SLVSFL4 June 2020 TPS2124
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 TPS2124 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.3 Detailed Design Description
The TPS2124 device can be configured to manually switch between IN1 and IN2 through an external GPIO. In this example, an external MCU signal is selecting between main power and auxiliary power to power a downstream load. By manually toggling the TPS2124, the device will switch between both sources, even if one supply is higher than the other supply. Ultimately, the main factor that will determine the switchover time between IN1 (5 V) and IN2 (3.3 V) is the output load.
Manual switchover can be enabled by configuring the TPS2124 for internal voltage reference control scheme (VREF). In the VREF scheme, if the voltage on PR1 is higher than the internal VREF voltage, 1.06 V (typical), the device will select IN1 as the output. If the voltage on PR1 drops below VREF, then the device will switch to IN2, as long as IN2 is presenting a valid input voltage. IN1 is commonly connected to PR1 with an external resistor divider. OV1 and OV2 can be configured to provide overvoltage protection. The ST pin can be pulled high with a resistor to provide feedback on the status of the system. If the status pin is high, IN1 is the output. If the pin is low, IN2 is the output. If this feature is not required, the ST pin can be connected to GND.
On the TPS2124, by connecting an external signal to the select pin (SEL), the device can override the PR1/VREF comparison. If the voltage on SEL is higher than VREF at approximately (1.06 V), then the device will select IN2, as shown on Table 2. If the voltage on SEL drops below VREF, then the device will switch to IN1 as long as PR1 >= VREF. Otherwise, the highest voltage input will be chosen between IN1 and IN2. In this example, since the IN1 is higher than IN2, at 5 V, it will be selected.
Figure 14 shows the application schematic for this design example on the TPS2124.
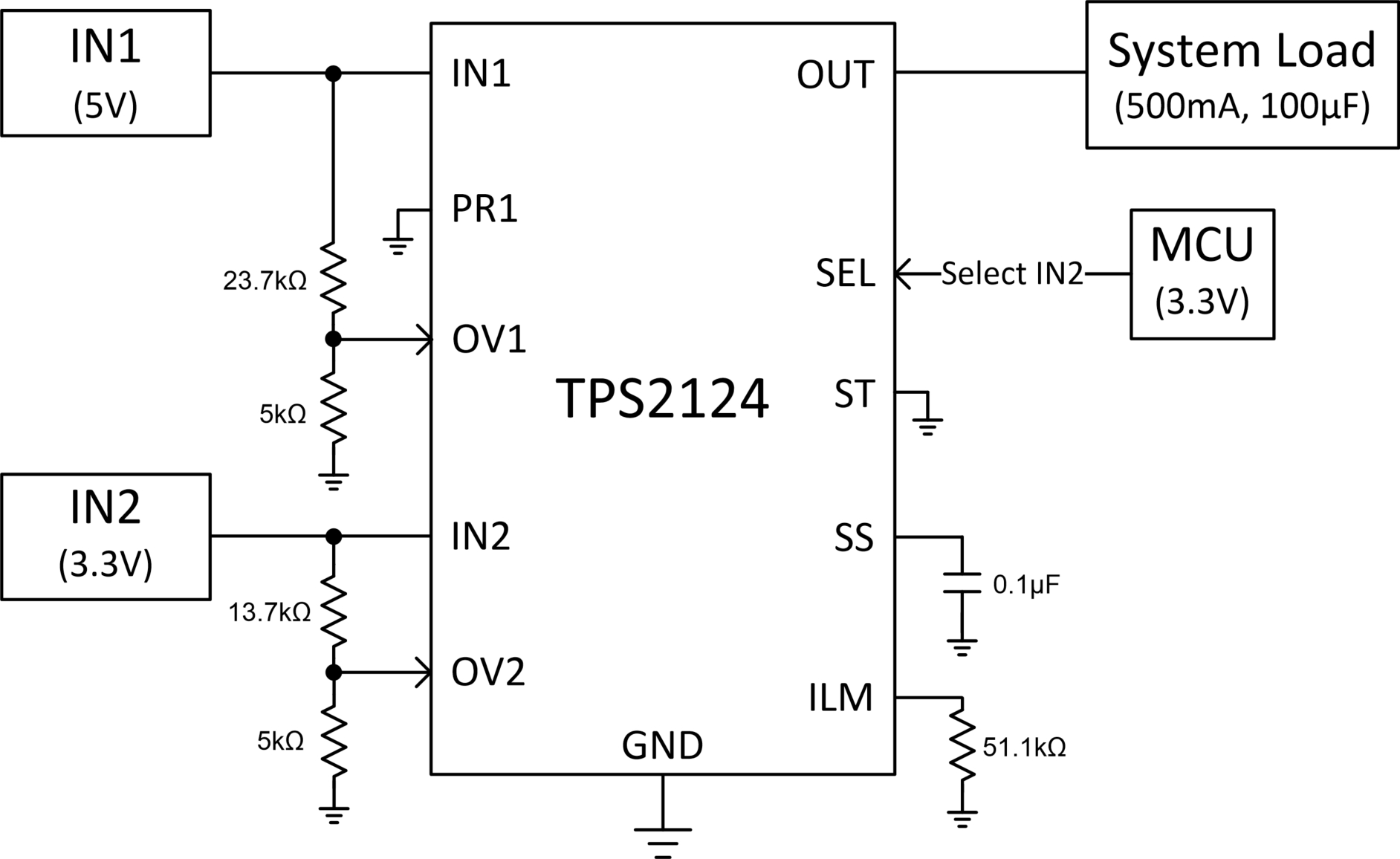 Figure 14. TPS2124 Manual Switchover
Figure 14. TPS2124 Manual Switchover