SLYY235 June 2024 DRV7308
- 1
- Overview
- At a glance
- How GaN increases inverter efficiency
- Motor performance improvement with GaN power switches
- Design considerations when using GaN in motor drives
- Impact on system efficiency
- Impact on audible noise
- Conducted and radiated emission considerations
- Impact on solution size
- Protected and reliable system designs
- Conclusion
- Additional resources
How GaN increases inverter efficiency
The conduction losses attributable to GaN FETs are proportional to the on-state resistance of the GaN, similar to a MOSFET. For an IGBT, however, conduction losses depend on the knee voltage and dynamic on-state resistance, which are typically higher than GaN FETs or MOSFETs.
As for switching losses, GaN FETs offer much lower losses compared to MOSFETs and IGBTs because of these reasons:
- GaN offers zero reverse recovery. With zero reverse recovery, it is possible to switch a GaN FET at a very high current slew rate (di/dt) and voltage slew rate (dv/dt). In MOSFETs, the body diode suffers from high zero reverse recovery, limiting the switching di/dt and dv/dt and causing additional losses and phase-node voltage ringing. With an IGBT, even the addition of an optimized antiparallel diode can still cause challenges related to reverse recovery.
- When switching off, IGBTs suffer from minority carrier recombination current, commonly known as tail current, which increases turnoff losses. GaN doesn’t have any tail current.
- GaN offers lower capacitance compared to IGBTs and MOSFETs, resulting in lower capacitive switching losses.
- Controlled and faster di/dt and controlled dv/dt help optimize voltage-current overlap losses during switching.
Figure 1 shows a theoretical inverter efficiency comparison between GaN-, IGBT- and MOSFET-based solutions with a 20kHz switching frequency, the phase-node voltage slew rate for the GaN-based inverter limited to 5V/ns, and an ambient temperature of 55°C. You can see that the GaN solution helps reduce power losses by at least half.
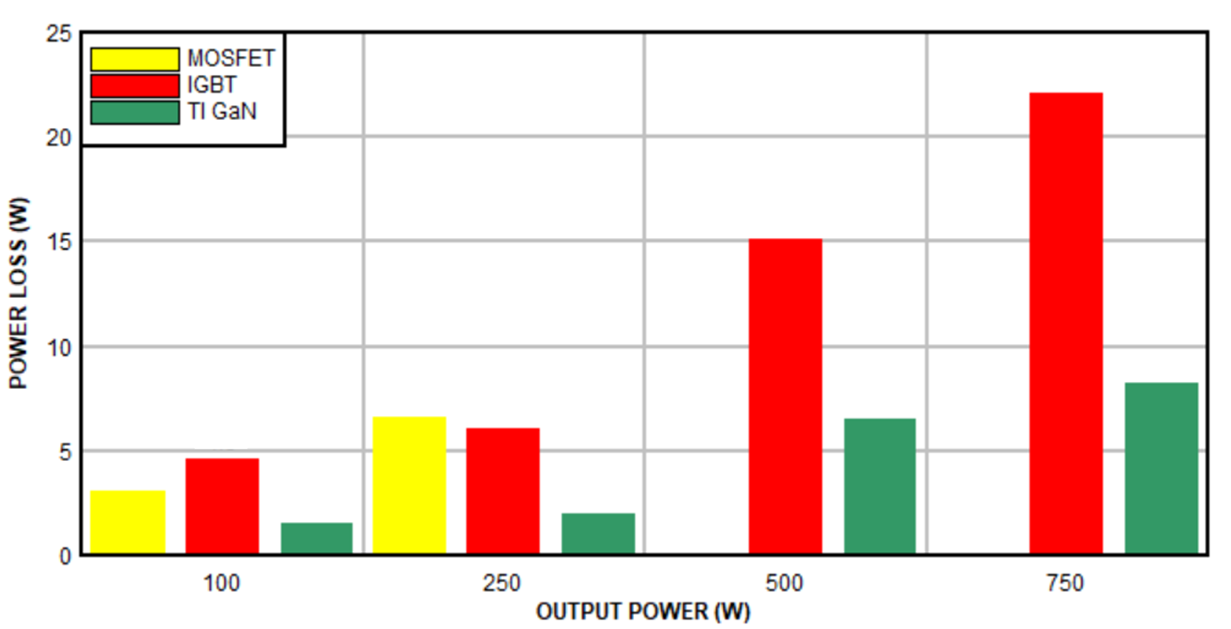 Figure 1 Efficiency comparison of GaN,
MOSFET and IGBT solutions.
Figure 1 Efficiency comparison of GaN,
MOSFET and IGBT solutions.Figure 2 compares the efficiency of the Texas Instruments (TI) DRV7308 three-phase GaN intelligent power module (IPM) to a 5A peak-current-rated IGBT IPM with a 300VDC supply at a 20kHz switching frequency with a fan motor that has 2m of cable at a 25°C ambient temperature, delivering 0.85A of root-mean-square winding current and 250W of inverter output power. The slew rate of the GaN IPM is configured for 5V/ns.
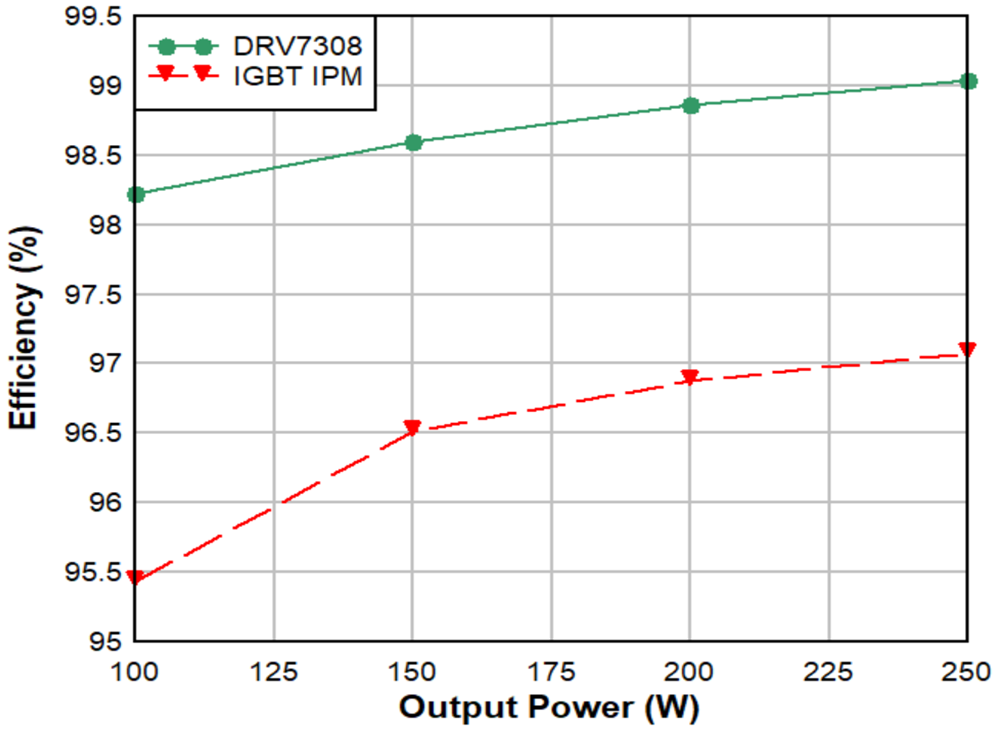 Figure 2 Efficiency comparison of the
DRV7308 and an IGBT IPM in a 250W application.
Figure 2 Efficiency comparison of the
DRV7308 and an IGBT IPM in a 250W application.