SLVSHA3A March 2024 – October 2024 TPS22996H-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
5.8 Typical AC Characteristics
AC Characteristics
CIN = 1 µF, CL = 0.1 µF, RL = 10 Ω, VON = 5 V, ION = 100 µA unless otherwise noticed

| VBIAS = 2.5 V |

| VBIAS = 2.5 V |

| VBIAS = 2.5 V |

| TAMB = 25 ℃ | VBIAS = 2.5 V |
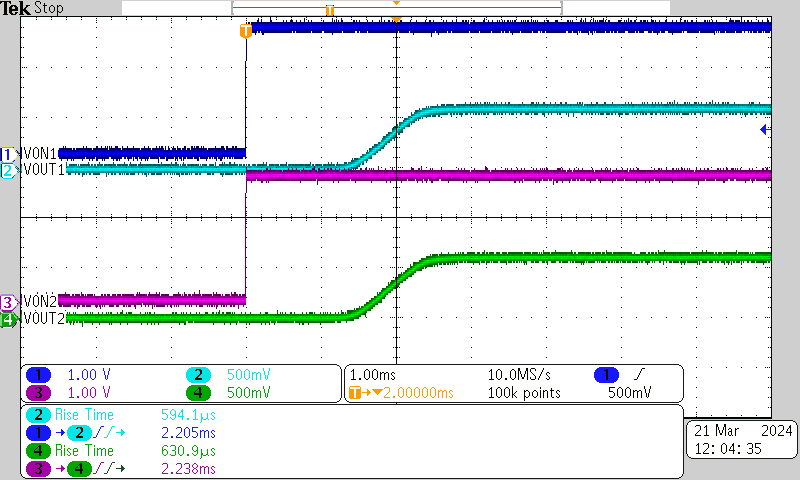
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 0.6 V | ION = 20 μA |
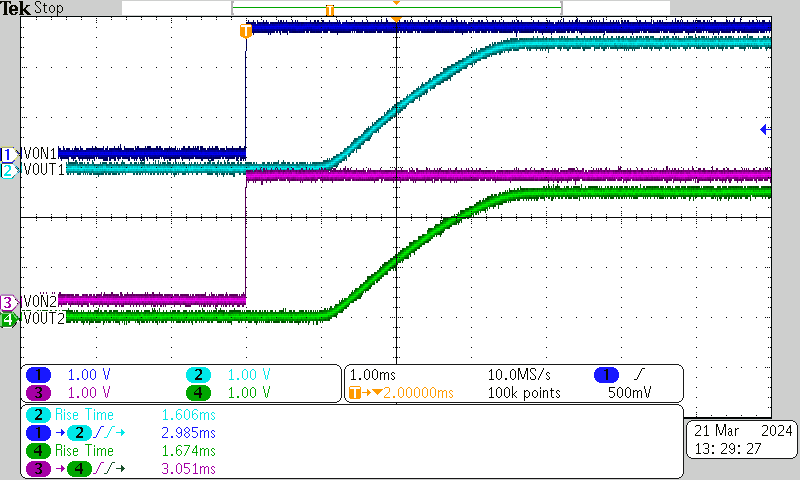
