SNAA374A November 2022 – December 2024 LMK6C , LMK6D , LMK6H , LMK6P
BAW Resonator Technology
BAW is a micro-resonator technology that enables the integration of high-precision and ultra-low jitter clocks directly into packages that contain other circuits. In the CDC6C and LMK6C LVCMOS BAW oscillator families, BAW is integrated with a co-located precision temperature sensor, a ultra-low jitter, low-power output divider, and a small power-reset-clock management system consisting of several low noise LDOs.Figure 1 shows the structure of the the BAW resonator technology. The structure includes a thin layer of piezoelectric film sandwiched between metal films and other layers that confine the mechanical energy. The BAW utilizes this piezoelectric transduction to generate a vibration.
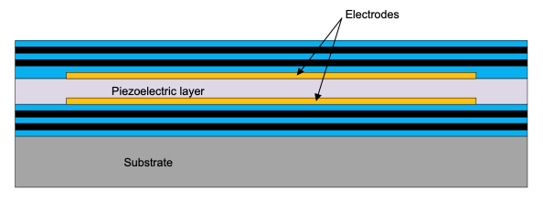 Figure 1 Basic Structure of a Bulk Acoustic Wave (BAW) Resonator
Figure 1 Basic Structure of a Bulk Acoustic Wave (BAW) ResonatorBAW Oscillator in Building Automation
Building automation systems maximize safety, robustness and reliability at a scalable level. To obtain better performance in applications such as IP camera, Video surveillance, and HVAC, a complex and reliable network of accurate clock data is required.
In advanced building automation systems such as the ones listed above, the following performance metrics are required:
- Higher density of product design with wide thermal performance and small layout size.
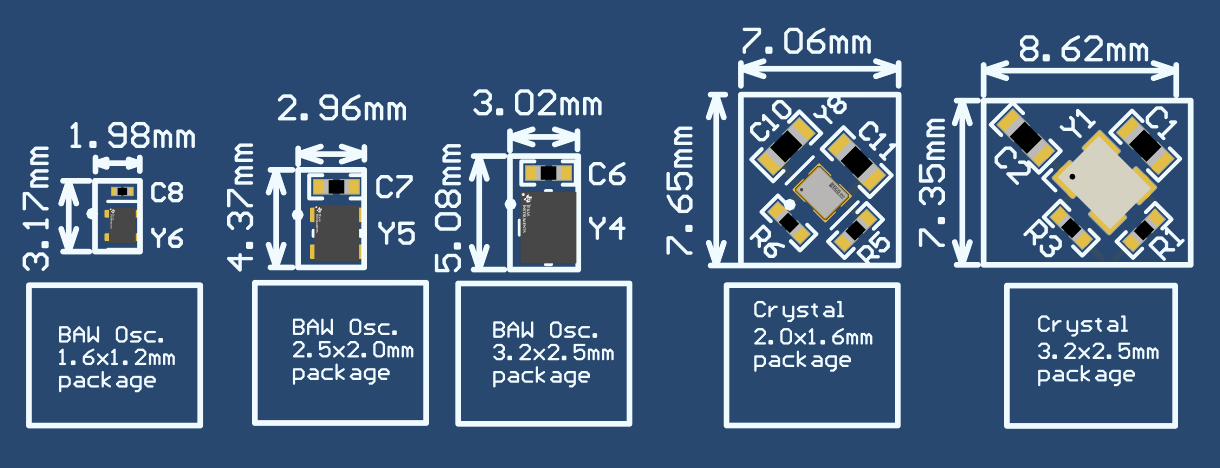 Figure 2 PCB Footprint Comparison of BAW Oscillator and Crystal
Figure 2 PCB Footprint Comparison of BAW Oscillator and Crystal - Higher performance with reliability protection for a variety of vibration and shock performance requirements.
