SNAS730A March 2018 – November 2018 LMX8410L
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Device Configurations and Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Map
- 7.6.1 R0 Register (Address = 0x0) [reset = X]
- 7.6.2 R1 Register (Address = 0x1) [reset = 0x3]
- 7.6.3 R2 Register (Address = 0x2) [reset = X]
- 7.6.4 R9 Register (Address = 0x9) [reset = X]
- 7.6.5 R10 Register (Address = 0xA) [reset = 0x80]
- 7.6.6 R11 Register (Address = 0xB) [reset = 0x10]
- 7.6.7 R14 Register (Address = 0xE) [reset = 0x70]
- 7.6.8 R36 Register (Address = 0x24) [reset = 0x64]
- 7.6.9 R37 Register (Address = 0x25) [reset = 0x200]
- 7.6.10 R38 Register (Address = 0x26) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.11 R39 Register (Address = 0x27) [reset = 0x2710]
- 7.6.12 R40 Register (Address = 0x28) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.13 R41 Register (Address = 0x29) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.14 R42 Register (Address = 0x2A) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.15 R43 Register (Address = 0x2B) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.16 R44 Register (Address = 0x2C) [reset = 0xA2]
- 7.6.17 R46 Register (Address = 0x2E) [reset = 0x1]
- 7.6.18 R58 Register (Address = 0x3A) [reset = 0x8000]
- 7.6.19 R59 Register (Address = 0x3B) [reset = 0x1]
- 7.6.20 R69 Register (Address = 0x45) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.21 R70 Register (Address = 0x46) [reset = 0xC350]
- 7.6.22 R75 Register (Address = 0x4B) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.23 R78 Register (Address = 0x4E) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.24 R79 Register (Address = 0x4F) [reset = 0x7000]
- 7.6.25 R80 Register (Address = 0x50) [reset = 0xA]
- 7.6.26 R81 Register (Address = 0x51) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.27 R82 Register (Address = 0x52) [reset = 0x23]
- 7.6.28 R83 Register (Address = 0x53) [reset = 0x2000]
- 7.6.29 R84 Register (Address = 0x54) [reset = 0x1900]
- 7.6.30 R88 Register (Address = 0x58) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.31 R94 Register (Address = 0x5E) [reset = 0x8080]
- 7.6.32 R95 Register (Address = 0x5F) [reset = X]
- 7.6.33 R103 Register (Address = 0x67) [reset = X]
- 7.6.34 R110 Register (Address = 0x6E) [reset = X]
- 7.6.35 R111 Register (Address = 0x6F) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.36 R112 Register (Address = 0x70) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.37 R121 Register (Address = 0x79) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.38 R123 Register (Address = 0x7B) [reset = 0x3]
- 7.6.39 R126 Register (Address = 0x7E) [reset = X]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
RGZ Package
48-Pin QFN
Top View
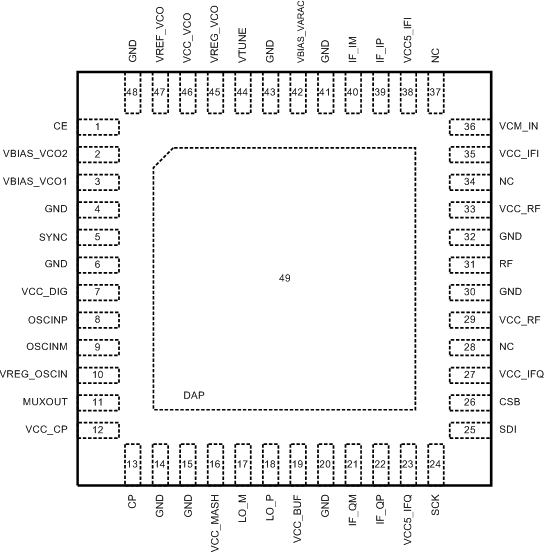
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NAME | ||
| 1 | CE | Input | Chip Enable input. Active HIGH powers on the device. 1.8V to 3.3V logic. |
| 2 | VBIAS_VCO2 | Bypass | VCO bias. Requires connecting 10-µF capacitor to VCO ground. Place close to pin. If using external LO, this pin should either be floated or configured the same way as internal LO mode. |
| 3 | VBIAS_VCO1 | Bypass | VCO bias. Requires connecting 10-µF capacitor to VCO ground. Place close to pin. If using external LO, this pin should either be floated or configured the same way as internal LO mode. |
| 4 | GND | Ground | VCO ground. VBIAS pin capacitors must bypass to this point. |
| 5 | SYNC | Input | Trigger pin for synchronizing multiple devices. If using external LO, tie this pin to GND. |
| 6 | GND | Ground | Digital ground. VCC_DIG bypass capacitors must bypass to this point. |
| 7 | VCC_DIG | Supply | Digital supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1-µF capacitor to digital ground. |
| 8 | OSCINP | Input | Reference input clock (+). High input impedance. Requires connecting series capacitor (0.1 µF recommended). If using external LO, tie this pin to GND. |
| 9 | OSCINM | Input | Reference input clock (–). High input impedance. Requires connecting series capacitor (0.1 µF recommended). If using external LO, tie this pin to GND. |
| 10 | VREG_OSCIN | Bypass | Internal LDO output. Requires connecting 1-µF capacitor to digital ground. Place close to pin. If using external LO, this pin should either be floated or configured the same way as internal LO mode. |
| 11 | MUXOUT | Output | Readback or lock detect output. Pin mode configured by internal register settings. |
| 12 | VCC_CP | Supply | Charge pump supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to charge pump ground. Place close to pin. This pin must be connected to VCC, even if using external LO. |
| 13 | CP | Output | Charge pump output. TI recommends connecting C1 of loop filter close to pin. If using external LO, this pin should either be floated or configured the same way as internal LO mode. |
| 14 | GND | Ground | Charge pump ground. VCC_CP bypass capacitors must bypass to this point. |