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | ION = 20 μA |
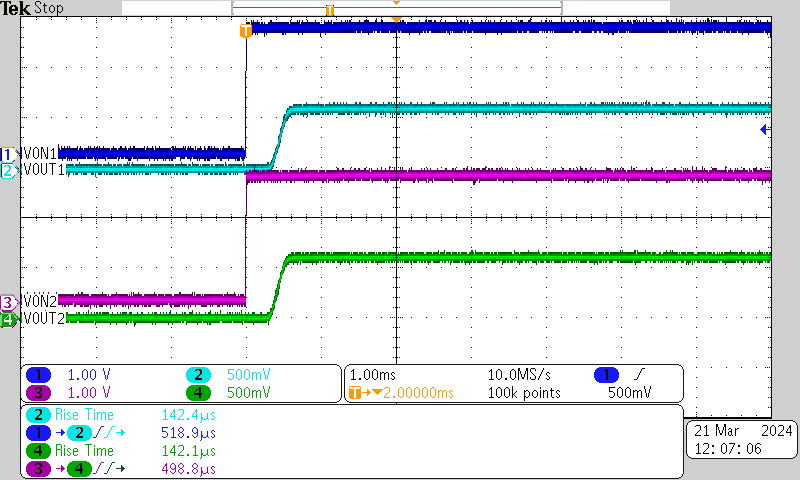
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 0.6 V | ION = 100 μA |
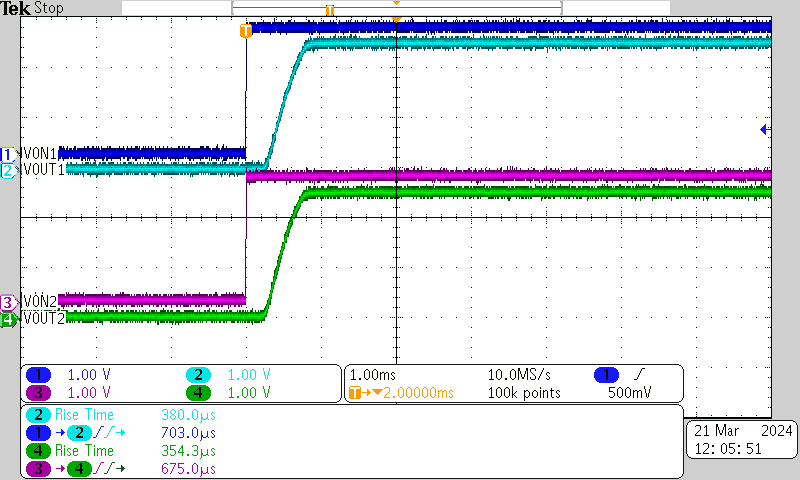
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | ION = 100 μA |
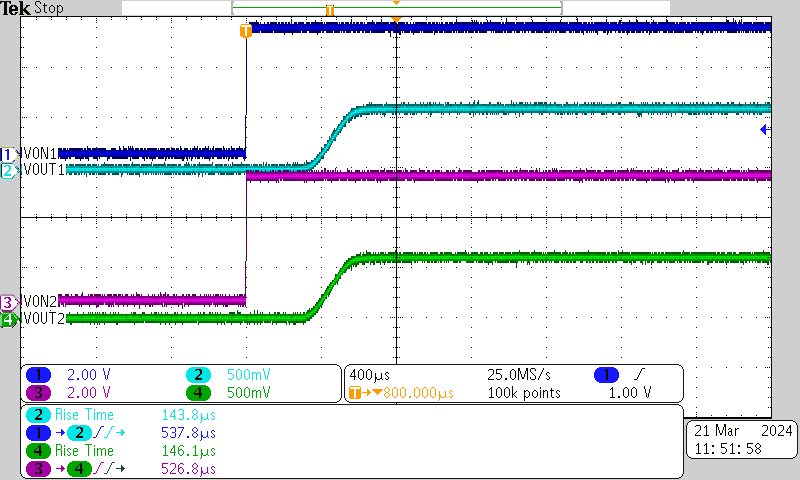
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 0.6 V | ION = 100 μA |
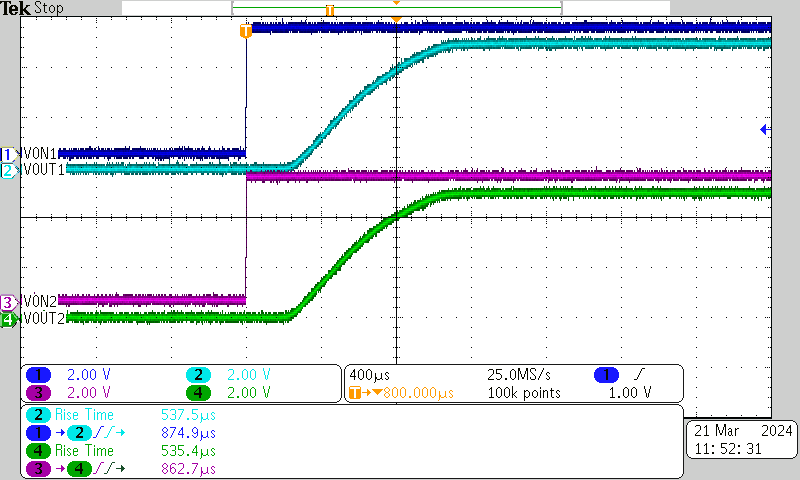
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 5 V | ION = 100 μA |