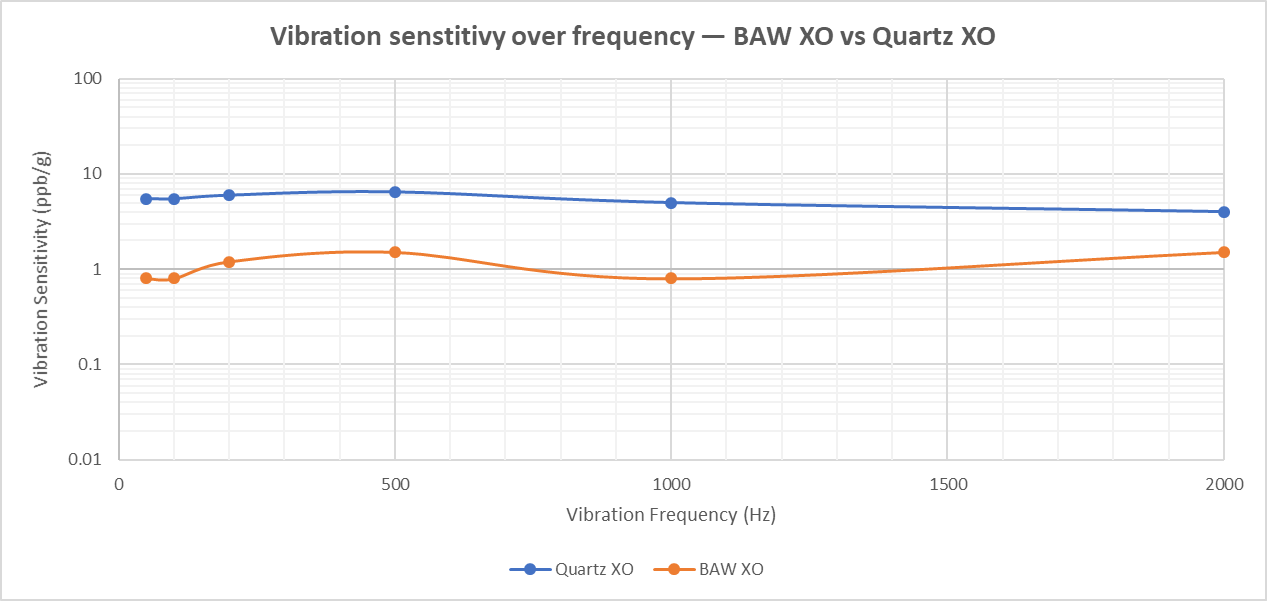 Figure 3 BAW Oscillator Vibration Sensitivity
Figure 3 BAW Oscillator Vibration Sensitivity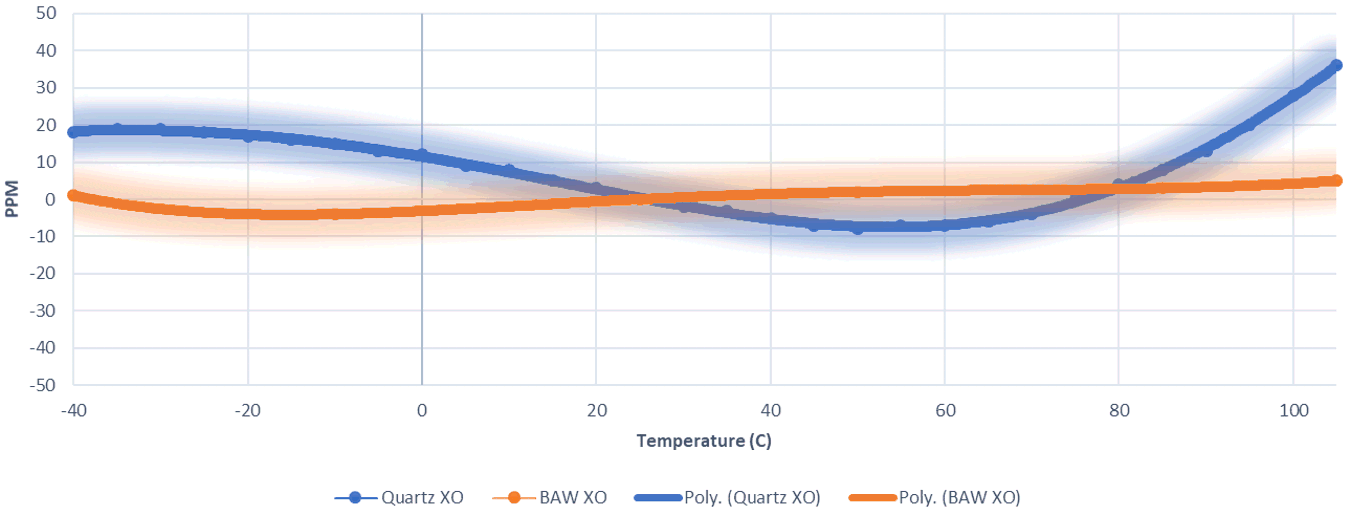 Figure 4 Temperature Stability Comparison of BAW Oscillator and Quartz
Figure 4 Temperature Stability Comparison of BAW Oscillator and Quartz - Low jitter to achieve optimal BER performance in system.
