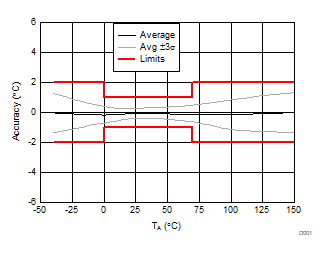
at TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
| VDD = 2.3 to 5.5V, IOUT = 0µA, CLOAD = 1000pF |

| IOUT = from 0µA to 100µA, CLOAD = 1000pF |

| VDD = 2.3V, CLOAD = 1000pF |
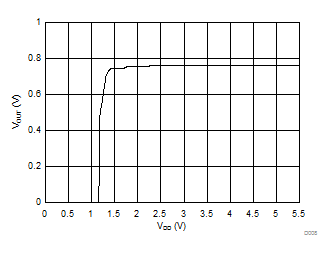 Figure 5-7 Output Voltage vs Power Supply
Figure 5-7 Output Voltage vs Power Supply
| TA = 25°C, VDD Ramp Rate = 5V/ms |

| TA = 25°C, VDD = 5V, IOUT = 100µA |
 Figure 5-13 Output Noise Density
Figure 5-13 Output Noise Density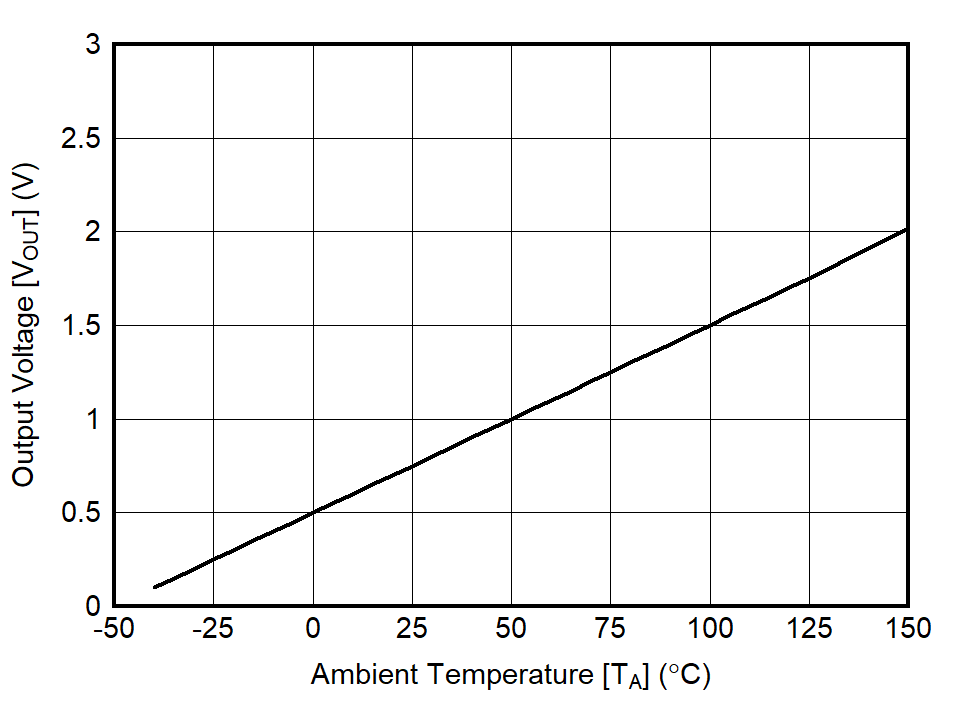
| IOUT = 0µA, CLOAD = 1000pF |

| IOUT = 0µA, CLOAD = 1000pF |

| VDD = 2.3 to 5.5V, IOUT = 0µA, CLOAD = 1000pF |
 Figure 5-8 Output vs. Settling Time to Step VDD
Figure 5-8 Output vs. Settling Time to Step VDD
| 0.5 × 0.5 inch PCB, Air 25°C to Fluid Bath 150°C |
 Figure 5-12 PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 5-12 PSRR vs Frequency











