SNVA866A February 2019 – January 2023 LM5155 , LM5155-Q1 , LM51551 , LM51551-Q1
- How to design an Isolated Flyback using LM5155
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Example Application
- 3Calculations and Component Selection
- 4Component Selection Summary
- 5Small Signal Frequency Analysis
- 6Revision History
3.3 Current Sense Resistor Calculations
Selection of the current sense network components is described in this section. Figure 3-1 shows the four components that make up the current sense network of the LM5155. RS is the current sense resistor. This resistor senses the switch current for the control loop, and sets the peak current limit value. RF and CF form a low pass filter. This filter helps reduce the impact of any high frequency noise on the current sense signal. RSL sets the external slope compensation and is optional. In some applications the internal slope compensation of the LM5155 will not be sufficient and RSL will be required.
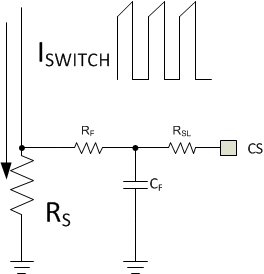 Figure 3-1 LM5155 Current Sense Network
Figure 3-1 LM5155 Current Sense Network