SNAU310 June 2024 LMKDB1102 , LMKDB1202
4.1 Typical Phase Noise Characteristic
Figure 5-1 shows a typical phase noise performance for 156.25MHz reference clock input from the SMA100B. Both the LMKDB1202 and the LMKDB1102 have the same performance.
LMKDB1x02EVM was configured in cascade mode to get these measurements, which were obtained by following these steps:
- SMA100B → LMKDB1x02EVM input. Then, LMKDB1x02EVM to secondary LMKDB1x02 EVM. This was done to get a fast slew rate at the input. Other methods like clipping a circuit can be used to get a desired slew rate and square wave form as well outputted from the SMA100B.
- Output phase noise is measured through a Balun to the differential waveform from the LMKDB1x02 into a single-ended waveform for the phase noise analyzer.
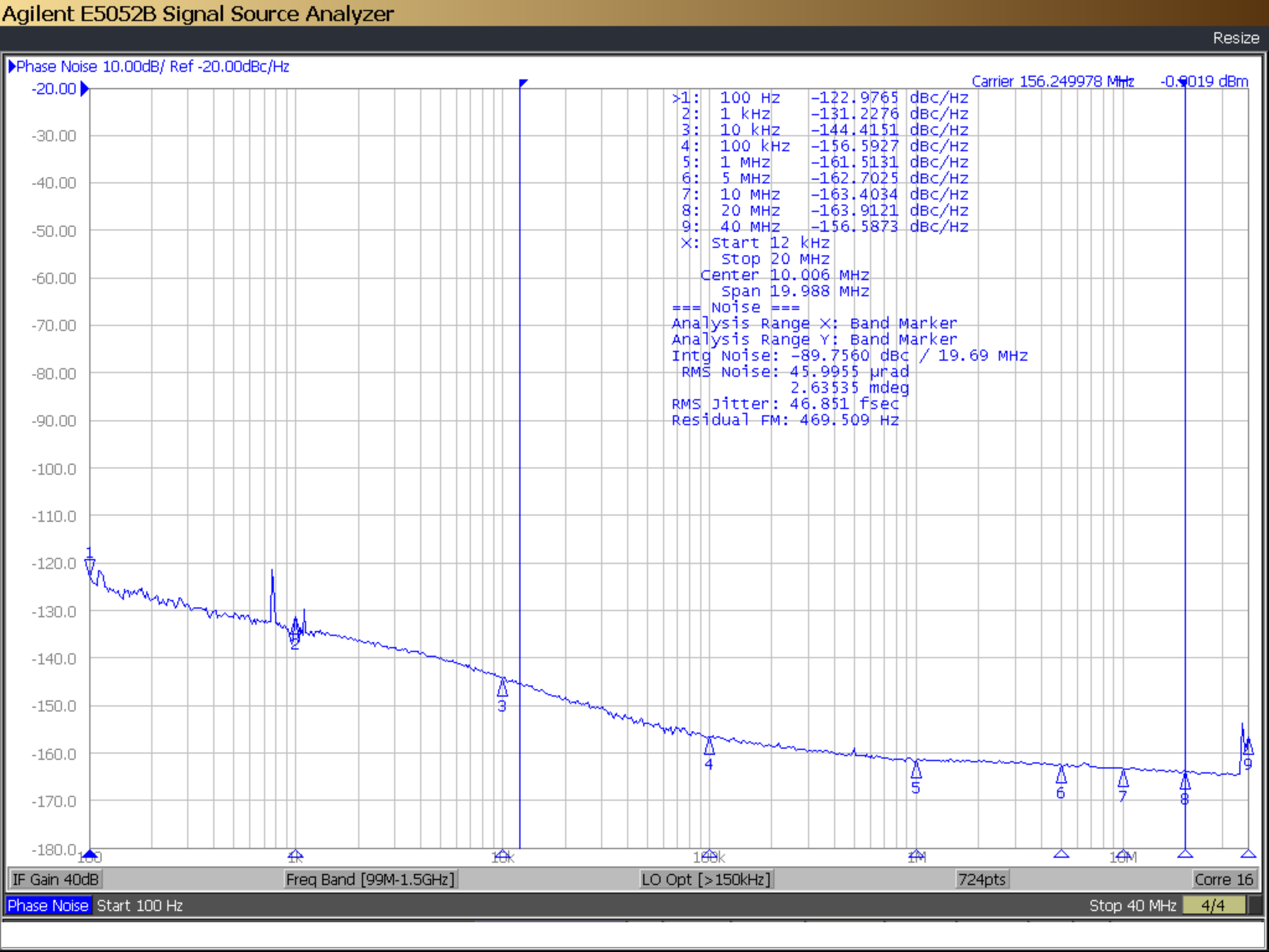
Figure 4-1 LMKDB1x02 Output Clock Phase Noise