SNOSDB7 December 2020 LM74500-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Reverse Battery Protection for Automotive Body Control Module Applications
- 9.2 Reverse Polarity Protection
- 9.3 Application Information
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.1.4 Selection of TVS Diodes and MOSFET for 24-V Battery Protection Applications
Typical 24-V battery protection application circuit shown in Figure 9-6 uses two uni-directional TVS diodes to protect from positive and negative transient voltages.
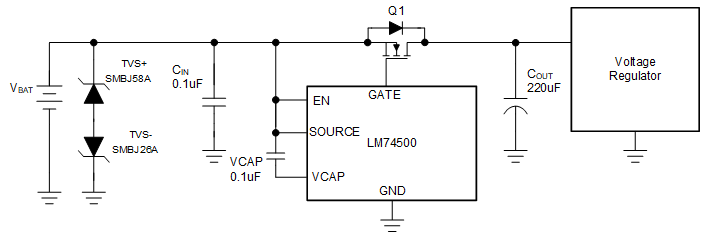 Figure 9-6 Typical 24-V Battery Protection with Two
Uni-Directional TVS
Figure 9-6 Typical 24-V Battery Protection with Two
Uni-Directional TVSThe breakdown voltage of the TVS+ should be higher than 48-V jump start voltage, less than the absolute maximum ratings of source and enable pin of LM74500-Q1 (65 V) and should withstand 65-V suppressed load dump. The breakdown voltage of TVS- should be lower than maximum reverse battery voltage –32 V, so that the TVS- is not damaged due to long time exposure to reverse connected battery.
During ISO 7637-2 pulse 1, the input voltage goes up to –600 V with a generator impedance of 50 Ω. Single bi-directional TVS cannot be used for 24-V battery protection because breakdown voltage for TVS+ ≥ 48V, maximum negative clamping voltage is ≤ –65 V . Two uni-directional TVS connected back-back needs to be used at the input. For positive side TVS+, SMBJ58A with the breakdown voltage of 64.4 V (minimum), 67.8 (typical) is recommended. For the negative side TVS-, SMBJ26A with breakdown voltage close to 32 V (to withstand maximum reverse battery voltage –32 V) and maximum clamping voltage of 42 V is recommended.
For 24-V battery protection, a 75-V rated MOSFET is recommended to be used along with SMBJ26A and SMBJ58A connected back-back at the input.