| 15 | GND | Ground | MASH engine ground. VCC_MASH bypass capacitors must bypass to this point. |
| 16 | VCC_MASH | Supply | MASH engine supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to MASH engine ground. Place close to pin. This pin must be connected to VCC, even if using external LO. |
| 17 | LO_M | Input/Output | Internal LO differential output (–) or external LO differential input (–). In differential output mode, requires connecting 50-Ω resistor pullup to VCC as close as possible to pin. In differential input mode, remove the pull up resistors or inductors. The input should be capacitively coupled with internal biasing. See LO Interface for more information. |
| 18 | LO_P | Input/Output | Internal LO differential output (+) or external LO differential input (+). In differential output mode, requires connecting 50-Ω resistor pullup to VCC as close as possible to pin. In differential input mode, remove the pull up resistors or inductors. The input should be capacitively coupled with internal biasing. See LO Interface for more information. |
| 19 | VCC_BUF | Supply | LO buffer supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to VCO ground. This pin must be connected to VCC, even if using external LO. |
| 20 | GND | Ground | IF amplifier Q-channel ground. Q-channel VCC5 bypass capacitors must bypass to this point. |
| 21 | IF_QM | Output | IF amplifier Q-channel differential output (–). TI recommends connecting series 50-Ω resistor close to pin. |
| 22 | IF_QP | Output | IF amplifier Q-channel differential output (+). TI recommends connecting series 50-Ω resistor close to pin. |
| 23 | VCC5_IFQ | Supply | IF amplifier Q-channel 5-V supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to IF amplifier Q-channel ground. Place close to pin. |
| 24 | SCK | Input | SPI clock signal. High impedance CMOS input. 1.8-V to 3.3-V logic. |
| 25 | SDI | Input | SPI data signal. High impedance CMOS input. 1.8-V to 3.3-V logic. |
| 26 | CSB | Input | SPI chip select signal. High impedance CMOS input. 1.8-V to 3.3-V logic. |
| 27 | VCC_IFQ | Supply | IF mixer Q-channel supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to digital ground. |
| 28 | NC | N/A | No connect. Pin is not internally connected and may be floated or shorted to other nodes. |
| 29 | VCC_RFQ | Supply | RF Q-channel supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to digital ground. |
| 32 | GND | Ground | RF input path ground. |
| 31 | RF | Input | RF input. Single-ended. Must be AC coupled. |
| 32 | GND | Ground | RF input path ground. |
| 33 | VCC_RFI | Supply | RF I-channel supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to digital ground. |
| 34 | GND | Ground | Should be connected IF ground. |
| 35 | VCC_IFI | Supply | IF mixer I-channel supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to digital ground. |
| 36 | VCM_IN | Input | Common-mode voltage input. When the VCM_CONFIG register is set to external (0xF), the voltage on this pin sets the common-mode voltage of the IF amplifiers. |
| 37 | NC | Ground | Connect this pin to IF ground. |
| 38 | VCC5_IFI | Supply | IF amplifier I-channel 5-V supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1 µF and 100 pF to IF amplifier I-channel ground. Place close to pin. |
| 39 | IF_IP | Output | IF amplifier I-channel differential output (+). TI recommends connecting series 50-Ω resistor close to pin. |
| 40 | IF_IM | Output | IF amplifier I-channel differential output (–). TI recommends connecting series 50-Ω resistor close to pin. |
| 41 | GND | Ground | IF amplifier I-channel ground. I-channel VCC5 bypass capacitors should bypass to this point. |
| 42 | VBIAS_VARAC | Bypass | VCO varactor bias. Requires connecting 10µF capacitor to VCO ground. If using external LO, this pin should either be floated or configured the same way as internal LO mode. |
| 43 | GND | Ground | VCO ground. Varactor bias bypass capacitor should bypass to this point. |
| 44 | VTUNE | Input | VCO tuning voltage input. If using internal LO, connect the output of the loop filter to this point. If using external LO, tie this pin to GND. |
| 45 | VREG_VCO | Bypass | VCO LDO output node. Requires connecting 10-µF capacitor to VCO ground. Place close to pin. This capacitor must be present even if used in external LO mode. |
| 46 | VCC_VCO | Supply | VCO supply. TI recommends connecting 0.1-µF and 100-pF capacitors to VCO ground. This pin must be connected to VCC, even if using external LO. |
| 47 | VREF_VCO | Bypass | VCO LDO reference node. Requires connecting 1-µF capacitor to VCO ground. If using external LO, this pin should either be floated or configured the same way as internal LO mode. |
| 48 | GND | Ground | VCO ground. VCO LDO, LDO reference, and supply bypass capacitors must bypass to this point. |
| 49 | PAD | Ground | Die attach pad. Internally connected to ground. TI recommends shorting ground pins to this pad on the same plane, if possible. |