SLVSHA3A March 2024 – October 2024 TPS22996H-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
8.4.3 Power Dissipation
The maximum IC junction temperature must be restricted to 150°C under normal operating conditions. To calculate the maximum allowable power dissipation, PD(max) for a given output current and ambient temperature, use Equation 3.
Equation 3. 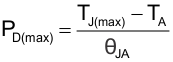
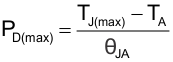
where
- PD(max) is the maximum allowable power dissipation.
- TJ(max) is the maximum allowable junction temperature (150°C for the TPS22996H).
- TA is the ambient temperature of the device.
- θJA is the junction to air thermal impedance. See Section 5.4. This parameter is highly dependent upon board layout.