SLYT803B october 2020 – october 2020 BQ24610 , BQ25713 , BQ25790 , LM66100 , LM74700-Q1
- 1
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Understanding Battery Packs
- 3 Stackability Requirements for Battery Packs
- 4 A Multibattery Management System Design
- 5 Battery Charging
- 6 Battery Gauging and Protection
- 7 DC-to-DC Converter or Controller Stage (Boost or Buck-boost Stage)
- 8 ORing Control
- 9 Load Sharing
- 10Conclusion
- 11References
- 12Related Web Sites
5 Battery Charging
A 4S battery voltage ranges from 14.4 V to 16.8 V. Most battery chargers come with power-path management, which means that the output of the battery charger can come from either the input voltage or the battery voltage. This power-path management happens dynamically. Depending on whether the input voltage is 12 V or 24 V, the battery charger needs to be either a boost or a buck charger, respectively.
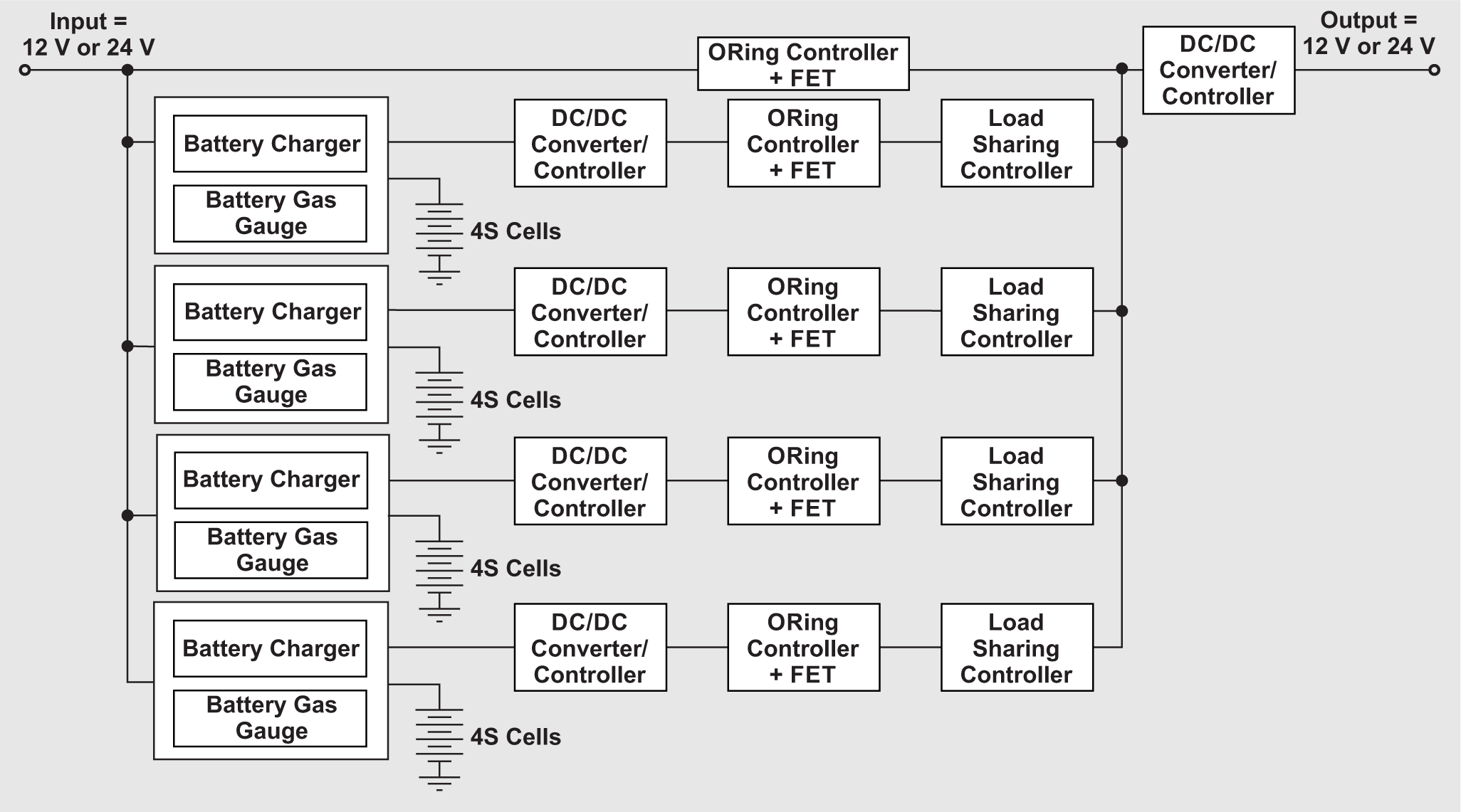 Figure 2 Multibattery Management System
for a 4S4P Battery Pack
Figure 2 Multibattery Management System
for a 4S4P Battery PackBased on the charging and discharging currents, a battery charger can have external or integrated field-effect transistors (FETs). For example, as shown in Figure 3, the BQ25713 from Texas Instruments (TI) is a one- to four-cell buck-boost battery charger controller that can work with a 12-V input. The BQ24610 is a stand-alone one- to six-cell synchronous buck battery charger controller that can work with a 24-V input. Both of these devices are charger controllers and use external FETs to support higher currents. If the load current is 5 A or less, a third device, the BQ25790, is a more suitable charger with integrated FETs.
Faster battery charging requires higher current; over time, this can accelerate cell aging. Lithium plating (a deposition of metallic lithium) can form during charging, resulting in reduced performance for rechargeable batteries. Plating can also occur when charging at low temperatures. With TI Impedance Track™ and smart charging technology, batteries can have increased longevity by predicting the remaining battery capacity with greater than 99% accuracy, as well as supporting the fastest possible charging without additional degradation.
A large battery in an ultrasound scanner does not necessarily mean that the battery will last longer. Battery capacity is affected by many parameters, such as current, voltage and temperature. Two important factors to consider are battery life (or the number of obtainable cycles from the battery) and run time (or being able to confidently use all of the available battery capacity with no surprises, such as early shutdown).