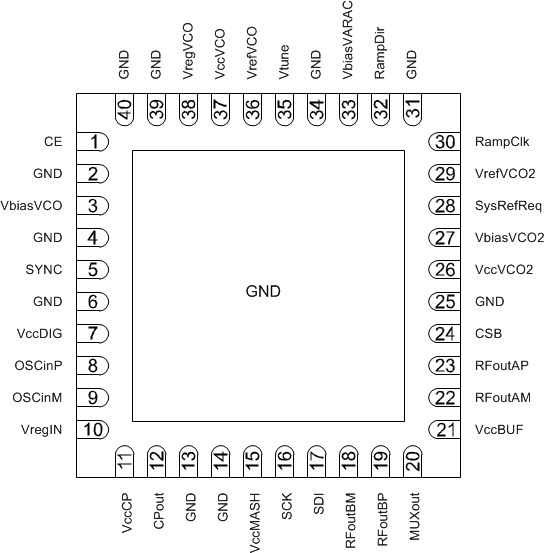
| 1 |
CE |
Input |
Chip enable input. Active HIGH powers on the device. |
| 2, 4, 25, 31, 34, 39, 40 |
GND |
Ground |
VCO ground. |
| 3 |
VbiasVCO |
Bypass |
VCO bias. Requires a 10-µF capacitor connected to VCO ground. Place close to pin. |
| 5 |
SYNC |
Input |
Phase synchronization pin. Has programmable threshold. |
| 6, 14 |
GND |
Ground |
Digital ground. |
| 7 |
VccDIG |
Supply |
Digital supply. TI recommends bypassing with decoupling capacitor to digital ground. |
| 8 |
OSCinP |
Input |
Reference input clock (+). High-impedance self-biasing pin. Requires AC-coupling capacitor.
(0.1 µF recommended) |
| 9 |
OSCinM |
Input |
Reference input clock (–). High impedance self-biasing pin. Requires AC-coupling capacitor.
(0.1 µF recommended) |
| 10 |
VregIN |
Bypass |
Input reference path regulator output. Requires a 1-µF capacitor connected to ground. Place close to pin. |
| 11 |
VccCP |
Supply |
Charge pump supply. TI recommends bypassing with decoupling capacitor to charge pump ground. |
| 12 |
CPout |
Output |
Charge pump output. TI recommends connecting C1 of loop filter close to pin. |
| 13 |
GND |
Ground |
Charge pump ground. |
| 15 |
VccMASH |
Supply |
Digital supply. TI recommends bypassing with decoupling capacitor to digital ground. |
| 16 |
SCK |
Input |
SPI clock. High impedance CMOS input. 1.8-V to 3.3-V logic. |
| 17 |
SDI |
Input |
SPI data. High impedance CMOS input. 1.8-V to 3.3-V logic. |
| 18 |
RFoutBM |
Output |
Differential output B (–). Requires a pullup (typically 50-Ω resistor) connected to Vcc as close to the pin as possible. Can be used as an output signal or SYSREF output. |
| 19 |
RFoutBP |
Output |
Differential output B (+). Requires a pullup (typically 50-Ω resistor) connected to Vcc as close to the pin as possible. Can be used as an output signal or SYSREF output. |
| 20 |
MUXout |
Output |
Multiplexed output pin — lock detect, readback, diagnostics, ramp status. |
| 21 |
VccBUF |
Supply |
Output buffer supply. TI recommends bypassing with decoupling capacitor to RFout ground. |
| 22 |
RFoutAM |
Output |
Differential output A (–). Requires connecting a 50-Ω resistor pullup to Vcc as close to the pin as possible. |
| 23 |
RFoutAP |
Output |
Differential output A (+). Requires connecting a 50-Ω resistor pullup to Vcc as close to the pin as possible. |
| 24 |
CSB |
Input |
SPI latch. Chip Select Bar. High-impedance CMOS input. 1.8-V to 3.3-V logic. |
| 26 |
VccVCO2 |
Supply |
VCO supply. TI recommends bypassing with decoupling capacitor to VCO ground. |
| 27 |
VbiasVCO2 |
Bypass |
VCO bias. Requires a 1-µF capacitor connected to VCO ground. |
| 28 |
SysRefReq |
Input |
SYSREF request input for JESD204B support. |
| 29 |
VrefVCO2 |
Bypass |
VCO supply reference. Requires a 10-µF capacitor connected to VCO ground. |
| 30 |
RampClk |
Input |
Input pin for ramping mode that can be used to clock the ramp in manual ramping mode or as a trigger input. |
| 32 |
RampDir |
Input |
Input pin for ramping mode that can be used to change ramp direction in manual ramping mode or as a trigger input. |
| 33 |
VbiasVARAC |
Bypass |
VCO Varactor bias. Requires a 10-µF capacitor connected to VCO ground. |
| 35 |
Vtune |
Input |
VCO tuning voltage input. |
| 36 |
VrefVCO |
Bypass |
VCO supply reference. Requires a 10-µF capacitor connected to VCO ground. |
| 37 |
VccVCO |
Supply |
VCO supply. Recommend bypassing with decoupling capacitor to ground. |
| 38 |
VregVCO |
Bypass |
VCO regulator node. Requires a 1-µF capacitor connected to ground. |
| DAP |
GND |
Ground |
Die Attached Pad. Used for RFout ground. |