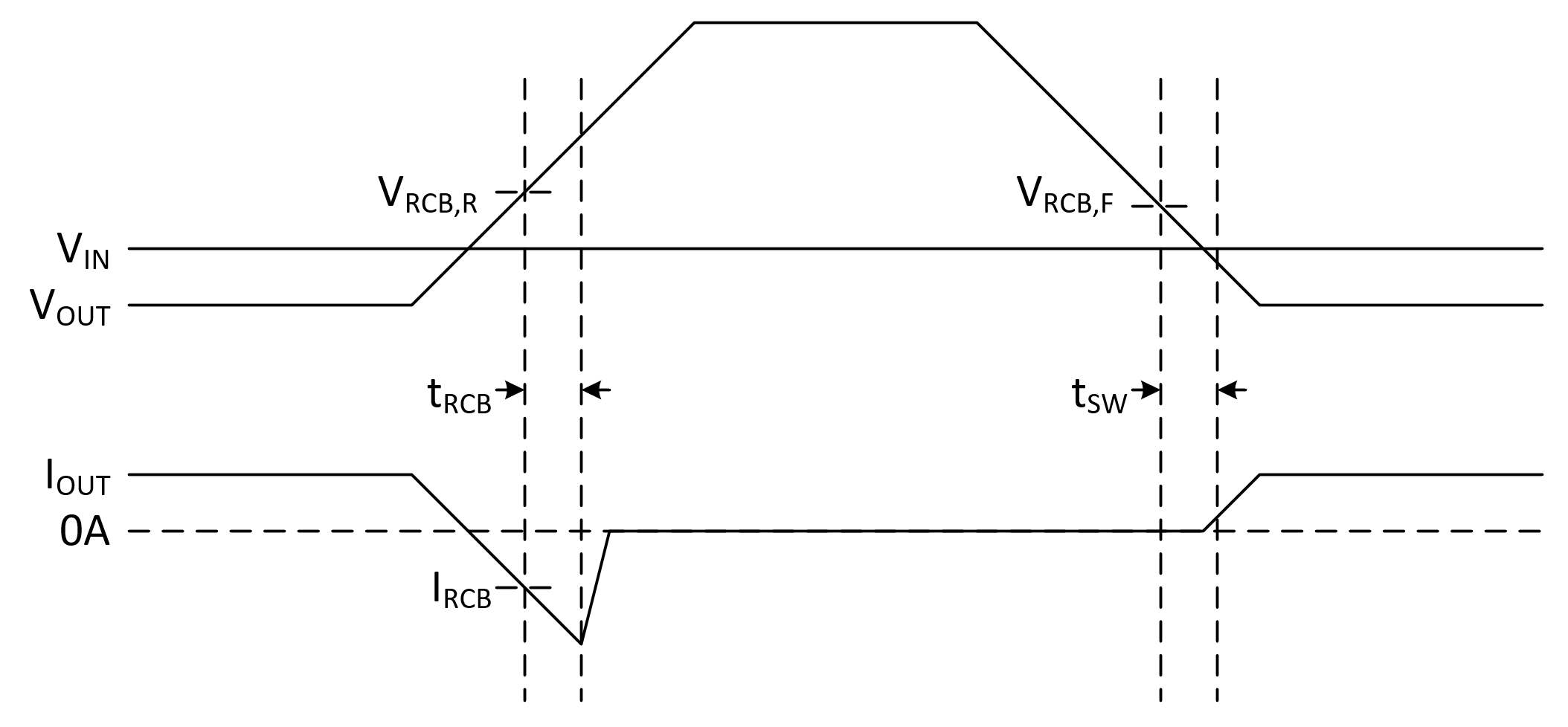 Figure 7-1 Reverse Current Blocking Behavior
Figure 7-1 Reverse Current Blocking BehaviorIf RCB is expected to occur, it is recommended to clamp the output or use a high output capacitance (about 100µF). This will prevent voltage spikes from damaging the device due to output inductance.