SNAS395F December 2007 – October 2016 DAC121C081 , DAC121C085
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
For best accuracy and minimum noise, the printed-circuit board containing the DAC121C081 should have separate analog and digital areas. The areas are defined by the locations of the analog and digital power planes. Both of these planes should be located on the same board layer. There should be a single ground plane. A single ground plane is preferred if digital return current does not flow through the analog ground area. Frequently a single ground plane design uses a fencing technique to prevent the mixing of analog and digital ground current. Separate ground planes should only be used when the fencing technique is inadequate. The separate ground planes must be connected in one place, preferably near the DAC121C081. Special care is required to ensure that digital signals with fast edge rates do not pass over split ground planes. They must always have a continuous return path below their traces.
The DAC121C081 power supply should be bypassed with a 4.7-µF and a 0.1-µF capacitor as close as possible to the device with the 0.1 µF right at the device supply pin. The 4.7-µF capacitor should be a tantalum type and the 0.1-µF capacitor should be a low ESL, low ESR type. The power supply for the DAC121C081 should only be used for analog circuits.
Avoid crossover of analog and digital signals and keep the clock and data lines on the component side of the board. These clock and data lines should have controlled impedances.
11.2 Layout Example
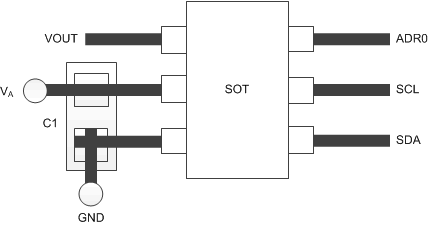 Figure 35. Layout Example
Figure 35. Layout Example