SLYY235 June 2024 DRV7308
- 1
- Overview
- At a glance
- How GaN increases inverter efficiency
- Motor performance improvement with GaN power switches
- Design considerations when using GaN in motor drives
- Impact on system efficiency
- Impact on audible noise
- Conducted and radiated emission considerations
- Impact on solution size
- Protected and reliable system designs
- Conclusion
- Additional resources
Design considerations when using GaN in motor drives
Designers often have to consider how dv/dt affects motor insulation, bearing lifetime, electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reliability.
The DRV7308 incorporates an integrated predriver slew-rate control circuit that controls dv/dt at the phase node. It is possible to control the slew-rate settings down to 5V/ns and to configure the slew rate as a trade-off between the motor winding insulation and switching-loss optimization. The lower slew-rate settings of the DRV7308 cover the ranges offered by existing IGBTs, while higher slew rates help hold switching losses to much lower values.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the phase-node switching voltage of the DRV7308 at a 1A load, at 300V, with a 10V/ns slew-rate setting and a 2m motor cable. The zero reverse recovery of the GaN FET with lower parasitics and predriver slew-rate control help achieve a clean voltage switching waveform.
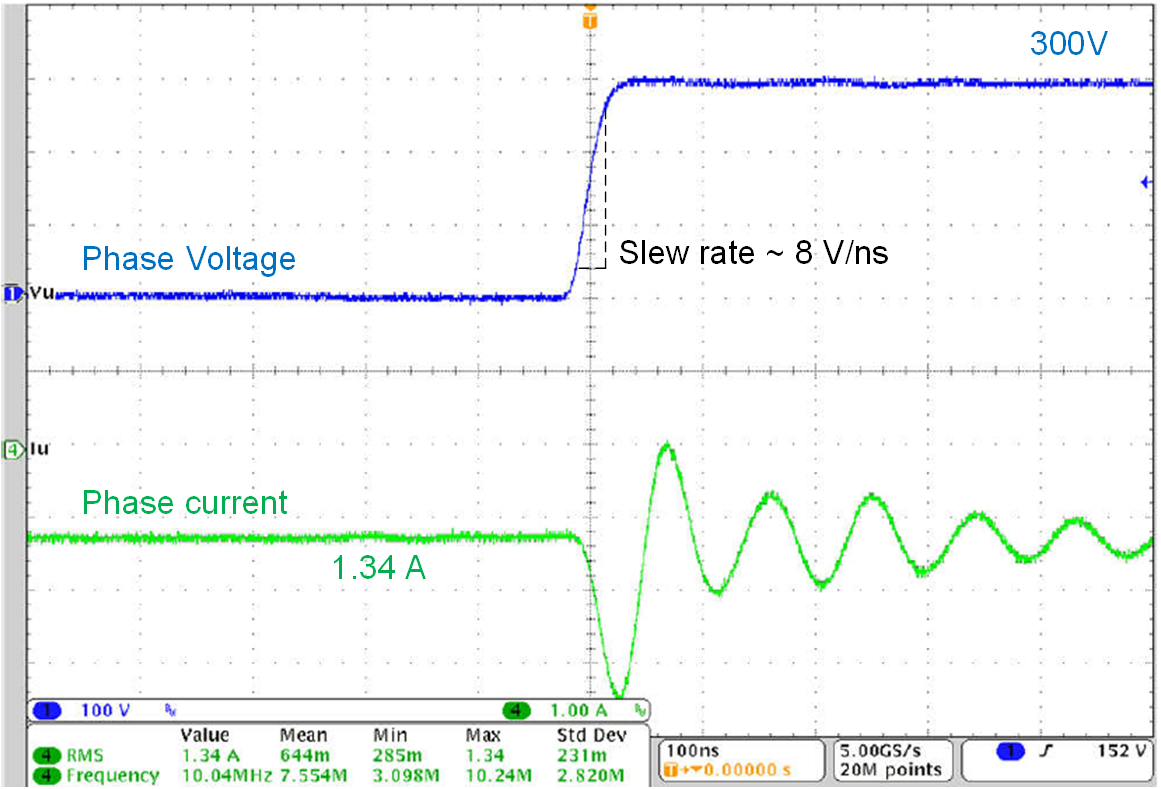 Figure 4 Phase-node voltage rising slew
rate with a 2m cable and fan motor.
