SNLA443 December 2023 DP83869HM
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1DP83869 Application Overview
- 2Troubleshooting the Application
- 3Operational Mode Clarification
- 4Tools and References
- 5Summary
- 6References
3.1 Bridge Modes
The DP83869HM supports two types of Bridge Modes to translate data between two MAC interface types. The two types are:
- RGMII-to-SGMII mode
- SGMII-to-RGMII mode
The naming convention implies MAC-to-PHY and the functionality of the DP83869HM changes depending on which mode is selected. More information can be found in the Bridge Modes section of the data sheet.
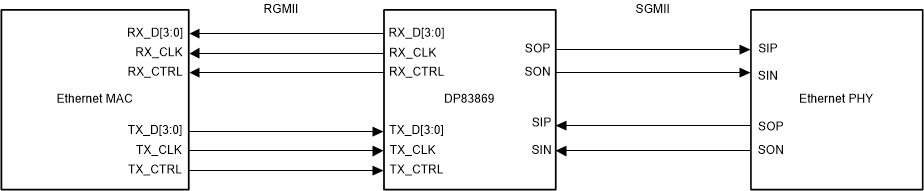 Figure 3-1 DP83869HM RGMII-to-SGMII Bridge
Figure 3-1 DP83869HM RGMII-to-SGMII Bridge Figure 3-2 DP83869HM SGMII-to-RGMII Bridge
Figure 3-2 DP83869HM SGMII-to-RGMII Bridge