SNVA382B January 2009 – September 2024 LM22670 , LM22670-Q1 , LM22671 , LM22671-Q1 , LM22672 , LM22672-Q1 , LM22673 , LM22673-Q1 , LM22674 , LM22674-Q1 , LM22675 , LM22675-Q1 , LM22676 , LM22676-Q1 , LM22677 , LM22678 , LM22679 , LM22680 , LMR16006
Abstract
Power management applications, typically located on the front line of the automotive electronics system, can be subject to wide input operating voltage extremes resulting from load-dump and cold-cranking conditions. Careful selection of the power management electronics can provide added margin and protection to the automotive electronics system. The simplest design is provided by a power management switch-mode power supply, such as the LM2267x/80 family of SIMPLE SWITCHER® regulators, which integrates a power MOSFET and sustains a wide steady-state input voltage range.
Load Dump
Load dump occurs when the automobile battery is disconnected while the engine and the alternator are running. The resultant voltage transient may be as high as 120V, and 400ms in duration. With such a severe voltage transient, this presents a challenge to the engineer designing the power management system. It is not economically practical to design a power supply option that operates up to 120V only to accommodate load-dump line transients. Modern automobiles typically have a centralized load-dump protection scheme that limits the voltage during load-dump conditions to much lower voltages. Diode shunt devices such as transient voltage suppression diodes (TVS) may be used to clamp the maximum voltage a power supply will see at its input. Other protection circuits involving high-side MOSFETs, as described in AN-1533 Over Voltage Protection Circuit for Automotive Load Dump (SNVA190) also can be used to protect the application during load-dump situations. However, even with the use of these transient protection devices, the selected power management IC must provide an added margin of protection.
A typical input voltage waveform during a load-dump condition is shown in Typical Load-Dump Profile.
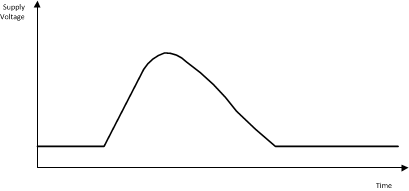 Typical Load-Dump Profile
Typical Load-Dump ProfileComparing different design methods for reliability, simplicity, and cost often supports the selection of a power management IC with a maximum input operating voltage of approximately 40V. The new LM2267x/80 SIMPLE SWITCHER family provides a maximum input operating voltage of 42V to allow additional protection headroom.
Cold Cranking
During the startup of a combustion engine, also known as cold crank, the battery supplies a large current to the electric starter motor. Under this condition, the battery voltage sags dramatically. Typical Cold-Cranking Profile shows a typical cold-cranking profile. The initial voltage collapse to 'V low' is due to the initial peak current needed to start turning the combustion engine. Once the combustion engine is turning, the voltage of the battery plateaus to the 'V plateau' voltage level and finally, when the electric starter motor is disabled, the battery voltage rises to its charging voltage level.
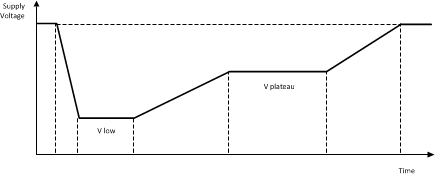 Typical Cold-Cranking Profile
Typical Cold-Cranking ProfileIt is becoming increasingly important for automotive subsystems to operate during engine cold-cranking conditions. To increase fuel economy, some new automobiles are being equipped with automated start-stop systems that shut down the combustion engine when the automobile is stopped at a traffic light or in a traffic jam. As the break pedal or the clutch is released, the electric starter motor cold cranks the battery to get the combustion engine operating. For safety and convenience, the power management system must sustain the input operating voltage levels, in such start-stop systems, to insure continuous operation of electronic components found in navigation systems, dashboard electronics, LED break lights, or headlights. This requires power management choices capable of operation at very low minimum input operating voltages.
For systems where the 'V low' voltage level is 4.5V or above, the LM2267x SIMPLE SWITCHER family provides a good option. See the Series of New SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators with Very Wide Input Voltage Range from 4.5V to 42V and the Example Circuit With Very Wide Input Voltage Range and Low Component Count for a list of devices, features, and an example circuit of the new SIMPLE SWITCHER family.
| Device | Current | RT/SYNC | Enable | Soft-Start | IADJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM22671 | 0.5A | X | X | X | |
| LM22674 | 0.5A | X | |||
| LM22672 | 1A | X | X | X | |
| LM22675 | 1A | X | |||
| LM22680 | 2A | X | X | X | |
| LM22670 | 3A | X | X | ||
| LM22673 | 3A | X | X | ||
| LM22676 | 3A | X | |||
| LM22677 | 5A | X | X | ||
| LM22678 | 5A | X | |||
| LM22679 | 5A | X | X |
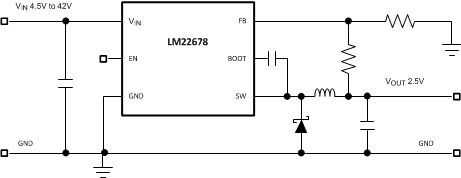 Example Circuit With Very Wide Input Voltage Range and Low Component
Count
Example Circuit With Very Wide Input Voltage Range and Low Component
CountWide Input Voltage Range Rules
Earlier generations of SIMPLE SWITCHER regulator families remain popular in automotive applications due to their ease of use, low component count, and wide input voltage range. The newest LM2267x/80 SIMPLE SWITCHER family meets and exceeds these requirements while adding further refined features such as a higher switching frequency, an even wider input operating voltage range, and improved WEBENCH® online simulation design support.
AECQ100 qualification for the LM2267x/80 is planned.