SNAS724A February 2018 – April 2018 LMK05028
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Oscillator Input (XO_P/N)
- 9.3.2 TCXO/OCXO Input (TCXO_IN)
- 9.3.3 Reference Inputs (INx_P/N)
- 9.3.4 Clock Input Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.5 Reference Input Mux Selection
- 9.3.6 Hitless Switching
- 9.3.7 Gapped Clock Support on Reference Inputs
- 9.3.8 Input Clock and PLL Monitoring, Status, and Interrupts
- 9.3.9
PLL Channels
- 9.3.9.1 PLL Frequency Relationships
- 9.3.9.2 Analog PLL (APLL)
- 9.3.9.3 APLL XO Doubler
- 9.3.9.4 APLL Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and Charge Pump
- 9.3.9.5 APLL Loop Filter
- 9.3.9.6 APLL Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
- 9.3.9.7 APLL VCO Post-Dividers (P1, P2)
- 9.3.9.8 APLL Fractional N Divider (N) With SDM
- 9.3.9.9 REF-DPLL Reference Divider (R)
- 9.3.9.10 TCXO/OCXO Input Doubler and M Divider
- 9.3.9.11 TCXO Mux
- 9.3.9.12 REF-DPLL and TCXO-DPLL Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- 9.3.9.13 REF-DPLL and TCXO-DPLL Loop Filter
- 9.3.9.14 REF-DPLL and TCXO-DPLL Feedback Dividers
- 9.3.10 Output Clock Distribution
- 9.3.11 Output Channel Muxes
- 9.3.12 Output Dividers
- 9.3.13 Clock Outputs (OUTx_P/N)
- 9.3.14 Glitchless Output Clock Start-Up
- 9.3.15 Clock Output Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.16 Output Synchronization (SYNC)
- 9.3.17 Zero-Delay Mode (ZDM) Configuration
- 9.3.18 PLL Cascading With Internal VCO Loopback
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.8.4 PLL Lock Detectors
The loss-of-lock (LOL) status is available for each APLL and DPLL. The APLLs are monitored for loss-of-frequency lock only. The REF-DPLLs are monitored for both loss-of-frequency lock (LOFL) and loss-of-phase lock (LOPL). The DPLL lock threshold and loss-of-lock threshold are programmable for both LOPF and LOFL detectors.
Each DPLL frequency lock detector will clear its LOFL flag when the DPLL's frequency error relative the selected reference input is less than the lock ppm threshold. Otherwise, it will set the LOFL flag when the DPLL's frequency error is greater than the unlock ppm threshold. The ppm delta between the lock and unlock thresholds provides hysteresis to prevent the LOFL flag from toggling when the DPLL frequency error is crossing these thresholds.
A measurement averaging factor is also used in computing the frequency lock detector register settings. A higher averaging factor increases the measurement delay to set or clear the LOFL flag. Higher averaging may be useful when locking to an input with high wander or when the DPLL is configured with a narrow loop bandwidth. Note that higher averaging reduces the maximum frequency ppm thresholds that can be configured.
Each DPLL phase lock detector will clear its LOPL flag when the DPLL's phase error is less than the phase lock threshold. Otherwise, it will set the LOPL flag when greater than the phase unlock threshold.
The APLL and DPLL lock detector flags can be observed through the status pins and the status bits.
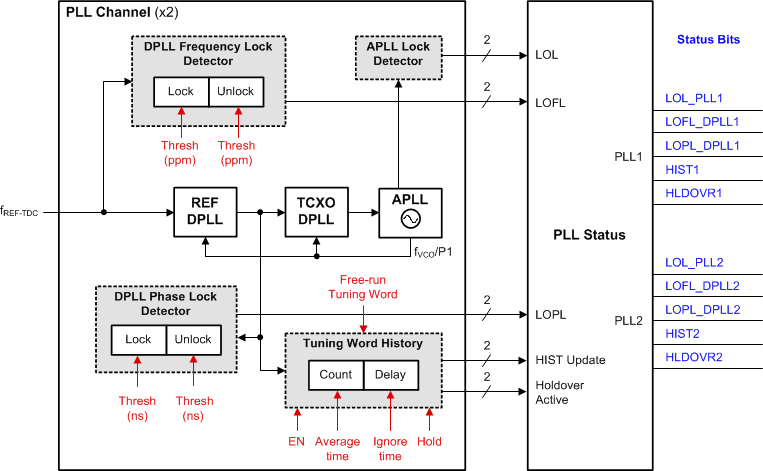 Figure 39. DPLL and APLL Lock Detectors
Figure 39. DPLL and APLL Lock Detectors