SLYA080 july 2023 TMAG5273
2 Using 3D Hall Sensor for Angle Measurement
TI offers several different types of Hall-effect sensors: switches, latches, single-axis linear, and 3D linear sensors. Linear Hall sensors output analog or digital signals, and when the strength of the external magnetic field changes, the output also changes. Unlike single-axis sensors, 3D linear sensors can use the magnetic field data from all three directions to calculate angle and magnitude. An integrated angle calculation engine (CORDIC) provides full 360° angular position information for both on-axis and off-axis angle measurement topologies, as seen in Figure 2-1. The angle calculation is performed using two user-selected magnetic axes. The three axes of sensitivity of a 3D linear Hall-effect sensor are defined as shown in Figure 2-2.
 Figure 2-1 On-Axis and
Off-Axis Angle Measurement
Figure 2-1 On-Axis and
Off-Axis Angle Measurement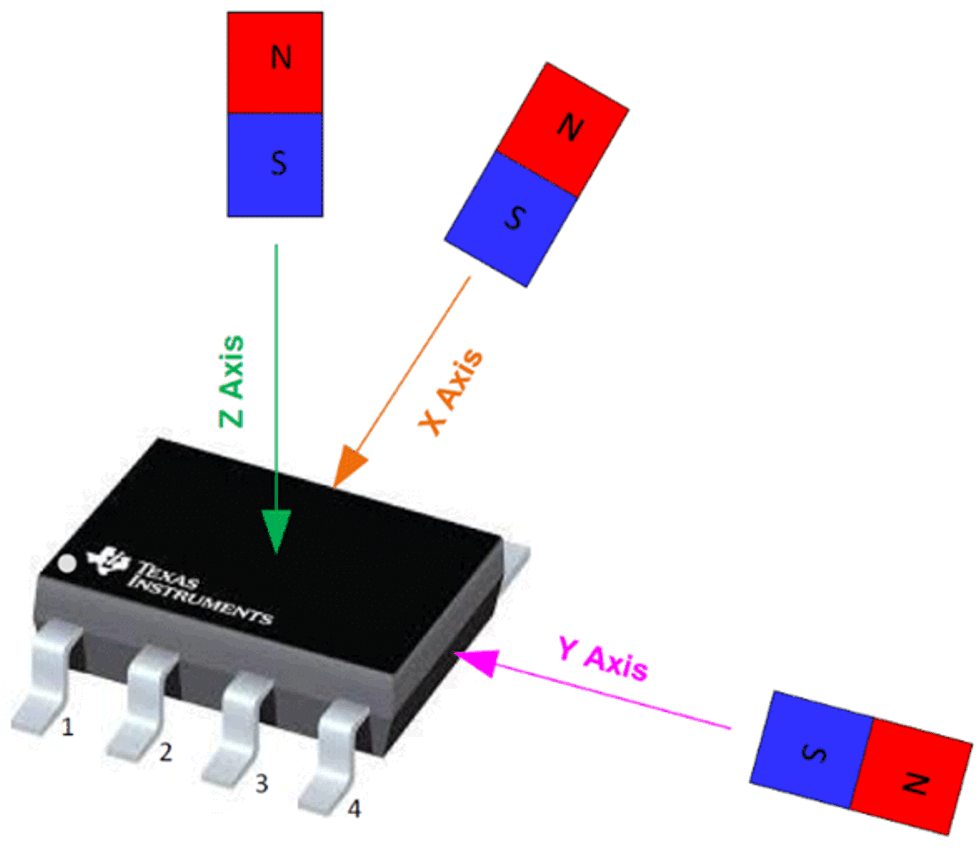 Figure 2-2 3D Linear
Hall-Effect Sensor Axis
Figure 2-2 3D Linear
Hall-Effect Sensor Axis