SNVA964 June 2020 LP8866-Q1
2.1 Spread Spectrum
Spread spectrum technique is widely used in Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) to reduce EMI around the switching frequency and its harmonics by dispersing the spectral energy of the switching signals. The spread spectrum variation range of the LP8866-Q1 device is programmable from ± 3.3% to ± 7.2% from the central switching frequency. The default variation is ± 5.3%. It can be seen from Figure 7 that enabling the spread spectrum feature of ± 5.3% variation can reduce the third switching frequency harmonics (1.2 MHz) radiated emissions average data by up to 14.48 dB and ± 5.3% variation can contribute to 3.86 dB lower result compared with ± 3.3% variation.
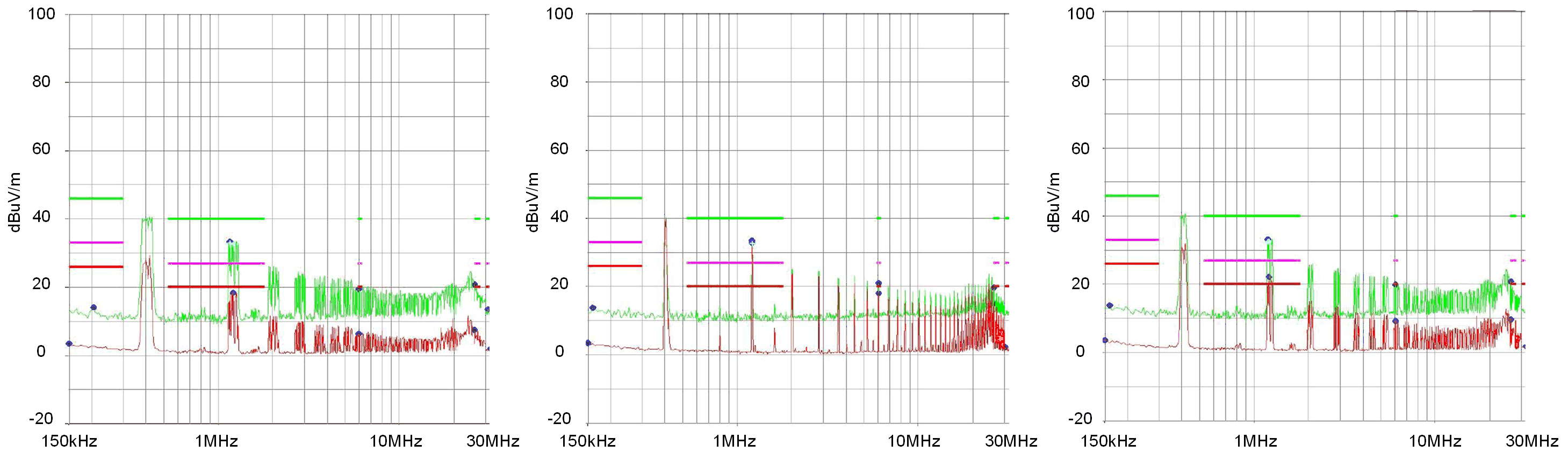
| (a) Spread spectrum enabled
(± 5.3% variation) |
(b) Spread spectrum enabled
(± 3.3% variation) |
(c) Spread spectrum disabled |
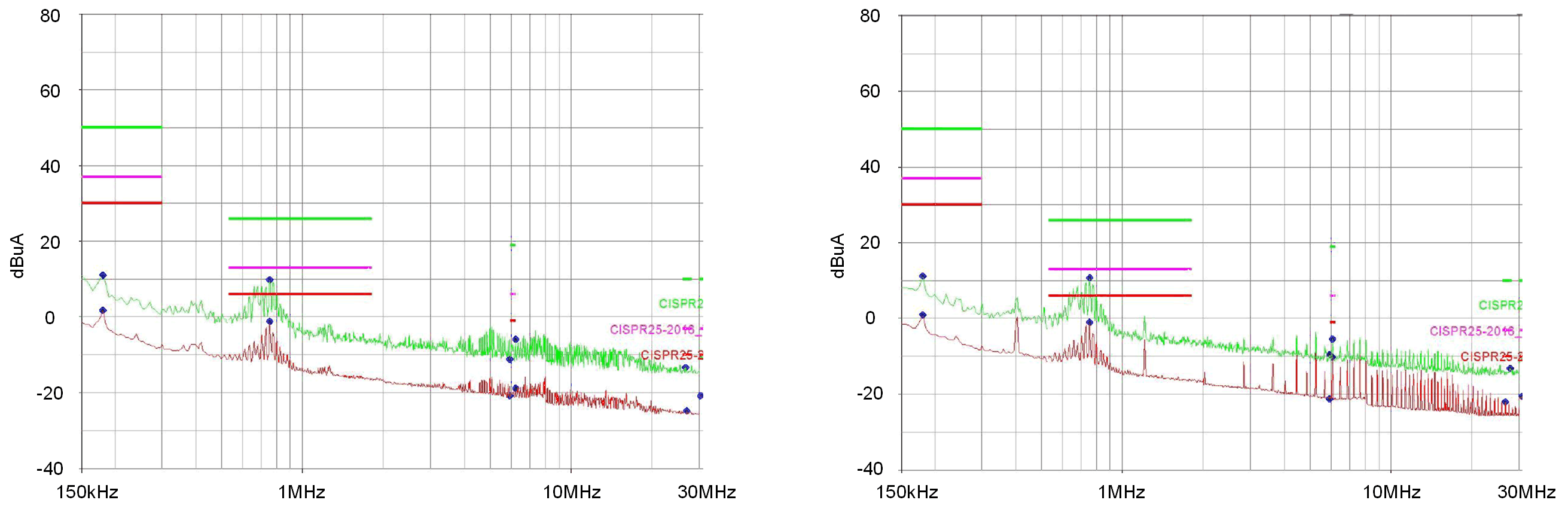
| (a) Spread spectrum enabled (± 5.3% variation) | (b) Spread spectrum disabled |