SNOSDB7 December 2020 LM74500-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Reverse Battery Protection for Automotive Body Control Module Applications
- 9.2 Reverse Polarity Protection
- 9.3 Application Information
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.1.3 Selection of TVS Diodes for 12-V Battery Protection Applications
TVS diodes are used in automotive systems for protection against transients. In the 12-V battery protection application circuit shown in Figure 9-5, a bi-directional TVS diode is used to protect from positive and negative transient voltages that occur during normal operation of the car and these transient voltage levels and pulses are specified in ISO 7637-2 and ISO 16750-2 standards.
The two important specifications of the TVS are breakdown voltage and clamping voltage. Breakdown voltage is the voltage at which the TVS diode goes into avalanche similar to a zener diode and is specified at a low current value typical 1 mA and the breakdown voltage should be higher than worst case steady state voltages seen in the system. The breakdown voltage of the TVS+ should be higher than 24-V jump start voltage and 35-V suppressed load dump voltage and less than the maximum input voltage rating of LM74500-Q1 (65 V). The breakdown voltage of TVS- should be higher than maximum reverse battery voltage –16 V, so that the TVS- is not damaged due to long time exposure to reverse connected battery.
Clamping voltage is the voltage the TVS diode clamps in high current pulse situations and this voltage is much higher than the breakdown voltage. TVS diodes are meant to clamp transient pulses and should not interfere with steady state operation. In the case of an ISO 7637-2 pulse 1, the input voltage goes up to –150 V with a generator impedance of 10 Ω. This translates to 15 A flowing through the TVS - and the voltage across the TVS would be close to its clamping voltage.
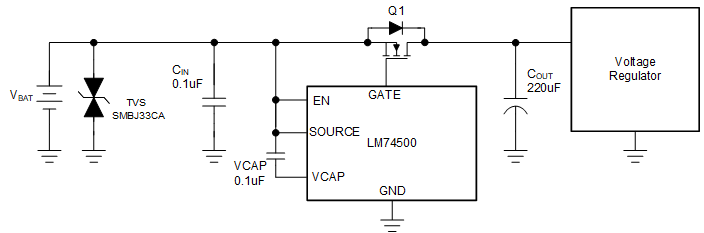 Figure 9-5 Typical 12-V Battery
Protection with Single Bi-Directional TVS
Figure 9-5 Typical 12-V Battery
Protection with Single Bi-Directional TVSThe next criterion is that the absolute minimum rating of source voltage of the LM74500-Q1 (–65 V) and the maximum VDS rating MOSFET are not exceeded. In the design example, 60-V rated MOSFET is chosen.
SMBJ series of TVS' are rated up to 600-W peak pulse power levels. This is sufficient for ISO 7637-2 pulses and suppressed load dump (ISO-16750-2 pulse B).