SNAS736C June 2017 – April 2019 LMX2595
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Reference Oscillator Input
- 7.3.2 Reference Path
- 7.3.3 PLL Phase Detector and Charge Pump
- 7.3.4 N-Divider and Fractional Circuitry
- 7.3.5 MUXout Pin
- 7.3.6 VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator)
- 7.3.7 Channel Divider
- 7.3.8 VCO Doubler
- 7.3.9 Output Buffer
- 7.3.10 Power-Down Modes
- 7.3.11 Phase Synchronization
- 7.3.12 Phase Adjust
- 7.3.13 Fine Adjustments for Phase Adjust and Phase SYNC
- 7.3.14 Ramping Function
- 7.3.15 SYSREF
- 7.3.16 SysRefReq Pin
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 General Registers R0, R1, & R7
- 7.6.2 Input Path Registers
- 7.6.3 Charge Pump Registers (R13, R14)
- 7.6.4 VCO Calibration Registers
- 7.6.5 N Divider, MASH, and Output Registers
- 7.6.6 SYNC and SysRefReq Input Pin Register
- 7.6.7 Lock Detect Registers
- 7.6.8 MASH_RESET
- 7.6.9 SysREF Registers
- 7.6.10 CHANNEL Divider And VCO Doubler Registers
- 7.6.11 Ramping and Calibration Fields
- 7.6.12 Ramping Registers
- 7.6.13 Readback Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics

| fOSC = 100 MHz | Jitter = 55.8 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |
| fPD = 200 MHz |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | Jitter = 46.8 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |
| fPD = 200 MHz |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | Jitter = 46.87 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |
| fPD = 200 MHz |


| fOSC = 100 MHz | fOUT = 2 × 8.5 GHz = 17 GHz | |
| fPD = 200 MHz | Jitter = 55.0 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | fOUT = 2 × 9.5 GHz = 19 GHz | |
| fPD = 200 MHz | Jitter = 54.7 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) |


| CalTime = 33.6 µs = 5.8 µs (Core) + 14 µs (Fcal) + 13.8 µs (Ampcal) | ||
| fOSC = 200 MHz, fPD = 100 MHz, fVCO = 7.5 - 14 GHz, CHDIV = 2 | ||

| fVCO = 12 GHz | fPD = 100 MHz | |

| fVCO = 8 GHz, Narrow Loop Bandwidth (<100 Hz) |
| Single-ended output with resistor pullup. | OUTA_PWR = 20 |
| DBLR_IBIAS_CTRL1 = 3115 |

| This noise adds to the scaled VCO Noise when the channel divider is used. |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | Jitter = 52.6 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |
| fPD = 200 MHz |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | Jitter = 46.9 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |
| fPD = 200 MHz |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | Jitter = 44.1 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |
| fPD = 200 MHz |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | fOUT = 2 × 8 GHz = 16 GHz | |
| fPD = 200 MHz | Jitter = 52.9 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) | |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | fOUT = 2 × 9 GHz = 18 GHz | |
| fPD = 200 MHz | Jitter = 52.6 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) |

| fOSC = 100 MHz | fOUT = 2 × 10 GHz = 20 GHz | |
| fPD = 200 MHz | Jitter = 52.7 fs (100 Hz - 100 MHz) |

| The glitches in the plot are due to the inability of the measurement equipment to track the VCO while calibrating. |

| CalTime = 25.2 µs = 1.3 µs (Core) + 9.1 µs (Fcal) +14.8 µs (Ampcal) | ||
| fOSC = 200 MHz, fPD = 100 MHz, fVCO = 7.5 GHz - 14 GHz, CHDIV = 2 |

| fOSC = 200 MHz | fVCO = 14.8 GHz |

fVCO = 8 GHz, Narrow Loop Bandwidth (<100 Hz)

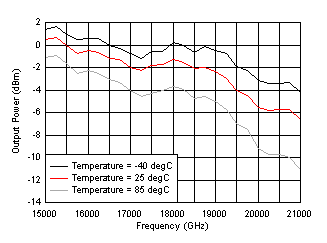
| Single-ended output with resistor pullup and OUTx_PWR = 50. Note that Near 13.3 to 14.3 GHz, output power can be impacted at hot temperature. See the Application Information section for more information. |