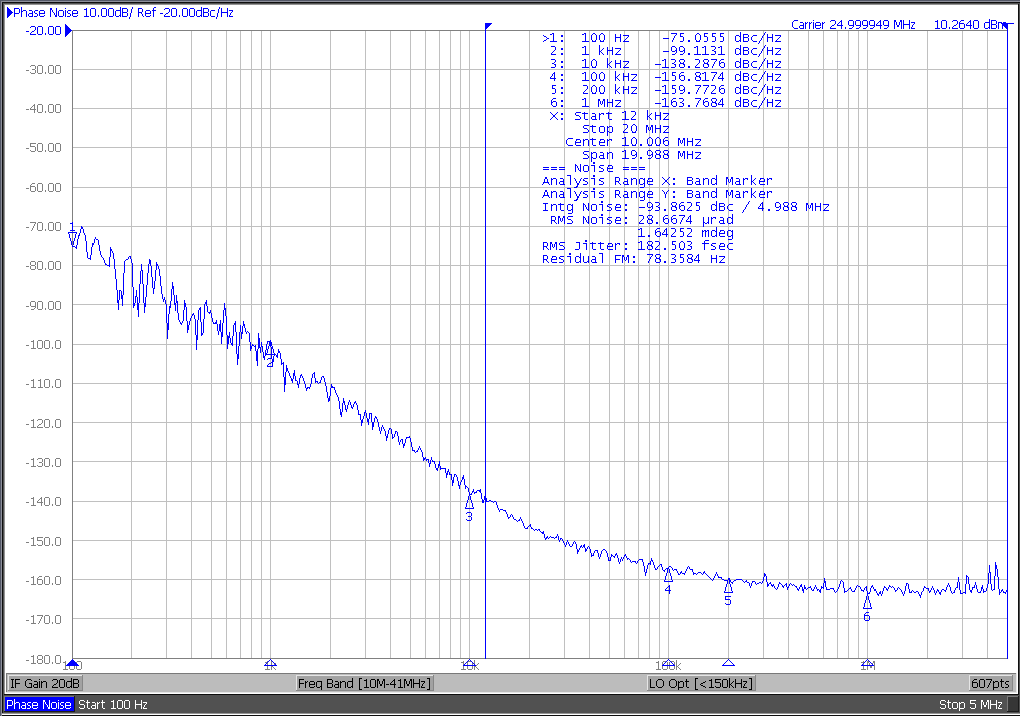 Figure 5 LMK6C BAW Oscillator 25 MHz Phase Noise Performance
Figure 5 LMK6C BAW Oscillator 25 MHz Phase Noise Performance
In Building automation systems, the CDC6C and LMK6C BAW oscillators can be used as a reference clock for the following devices:
| Devices | Frequencies |
|---|---|
| Audio | 12.288MHz/24.576MHz |
| 100M Ethernet | 25MHz |
| MCU | 16MHz/25MHz |
| Image Sensor | 37.125MHz/54MHz |
| SoC system clock | 48MHz/50MHz |
| WIFI/BLE | 38.4MHz/48MHz |
| HDMI/SDI | 297MHz |
| Gb Ethernet | 125MHz |
For all of the frequencies listed above, jitter performance, reliability, and stability are key performance factors. All of these metrics can be met with a BAW oscillator solution.
Figure 6 shows the typical block diagrams for IP-Camera and HVAC systems. For IP-Camera applications, the BAW oscillator can be used as a reference clock for the ASIC, MCU, Image Sensor, Audio Codec, HDMI/SDI, and Ethernet PHYs. For HVAC systems, the BAW oscillator can be used as a reference to the WIFI/BLE, MCU, FPGA, and Ethernet PHYs.
 Figure 6 Typical Block Diagrams of BAW Oscillator Used in Building Automation
Figure 6 Typical Block Diagrams of BAW Oscillator Used in Building Automation| Devices | Type | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMK6C/D/P/H | Ultra-low Jitter Oscillator (LVCMOS, LVDS, LVPECL, and HCSL output formats) | Reference clock for ASIC, MCU, Image Sensor, Audio Codec, HDMI/SDI, and Ethernet PHYs | Any frequency between 1MHz to 400MHz, ± 25ppm frequency accuracy, 200fs RMS jitter |
CDC6C | Low-Power LVCMOS Oscillator | Reference clock for ASIC, MCU, Image Sensor, Audio Codec, and Ethernet PHYs | Standard frequencies between 250kHz and 200MHz, ± 50ppm frequency accuracy, 1 ps RMS jitter |
| LMK1Cxxxx | 1:x LVCMOS buffer | Fan out to clock MCU, PHYs, and HDMI/SDI | 1.8V - 3.3V supply, ultra-low additive jitter of 20 fs |
| TPL5010 | Nanotimer | Ultra-Low Power System Timer with Power Gating Functionality | 1.8V to 5.5V supply, 35nA typical current consumption |