SNAS736C June 2017 – April 2019 LMX2595
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Reference Oscillator Input
- 7.3.2 Reference Path
- 7.3.3 PLL Phase Detector and Charge Pump
- 7.3.4 N-Divider and Fractional Circuitry
- 7.3.5 MUXout Pin
- 7.3.6 VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator)
- 7.3.7 Channel Divider
- 7.3.8 VCO Doubler
- 7.3.9 Output Buffer
- 7.3.10 Power-Down Modes
- 7.3.11 Phase Synchronization
- 7.3.12 Phase Adjust
- 7.3.13 Fine Adjustments for Phase Adjust and Phase SYNC
- 7.3.14 Ramping Function
- 7.3.15 SYSREF
- 7.3.16 SysRefReq Pin
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 General Registers R0, R1, & R7
- 7.6.2 Input Path Registers
- 7.6.3 Charge Pump Registers (R13, R14)
- 7.6.4 VCO Calibration Registers
- 7.6.5 N Divider, MASH, and Output Registers
- 7.6.6 SYNC and SysRefReq Input Pin Register
- 7.6.7 Lock Detect Registers
- 7.6.8 MASH_RESET
- 7.6.9 SysREF Registers
- 7.6.10 CHANNEL Divider And VCO Doubler Registers
- 7.6.11 Ramping and Calibration Fields
- 7.6.12 Ramping Registers
- 7.6.13 Readback Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.11.1 General Concept
The SYNC pin allows one to synchronize the LMX2595 such that the delay from the rising edge of the OSCin signal to the output signal is deterministic. Initially, the devices are locked to the input, but are not synchronized. The user sends a synchronization pulse that is reclocked to the next rising edge of the OSCin pulse. After a given time, t1, the phase relationship from OSCin to fOUT will be deterministic. This time is dominated by the sum of the VCO calibration time, the analog setting time of the PLL loop, and the MASH_RST_CNT if used in fractional mode.
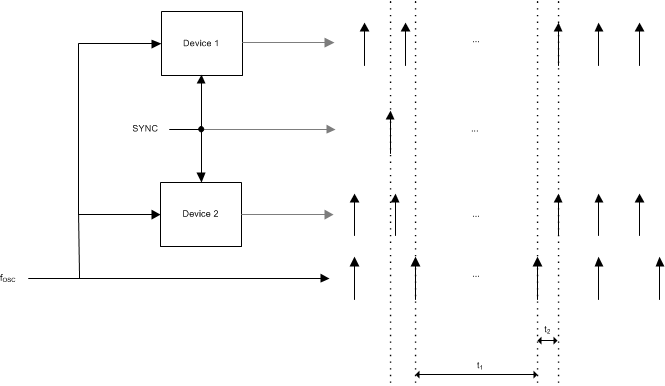 Figure 31. Devices Are Now Synchronized to OSCin Signal
Figure 31. Devices Are Now Synchronized to OSCin Signal When the SYNC feature is enabled, part of the channel divide may be included in the feedback path. This will be referred to as IncludedDivide
Table 12. IncludedDivide With VCO_PHASE_SYNC = 1
| OUTx_MUX | CHANNEL DIVIDER | INCLUDEDDIVIDE |
|---|---|---|
| OUTB_MUX = 1 ("VCO")
OUTA_MUX = 1 "VCO" or 2 "VCO Doubler" |
Don't Care | 1 |
| All Other Valid Conditions | Divisible by 3, but NOT 24 or 192 | SEG0 × SEG1 = 6 |
| All other values | SEG0 × SEG1 = 4 |