| VBIAS = 5 V |

| VBIAS = 5 V |

| VBIAS = 5 V |

| TAMB = 25 ℃ | VBIAS = 5 V |
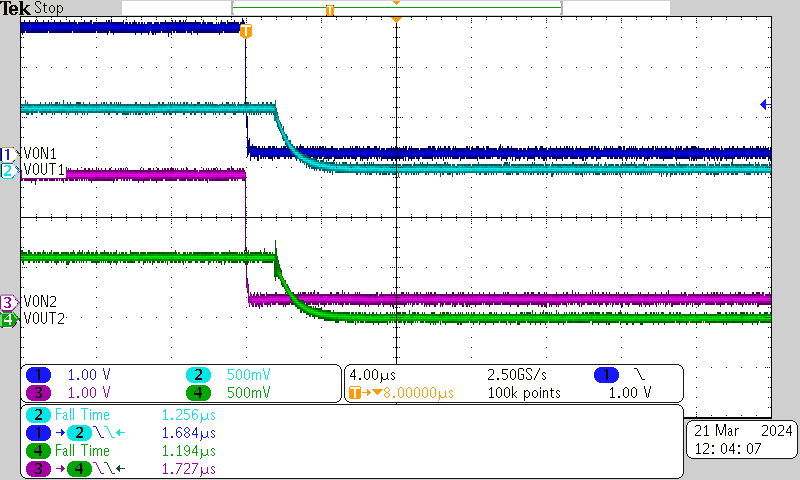
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 0.6 V | ION = 20 μA |
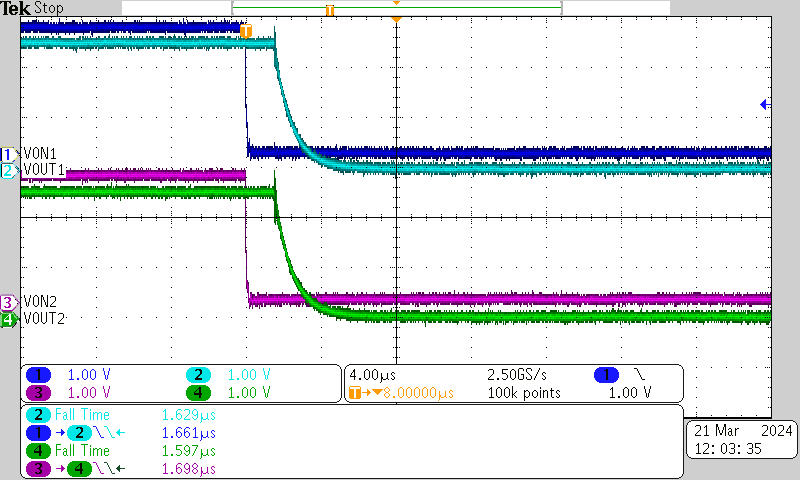
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | ION = 20 μA |
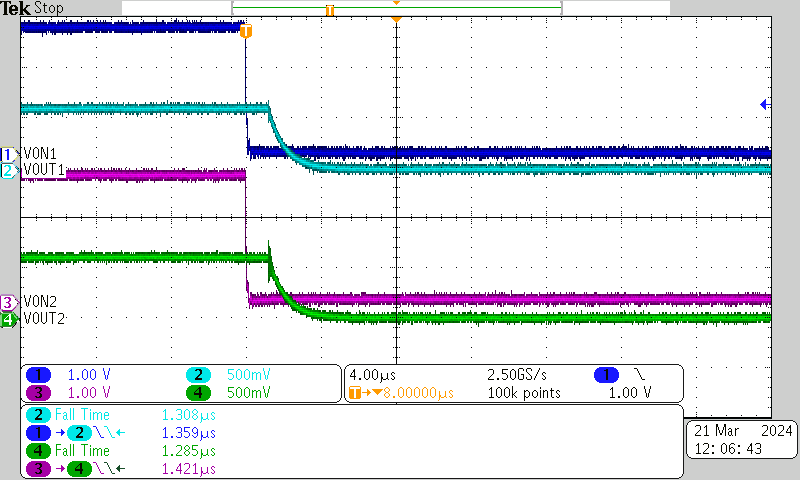
