SNVA941A June 2020 – November 2022 LM5156 , LM5156-Q1 , LM51561 , LM51561-Q1 , LM51561H , LM51561H-Q1 , LM5156H , LM5156H-Q1
- How to Design a Boost Converter Using the LM5156
- 1LM5156 Design Example
- 2Example Application
-
3Calculations and Component Selection
- 3.1 Switching Frequency
- 3.2 Inductor Calculation
- 3.3 Current Sense Resistor Calculation
- 3.4 Inductor Selection
- 3.5 Diode Selection
- 3.6 MOSFET Selection
- 3.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 3.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 3.9 UVLO Resistor Selection
- 3.10 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection.
- 3.11 Feedback Resistor Selection
- 3.12 Control Loop Compensation
- 3.13 Efficiency Estimation
- 4Component Selection Summary
- 5Small-Signal Frequency Analysis
- 6Revision History
3.3.1 Current Sense Resistor and Slope Compensation Resistor Selection
The current sense resistor is selected to avoid current limiting during the minimum supply voltage, VSUPPLY_min, and the maximum load current, ILOAD_max. Due to component tolerances and power loss of the regulator, the peak current limit should be set some margin above the calculate peak inductor current. A margin of 20% to 40% (MI_LIMIT = 0.2) is a good starting point. Equation 5 is used to calculate the desired peak inductor current limit value. In this design example, MI_LIMIT is selected to be 30%.
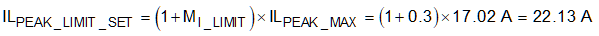
where
- ILPEAK_MAX is the maximum peak inductor current
Selecting the correct current sense resistor is an iterative process. The first step is to calculate the maximum current sense resistor, assuming that no external slope compensation is required (RSL = 0 Ω), using Equation 6.
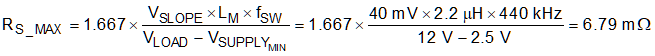
where
- VSL is the internal fixed internal slope compensation of the LM5156
Assuming that no external slope compensation is required, the current sense resistor value is calculated using Equation 7.
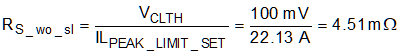
where
- VCLTH is the nominal current limit threshold of the LM5156
If the calculated RS_wo_sl resistance value is less than the RS_MAX resistance value, the RS_wo_sl is selected for the current sense resistor value (RS). If the calculated RS_wo_sl resistance value is greater than the calculated RS_MAX resistance value, there are two approaches to take; decrease the current sense resistor value or add external slope compensation.
- Decreasing the current sense resistor increases the effectiveness of the internal slope compensation. With no external slope compensation the peak inductor current limit will be constant regardless of the duty cycle. A lower current sense resistor results in a larger inductor peak current limit value, which increases the required saturation current rating of the inductor.
- Adding external slope compensation. The peak inductor current limit varies with supply voltage when external slope compensation is added.
External slope compensation is added by setting RSL to a non-zero value less than 1 kΩ. In applications where external slope compensation is added, RS is calculated using Equation 8.
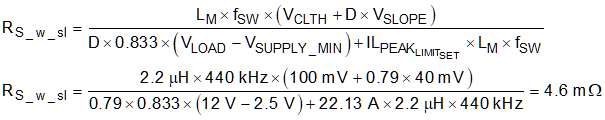
where
- 0.833 is the ratio of the total slope compensation to the sensed falling inductor current.
RSL is calculated using Equation 9.
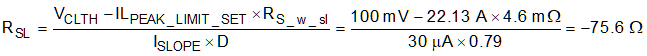
where
- ISLOPE is the slope compensation source of the LM5156
- D is the duty cycle at the minimum supply voltage
If the calculated RSL value exceeds the maximum value of the 1 kΩ, the down slope of the sensed inductor current needs to be reduce. To reduce the down slope of the inductor current, the inductance value of LM must be increased. If the LM inductance value is changed the current sense resistor calculations must be recalculated. If the calculated value of RSL is negative no external slope compensation is required.
For this design example a current sense resistor value is selected to be 4 mΩ (RS), which is the nearest standard resistor value to the calculated value in Equation 7. This value is selected to keep from triggering current limit protection during load transients. No external slope compensation is required and RSL is selected to be 0 Ω. The peak inductor current limit is calculated using Equation 10.
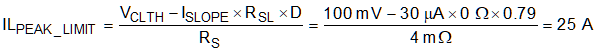
The peak inductor current limit is constant, regardless of the supply voltage, because there is no external slope compensation. For this design the inductor saturation current rating should be greater than 25 A.