SNLS044D May 2000 – July 2016 DS90LV047A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
- Use at least 4 PCB layers (top to bottom); LVDS signals, ground, power, TTL signals.
- Isolate TTL signals from LVDS signals, otherwise the TTL may couple onto the LVDS lines. It is best to put TTL and LVDS signals on different layers which are isolated by a power/ground plane(s).
- Keep drivers and receivers as close to the (LVDS port side) connectors as possible.
11.1.1 Power Decoupling Recommendations
Bypass capacitors must be used on power pins. Use high frequency ceramic (surface mount is recommended) 0.1-µF and 0.001-µF capacitors in parallel at the power supply pin with the smallest value capacitor closest to the device supply pin. Additional scattered capacitors over the printed-circuit board improves decoupling. Multiple vias must be used to connect the decoupling capacitors to the power planes. A 10-µF (35-V) or greater solid tantalum capacitor must be connected at the power entry point on the printed-circuit board between the supply and ground.
11.1.2 Differential Traces
Use controlled impedance traces which match the differential impedance of your transmission medium (that is, cable) and termination resistor. Run the differential pair trace lines as close together as possible as soon as they leave the IC (stubs must be < 10 mm long). This helps eliminate reflections and ensure noise is coupled as common-mode. In fact, we have seen that differential signals which are 1 mm apart radiate far less noise than traces 3 mm apart since magnetic field cancellation is much better with the closer traces. In addition, noise induced on the differential lines is much more likely to appear as common-mode which is rejected by the receiver.
Match electrical lengths between traces to reduce skew. Skew between the signals of a pair means a phase difference between signals, which destroys the magnetic field cancellation benefits of differential signals and EMI, results.
NOTE
The velocity of propagation, v = c/Er where c (the speed of light) = 0.2997mm/ps or 0.0118 in/ps
Do not rely solely on the autoroute function for differential traces. Carefully review dimensions to match differential impedance and provide isolation for the differential lines. Minimize the number or vias and other discontinuities on the line.
Avoid 90° turns (these cause impedance discontinuities). Use arcs or 45° bevels.
Within a pair of traces, the distance between the two traces must be minimized to maintain common-mode rejection of the receivers. On the printed-circuit board, this distance must remain constant to avoid discontinuities in differential impedance. Minor violations at connection points are allowable.
11.1.3 Termination
Use a termination resistor which best matches the differential impedance or your transmission line. The resistor must be between 90 Ω and 130 Ω. Remember that the current mode outputs need the termination resistor to generate the differential voltage. LVDS does not work without resistor termination. Typically, connecting a single resistor across the pair at the receiver end will suffice.
Surface mount 1% to 2% resistors are best. PCB stubs, component lead, and the distance from the termination to the receiver inputs must be minimized. The distance between the termination resistor and the receiver should be < 10 mm (12 mm maximum).
11.2 Layout Example
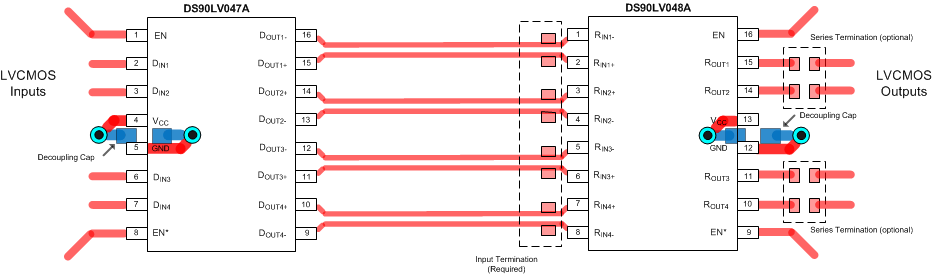 Figure 25. Layout Recommendation
Figure 25. Layout Recommendation