SLVSGW6 August 2024 TPS55287
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 VCC Power Supply
- 6.3.2 EXTVCC Power Supply
- 6.3.3 Operation Mode Setting
- 6.3.4 Input Undervoltage Lockout
- 6.3.5 Enable and Programmable UVLO
- 6.3.6 Soft Start
- 6.3.7 Shutdown and Load Discharge
- 6.3.8 Switching Frequency
- 6.3.9 Switching Frequency Dithering
- 6.3.10 Inductor Current Limit
- 6.3.11 Internal Charge Path
- 6.3.12 Output Voltage Setting
- 6.3.13 Output Current Monitoring and Cable Voltage Droop Compensation
- 6.3.14 Output Current Limit
- 6.3.15 Overvoltage Protection
- 6.3.16 Output Short Circuit Protection
- 6.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Maps
- 6.6.1 REF Register (Address = 0h, 1h)
- 6.6.2 IOUT_LIMIT Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 11100100h]
- 6.6.3 VOUT_SR Register (Address = 3h) [reset = 00000001h]
- 6.6.4 VOUT_FS Register (Address = 4h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 6.6.5 CDC Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 11100000h]
- 6.6.6 MODE Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 00100000h]
- 6.6.7 STATUS Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.2.7 Loop Stability
The TPS55287 uses average current control scheme. The inner current loop uses internal compensation and requires the inductor value must be larger than 1.2/fSW. The outer voltage loop requires an external compensation. The COMP pin is the output of the internal voltage error amplifier. An external compensation network comprised of resistor and ceramic capacitors is connected to the COMP pin.
The TPS55287 operates in buck mode or boost mode. Therefore, both buck and boost operating modes require loop compensations. The restrictive one of both compensations is selected as the overall compensation from a loop stability point of view. Typically for a converter designed either work in buck mode or boost mode, the boost mode compensation design is more restrictive due to the presence of a right half plane zero (RHPZ).
The power stage in boost mode can be modeled by Equation 18.
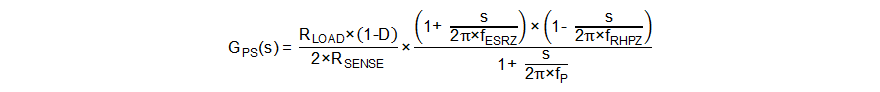
where
- RLOAD is the output load resistance.
- D is the switching duty cycle in boost mode.
- RSENSE is the equivalent internal current sense resistor, which is 0.055 Ω.
The power stage has two zeros and one pole generated by the output capacitor and load resistance. Use Equation 20 to Equation 22 to calculate them.
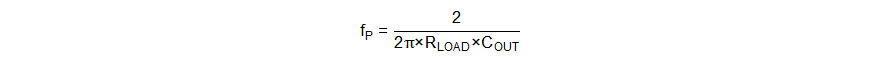
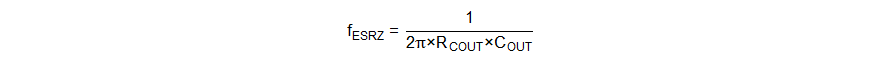

The internal transconductance amplifier together with the compensation network at the COMP pin constitutes the control portion of the loop. The transfer function of the control portion is shown by Equation 23.
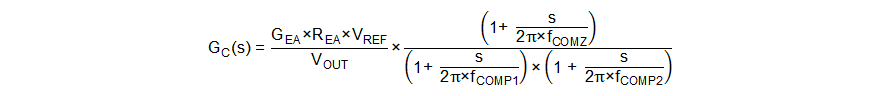
where
- GEA is the transconductance of the error amplifier.
- REA is the output resistance of the error amplifier.
- VREF is the reference voltage input to the error amplifier.
- VOUT is the output voltage.
- fCOMP1 and fCOMP2 are the pole’s frequency of the compensation network.
- fCOMZ is the zero’s frequency of the compensation network.
The total open-loop gain is the product of GPS(s) and GC(s). The next step is to choose the loop crossover frequency, fC, at which the total open-loop gain is 1, namely 0 dB. The higher in frequency that the loop gain stays above 0 dB before crossing over, the faster the loop response. It is generally accepted that the loop gain cross over 0 dB at the frequency no higher than the lower of either 1/10 of the switching frequency, fSW, or 1/5 of the RHPZ frequency, fRHPZ.
Then, set the value of RC, CC, and CP by Equation 24 to Equation 26.
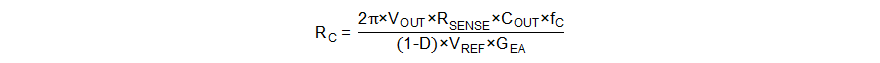
where
- fC is the selected crossover frequency.
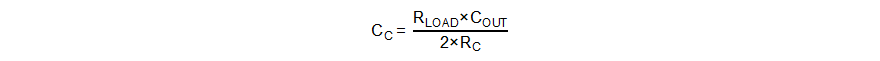

If the calculated CP is less than 10 pF, it can be left open.
Designing the loop for greater than 45° of phase margin and greater than 10-dB gain margin eliminates output voltage ringing during the line and load transient.