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 0.6 V | ION = 100 μA |
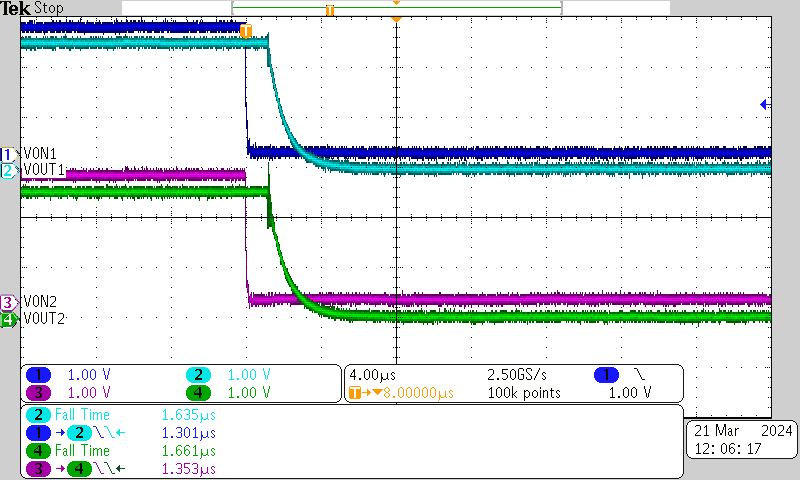
| VBIAS = 2.5 V | VIN = 2.5 V | ION = 100 μA |
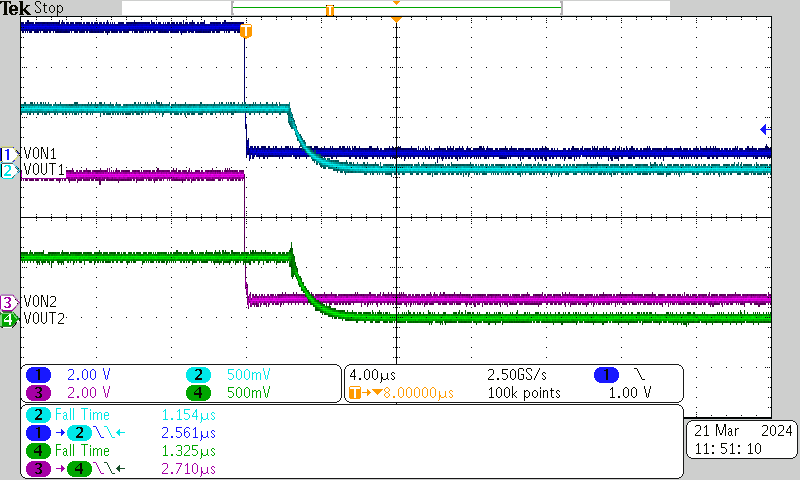
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 0.6 V | ION = 100 μA |
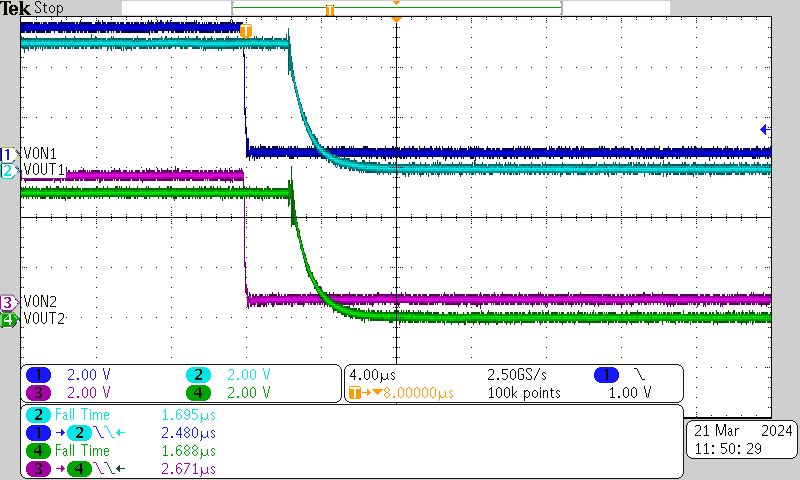
| VBIAS = 5 V | VIN = 5 V | ION = 100 μA |