Figure 4 Phase-node voltage rising slew
rate with a 2m cable and fan motor.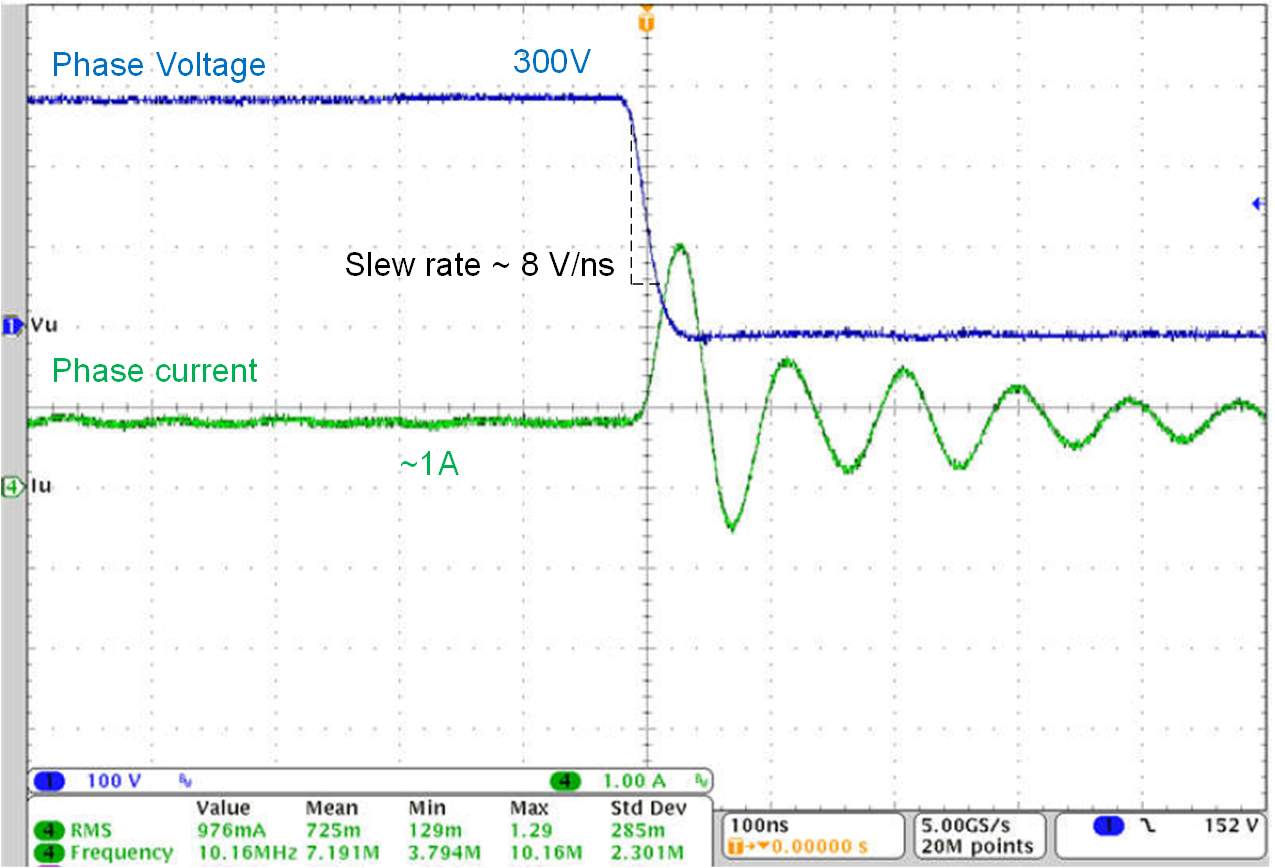 Figure 5 Phase-node voltage falling
slew rate with a 2m cable and fan motor.
Figure 5 Phase-node voltage falling
slew rate with a 2m cable and fan motor.